Volcano tourism
... when they saw the pictures on the TV in their living-room. Police think that more than 25,000 onlookers have visited Eyjafjallajökull in the weeks after the eruption. Special tours were offered and tour guides, often geologists and volcano experts, led the tourists to the best viewing places and gav ...
... when they saw the pictures on the TV in their living-room. Police think that more than 25,000 onlookers have visited Eyjafjallajökull in the weeks after the eruption. Special tours were offered and tour guides, often geologists and volcano experts, led the tourists to the best viewing places and gav ...
Lesson Plan by : Laura Murphy, Arnone School Title : Volcanoes
... 1) Volcanoes are vents, or openings, in the Earth 2) They let heat from deep inside the Earth escape. 3) Volcanoes spout steam, ash, gases, and melted rock. 4) Earth has three layers: the crust, mantle, and the core. 5) Deep down, 3 to 25 miles, below the crust is a soft, hot layer (the mantel). 6) ...
... 1) Volcanoes are vents, or openings, in the Earth 2) They let heat from deep inside the Earth escape. 3) Volcanoes spout steam, ash, gases, and melted rock. 4) Earth has three layers: the crust, mantle, and the core. 5) Deep down, 3 to 25 miles, below the crust is a soft, hot layer (the mantel). 6) ...
Chapter 29 Notes
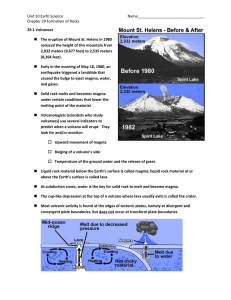
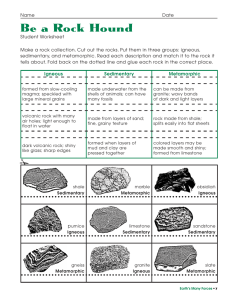
... A rock is a naturally formed solid usually made of one or more minerals. The terms igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic refer to the origin of a rock, how a rock was formed. Igneous rocks form by the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rocks usually contain crystals since the ...
... A rock is a naturally formed solid usually made of one or more minerals. The terms igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic refer to the origin of a rock, how a rock was formed. Igneous rocks form by the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rocks usually contain crystals since the ...
11-Heimaey- Living with Natural Hazards.indd
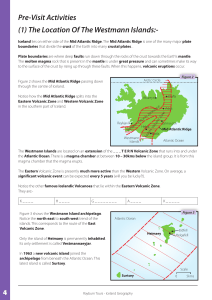
... Pre-Visit Activities (1) The Location Of The Westmann Islands:Iceland lies on either side of the Mid Atlantic Ridge. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is one of the many major plate boundaries that divide the crust of the Earth into many crustal plates. . Plate boundaries are where deep faults run down through ...
... Pre-Visit Activities (1) The Location Of The Westmann Islands:Iceland lies on either side of the Mid Atlantic Ridge. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is one of the many major plate boundaries that divide the crust of the Earth into many crustal plates. . Plate boundaries are where deep faults run down through ...
Volcanic Landforms
... • Composite volcanoes erupt in different ways at different times. These volcanoes are built in layers by multiple eruptions, sometimes recurring over hundreds of thousands of years, sometimes over a few hundred. Andesite magma (the most common but not the only magma type), tends to form composite co ...
... • Composite volcanoes erupt in different ways at different times. These volcanoes are built in layers by multiple eruptions, sometimes recurring over hundreds of thousands of years, sometimes over a few hundred. Andesite magma (the most common but not the only magma type), tends to form composite co ...
- ILM.COM.PK
... Figure 5.3 Common volcanic rock types (bottom labels) and their plutonic equivalents (top). The rock names reflect varying proportions of silica, iron, and magnesium, and thus of common silicate minerals. Rhyolite is the fine-grained, volcanic compositional equivalent of granite, and so on. ...
... Figure 5.3 Common volcanic rock types (bottom labels) and their plutonic equivalents (top). The rock names reflect varying proportions of silica, iron, and magnesium, and thus of common silicate minerals. Rhyolite is the fine-grained, volcanic compositional equivalent of granite, and so on. ...
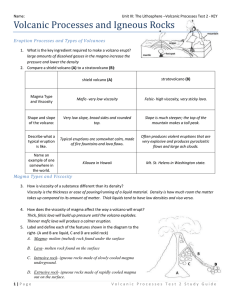
Volcanic Processes and Igneous Rocks
... 18. Define the following Volcanic Hazards and on the line, state if they are related to Shield or Stratovolcanoes: Stratovolcano Debris – Charred items that are air born and effect a small area Shield Lava Fountain – A spectacular display of molten rock being sprayed in the air Stratovolcano Lahar – ...
... 18. Define the following Volcanic Hazards and on the line, state if they are related to Shield or Stratovolcanoes: Stratovolcano Debris – Charred items that are air born and effect a small area Shield Lava Fountain – A spectacular display of molten rock being sprayed in the air Stratovolcano Lahar – ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... volcanoes. A cinder cone volcano is the most simple type of volcano. They are blobs and particles of congealed lava that is ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. ...
... volcanoes. A cinder cone volcano is the most simple type of volcano. They are blobs and particles of congealed lava that is ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. ...
Build a Volcano
... Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the surface of Earth. The term ...
... Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the surface of Earth. The term ...
msword - rgs.org
... Geo means ‘of the earth’ and ‘thermal’ means heat. Geothermal energy is therefore the heat that naturally occurs underground in volcanic areas. In many cases this geothermal energy is evident in the form of hot springs and geysers (fountains of hot water that shoot out intermittently from the spring ...
... Geo means ‘of the earth’ and ‘thermal’ means heat. Geothermal energy is therefore the heat that naturally occurs underground in volcanic areas. In many cases this geothermal energy is evident in the form of hot springs and geysers (fountains of hot water that shoot out intermittently from the spring ...
Volcano - The Disaster Center
... factors, including the type of lava erupted, the steepness of the ground, and the rate of lava production at the vent. Volcanic eruptions can be accompanied by other natural hazards: earthquakes, mudflows and flash floods, rockfalls and landslides, wildland fires, and (under special conditions) tsu ...
... factors, including the type of lava erupted, the steepness of the ground, and the rate of lava production at the vent. Volcanic eruptions can be accompanied by other natural hazards: earthquakes, mudflows and flash floods, rockfalls and landslides, wildland fires, and (under special conditions) tsu ...
Volcanoes: eruptive style and associated landforms
... 1.Volcanic eruption 2. Large volume of material extruded 3. Magma chamber empties 4. Volcano collapses into the empty magma chamber ...
... 1.Volcanic eruption 2. Large volume of material extruded 3. Magma chamber empties 4. Volcano collapses into the empty magma chamber ...
the free PDF resource
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
Volcanic Eruptions and Hazards
... middle of a plate. These are known as “hot spot” volcanoes and form because magma is able to reach the surface due to a weak/thin spot in the lithosphere. Examples: Hawaiian volcanoes and Yellowstone National Park. ...
... middle of a plate. These are known as “hot spot” volcanoes and form because magma is able to reach the surface due to a weak/thin spot in the lithosphere. Examples: Hawaiian volcanoes and Yellowstone National Park. ...
HST_CRF_04_02_03.qxd
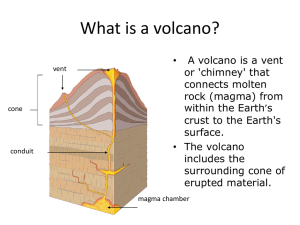
... 5. Which of the following can happen during an explosive volcanic eruption? calm lava flows hot debris, ash, and gas shooting into the air a rainbow lava fountains 6. What is ash? flowing lava tiny, dust-sized bits of rock big chunks of rock a gas WHAT IS INSIDE A VOLCANO? 7. What is a vent? a magma ...
... 5. Which of the following can happen during an explosive volcanic eruption? calm lava flows hot debris, ash, and gas shooting into the air a rainbow lava fountains 6. What is ash? flowing lava tiny, dust-sized bits of rock big chunks of rock a gas WHAT IS INSIDE A VOLCANO? 7. What is a vent? a magma ...
THIS Volcano powerpoint
... There is a great range in the severity of volcanic eruptions. Many eruptions are relatively quiet and are characterized by the calm, nonviolent extrusion of lava flows on the earth's surface. If the material is fluid in nature (solid and semi-solid) this type of flow is called Pyroclastic Flow (the ...
... There is a great range in the severity of volcanic eruptions. Many eruptions are relatively quiet and are characterized by the calm, nonviolent extrusion of lava flows on the earth's surface. If the material is fluid in nature (solid and semi-solid) this type of flow is called Pyroclastic Flow (the ...
Handout: Assignment 2 - Speech Services Niagara
... red-hot molten rock. In modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes. They still don’t know all the answers, but they know much about how a volcano works. Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep beneath the crust is the mantle, where ...
... red-hot molten rock. In modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes. They still don’t know all the answers, but they know much about how a volcano works. Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep beneath the crust is the mantle, where ...
Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive
... Stages of Volcanic Activity ......................................................................................................... 1 Eruption Stage .................................................................................................................... 1 Cooling and Inactive Stage ... ...
... Stages of Volcanic Activity ......................................................................................................... 1 Eruption Stage .................................................................................................................... 1 Cooling and Inactive Stage ... ...
chapter 4 volcanoes
... Stages of Volcanic Activity ......................................................................................................... 1 Eruption Stage .................................................................................................................... 1 Cooling and Inactive Stage ... ...
... Stages of Volcanic Activity ......................................................................................................... 1 Eruption Stage .................................................................................................................... 1 Cooling and Inactive Stage ... ...
VOLCANIC HAZARDS: INTRODUCTION
... Level of economic development and time of day may also be important ...
... Level of economic development and time of day may also be important ...
Skinner Chapter 7
... Read each question carefully before answering. Work at a steady pace, and you should have ample time to finish. _____________________________________________ 1. Volcanic eruptions are rare; normally there is an average of about one or two eruptions each year. 2. Explosive eruptions happen primarily ...
... Read each question carefully before answering. Work at a steady pace, and you should have ample time to finish. _____________________________________________ 1. Volcanic eruptions are rare; normally there is an average of about one or two eruptions each year. 2. Explosive eruptions happen primarily ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.