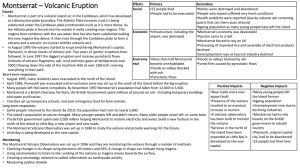
Montserrat * Volcanic Eruption
... • Montserrrat is part of a volcanic island arc in the Caribbean, which has developed •Health problems were reported (due by volcanic ash contaning at a destructive plate boundary. The Atlantic Plate (oceanic crust) is being quartz that can then cause silicosis) subducted under the Caribbean plate (c ...
... • Montserrrat is part of a volcanic island arc in the Caribbean, which has developed •Health problems were reported (due by volcanic ash contaning at a destructive plate boundary. The Atlantic Plate (oceanic crust) is being quartz that can then cause silicosis) subducted under the Caribbean plate (c ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Basaltic lavas are more fluid • Types of lava • Pahoehoe lava (resembles braids in ropes) • Aa lava (rough, jagged blocks) ...
... • Basaltic lavas are more fluid • Types of lava • Pahoehoe lava (resembles braids in ropes) • Aa lava (rough, jagged blocks) ...
ES11_Ch09_Lecture
... • Basaltic lavas are more fluid • Types of lava • Pahoehoe lava (resembles braids in ropes) • Aa lava (rough, jagged blocks) ...
... • Basaltic lavas are more fluid • Types of lava • Pahoehoe lava (resembles braids in ropes) • Aa lava (rough, jagged blocks) ...
Acid pyroclastic rocks from the Sheinovets caldera, Eastern
... Abstract. The Sheinovets caldera is located in the easternmost parts of the Eastern Rhodopes Paleogene volcanic area, beside the border with Greece. The caldera is filled up with more than 1000 m thick sequence of pyroclastic, epiclastic, and sedimentary rocks crossed by several rhyolite domes. This ...
... Abstract. The Sheinovets caldera is located in the easternmost parts of the Eastern Rhodopes Paleogene volcanic area, beside the border with Greece. The caldera is filled up with more than 1000 m thick sequence of pyroclastic, epiclastic, and sedimentary rocks crossed by several rhyolite domes. This ...
Volcanic Eruptions - Elliott County Schools
... are called volcanic ash. • Volcanic ash that is less than 0.25 mm in diameter is called volcanic dust. • Large pyroclastic particles that are less than 64 mm in diameter are called lapilli. ...
... are called volcanic ash. • Volcanic ash that is less than 0.25 mm in diameter is called volcanic dust. • Large pyroclastic particles that are less than 64 mm in diameter are called lapilli. ...
Rock Cycle - The School District of Palm Beach County
... as heat, pressure, compaction, cementation, weathering and erosion. Although the rock cycle is usually an extremely slow process, often taking millions of years, it is related to plate tectonics which can often be violent and dramatic, resulting in earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. SC.7.E.6.2 Iden ...
... as heat, pressure, compaction, cementation, weathering and erosion. Although the rock cycle is usually an extremely slow process, often taking millions of years, it is related to plate tectonics which can often be violent and dramatic, resulting in earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. SC.7.E.6.2 Iden ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... is called lava. The place in the Earth’s surface through which magma and other materials reach the surface is called a volcano. In some places, lava can build up to form a cone-shaped mountain. • The opening from which lava erupts is the vent. Volcanoes often have more than ...
... is called lava. The place in the Earth’s surface through which magma and other materials reach the surface is called a volcano. In some places, lava can build up to form a cone-shaped mountain. • The opening from which lava erupts is the vent. Volcanoes often have more than ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... is called lava. The place in the Earth’s surface through which magma and other materials reach the surface is called a volcano. In some places, lava can build up to forma cone-shaped mountain. • The opening from which lava erupts is the vent. Volcanoes often have more than ...
... is called lava. The place in the Earth’s surface through which magma and other materials reach the surface is called a volcano. In some places, lava can build up to forma cone-shaped mountain. • The opening from which lava erupts is the vent. Volcanoes often have more than ...
Volcanoes Part I: classification, deposits, and their distribution
... Pyroclastic material: Debris formed by a volcanic explosion. Results when magma is very viscous. Tephra: The general term for all pyroclastic material that is ejected from a volcano. Different terms apply according to the size of the tephra. (syn. Ejecta) ...
... Pyroclastic material: Debris formed by a volcanic explosion. Results when magma is very viscous. Tephra: The general term for all pyroclastic material that is ejected from a volcano. Different terms apply according to the size of the tephra. (syn. Ejecta) ...
Igneous Processes Page 1 of 2 Intrusive igneous activity I. Plutons
... c. Laccolith—bulged body parallel to sedimentary beds d. Batholith—large intrusive body perhaps hundreds of km wide B. May take millions of years to cool II. Origin of magma—formed by melting solid rock ...
... c. Laccolith—bulged body parallel to sedimentary beds d. Batholith—large intrusive body perhaps hundreds of km wide B. May take millions of years to cool II. Origin of magma—formed by melting solid rock ...
Lecture 4
... consolidation of magma takes place very close to the earth’s surface in the form of smaller sheet like bodies (known as sills and dykes) that fill cracks inside other rocks. Some extrusive generally have finer grained, smoother surfaces. Some extrusive materials, such as volcanic ash, bypasses the r ...
... consolidation of magma takes place very close to the earth’s surface in the form of smaller sheet like bodies (known as sills and dykes) that fill cracks inside other rocks. Some extrusive generally have finer grained, smoother surfaces. Some extrusive materials, such as volcanic ash, bypasses the r ...
Shield Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Cinder Cone Volcanoes
... Cinder cone volcanoes are smaller than shield volcanoes and composite volcanoes. If the eruption contains thick magma, the gas pressure shatters the rock within the volcano into small pieces. In other cases, the lava in the air may harden and fall as fragments. These small pieces are called cinders. ...
... Cinder cone volcanoes are smaller than shield volcanoes and composite volcanoes. If the eruption contains thick magma, the gas pressure shatters the rock within the volcano into small pieces. In other cases, the lava in the air may harden and fall as fragments. These small pieces are called cinders. ...
Mt. Vesuvius - Central Square School District
... This phase created a rain of ash and pumice over a broad area primarily to the south of Vesuvius, carried by prevailing winds. This phase lasted approximately eighteen hours, when approximately 2.5 meters (8.2 feet) of pumice stones fell on Pompeii. ...
... This phase created a rain of ash and pumice over a broad area primarily to the south of Vesuvius, carried by prevailing winds. This phase lasted approximately eighteen hours, when approximately 2.5 meters (8.2 feet) of pumice stones fell on Pompeii. ...
iss__st4_files/Comenius Volcanoes
... gas that is released. These clouds of gas and ash can rise up to kilometers in height, sometimes rising up so high that air traffic is influenced. These gases can so be extremely hot that they can destroy the engines of planes, meaning that planes cannot fly in the close proximity of these gas clouds. ...
... gas that is released. These clouds of gas and ash can rise up to kilometers in height, sometimes rising up so high that air traffic is influenced. These gases can so be extremely hot that they can destroy the engines of planes, meaning that planes cannot fly in the close proximity of these gas clouds. ...
DICHOTOMOUS KEY TO THE IGNEOUS ROCKS
... Igneous rocks break-up into two categories, Volcanic (extrusive) or Magmatic (underground from magmaintrusive). In general Extrusive or volcanic rocks either have holes (created from the gases that are released during and eruption) and are light weight or can be glassy and sharp. Intrusive, cool slo ...
... Igneous rocks break-up into two categories, Volcanic (extrusive) or Magmatic (underground from magmaintrusive). In general Extrusive or volcanic rocks either have holes (created from the gases that are released during and eruption) and are light weight or can be glassy and sharp. Intrusive, cool slo ...
Review Sheet Test 2
... water . Bowens Reaction Series Fig. 4.23; Ways to vary magma composition: crystal settling (also called magmatic differentiation), magma mixing, melting of crust Partial melting; pluton, magma, lava, Chapter 5: Volcanoes and other Igneous Activity: Especially note: Fig. 5.4, 5.6, 5.7, 5.14, 5.38, 5. ...
... water . Bowens Reaction Series Fig. 4.23; Ways to vary magma composition: crystal settling (also called magmatic differentiation), magma mixing, melting of crust Partial melting; pluton, magma, lava, Chapter 5: Volcanoes and other Igneous Activity: Especially note: Fig. 5.4, 5.6, 5.7, 5.14, 5.38, 5. ...
Rocks - Earth2Class
... • Dark-colored, finegrained, extrusive • Formed where lava erupted onto surface • Most widespread igneous rocks • Found locally in the Palisades along west shore of Hudson River, ...
... • Dark-colored, finegrained, extrusive • Formed where lava erupted onto surface • Most widespread igneous rocks • Found locally in the Palisades along west shore of Hudson River, ...
Rock and Rock Materials - Washington State University
... Further Subdivided By Depth & Relative Grain-Size: -Very deep = very slow = very large crystals -Medium or shallow depth = medium-size crystals ...
... Further Subdivided By Depth & Relative Grain-Size: -Very deep = very slow = very large crystals -Medium or shallow depth = medium-size crystals ...
Igneous Rock
... lava to __________, the more time mineral crystals have to grow and the ________________ the texture of the resulting igneous rock. Intrusive igneous rock (Plutonic) – The type of igneous rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies _________ the Earth’s surface. - Usually has a _________________ ...
... lava to __________, the more time mineral crystals have to grow and the ________________ the texture of the resulting igneous rock. Intrusive igneous rock (Plutonic) – The type of igneous rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies _________ the Earth’s surface. - Usually has a _________________ ...
The Rock Cycle
... We begin at the top of Figure Magma is molten material that forms inside Earth. Eventually magma cools and solidifies. This process, called crystallization, may occur either beneath the surface or, following a volcanic eruption, at the surface. In either situation, the resulting rocks are called ign ...
... We begin at the top of Figure Magma is molten material that forms inside Earth. Eventually magma cools and solidifies. This process, called crystallization, may occur either beneath the surface or, following a volcanic eruption, at the surface. In either situation, the resulting rocks are called ign ...
Earth Science Rocks PPT
... • Dark-colored, finegrained, extrusive • Formed where lava erupted onto surface • Most widespread igneous rocks • Found locally in the Palisades along west shore of Hudson River, ...
... • Dark-colored, finegrained, extrusive • Formed where lava erupted onto surface • Most widespread igneous rocks • Found locally in the Palisades along west shore of Hudson River, ...
Lab 4
... to seize (don’t drive through a tephra fall if you can help it!). Finally, if an eruption can send tephra to the top of the troposphere, or even into the stratosphere, the fine particles can block light and therefore reduce the amount of sunlight that reaches the surface of the earth. In effect, a b ...
... to seize (don’t drive through a tephra fall if you can help it!). Finally, if an eruption can send tephra to the top of the troposphere, or even into the stratosphere, the fine particles can block light and therefore reduce the amount of sunlight that reaches the surface of the earth. In effect, a b ...
Volcanoes - American Red Cross
... Volcanic eruptions fall into two broad types: (1) explosive and (2) quiet. Hazards from large explosive eruptions include widespread ashfall (fine glass particles), pyroclastic flows (mixtures of hot gases and pumice blocks), and massive lahars (volcanic mud or debris flows) that can endanger people ...
... Volcanic eruptions fall into two broad types: (1) explosive and (2) quiet. Hazards from large explosive eruptions include widespread ashfall (fine glass particles), pyroclastic flows (mixtures of hot gases and pumice blocks), and massive lahars (volcanic mud or debris flows) that can endanger people ...
Word format
... D. none of the above describe these two terms correctly 32. Which of the following descriptions is TRUE when talking about graded bedding? A. it typically forms when sediment is transported by the wind B. the sediment in a bed is all about the same size C. large sediment grains are at the bottom and ...
... D. none of the above describe these two terms correctly 32. Which of the following descriptions is TRUE when talking about graded bedding? A. it typically forms when sediment is transported by the wind B. the sediment in a bed is all about the same size C. large sediment grains are at the bottom and ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.