Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... • Composite cone (stratovolcano) –Most are located adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Fujiyama, Mount St. Helens) –Large, classic-shaped volcano (thousands of feet high and several miles wide at base) –Composed of interbedded lava flows and layers of pyroclastic debris ...
... • Composite cone (stratovolcano) –Most are located adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Fujiyama, Mount St. Helens) –Large, classic-shaped volcano (thousands of feet high and several miles wide at base) –Composed of interbedded lava flows and layers of pyroclastic debris ...
Chapter 6 Section 2 Notes
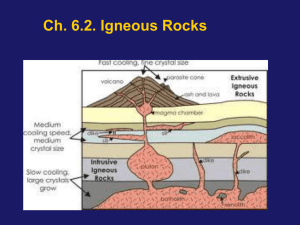
... B. Extrusive Igneous Rock Structures – Volcano: a vent through which magma, gases, or volcanic ash is expelled. ...
... B. Extrusive Igneous Rock Structures – Volcano: a vent through which magma, gases, or volcanic ash is expelled. ...
Positive effects of volcanic activity
... The Hawaiian Islands are at the southeastern end of a chain of volcanoes that began to form more than 70 million years ago. The largest and most southeastern island of the chain, Hawaii, consists of five volcanoes. Kilauea, Mauna Loa, and Hualalai have erupted in the past 200 years. Lo`ihi, the you ...
... The Hawaiian Islands are at the southeastern end of a chain of volcanoes that began to form more than 70 million years ago. The largest and most southeastern island of the chain, Hawaii, consists of five volcanoes. Kilauea, Mauna Loa, and Hualalai have erupted in the past 200 years. Lo`ihi, the you ...
Volcanoes - Pacific Disaster Net
... gas bubbles can escape from it, leading to more violent eruptions. However, if water is present during the eruption, even highly fluid magma can erupt explosively - these hydrovolcanic eruptions lead to violent steam explosions, fragmenting the magma into fine-grained ash. ...
... gas bubbles can escape from it, leading to more violent eruptions. However, if water is present during the eruption, even highly fluid magma can erupt explosively - these hydrovolcanic eruptions lead to violent steam explosions, fragmenting the magma into fine-grained ash. ...
Challenge and Extension - Effingham County Schools
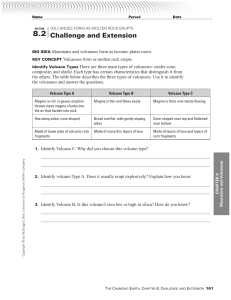
... Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it from the others. The table below describes the three types of volcanoes. Use it to identify the volcanoes and answer the questions. ...
... Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it from the others. The table below describes the three types of volcanoes. Use it to identify the volcanoes and answer the questions. ...
Sedimentary rock
... through geologic processes. They are inorganic substances they do not contain carbon) and have a crystalline structure. The study of minerals is called mineralogy. ...
... through geologic processes. They are inorganic substances they do not contain carbon) and have a crystalline structure. The study of minerals is called mineralogy. ...
Earthquakes
... Volcanoes cause fewer deaths than many other natural disasters. Generally some activity (earth trembles, smoke, ash) occurs before an eruption to warn people to leave. Sometimes the eruption is violent and sudden – these eruptions are the most dangerous. Most deaths in sudden eruptions are c ...
... Volcanoes cause fewer deaths than many other natural disasters. Generally some activity (earth trembles, smoke, ash) occurs before an eruption to warn people to leave. Sometimes the eruption is violent and sudden – these eruptions are the most dangerous. Most deaths in sudden eruptions are c ...
VOLCANO RESEARCH PAPER: Big scientific ideas for which you
... Volcanoes are mountains that are formed of molten rock that is pushed up to the Earth’s surface. Volcanic Eruptions- explosive or nonexplosive depending on the type of magma emitted (lava or pyroclastic) Explosive – caused by magma with high water content; produces mostly pyroclastic materials – Pyr ...
... Volcanoes are mountains that are formed of molten rock that is pushed up to the Earth’s surface. Volcanic Eruptions- explosive or nonexplosive depending on the type of magma emitted (lava or pyroclastic) Explosive – caused by magma with high water content; produces mostly pyroclastic materials – Pyr ...
GAPS Guidelines
... particles falling out of the lower atmosphere within hours or days after the eruption. Finer particles reaching the upper atmosphere have been known to circle the globe on high altitude wind currents for long periods of time. Because the material is airborne, prevailing wind direction and velocity a ...
... particles falling out of the lower atmosphere within hours or days after the eruption. Finer particles reaching the upper atmosphere have been known to circle the globe on high altitude wind currents for long periods of time. Because the material is airborne, prevailing wind direction and velocity a ...
Igneous Rocks
... from white or gray to pink, depending on which colour of feldspar is present. Granite is a very common continental igneous rock found in many mountainous areas. Obsidian, a volcanic rock with a glassy texture, is moderately hard and brittle, with conchoidal fracture. Obsidian’s chemical composition ...
... from white or gray to pink, depending on which colour of feldspar is present. Granite is a very common continental igneous rock found in many mountainous areas. Obsidian, a volcanic rock with a glassy texture, is moderately hard and brittle, with conchoidal fracture. Obsidian’s chemical composition ...
Document
... depths of 80 to 100 km below the earth’s surface. Once tiny droplets of magma are formed, they begin to rise because the magma is less dense than the solid rock surrounding it. For magma to rise is, it generally moves upward toward lower pressure regions, squeezing into spaces between minerals withi ...
... depths of 80 to 100 km below the earth’s surface. Once tiny droplets of magma are formed, they begin to rise because the magma is less dense than the solid rock surrounding it. For magma to rise is, it generally moves upward toward lower pressure regions, squeezing into spaces between minerals withi ...
Long ago in Mexico, a great Aztec king had a daughter named
... named Iztaccíhuatl. Iztaccíhuatl was a wonderful young woman. She was smart, kind, and very beautiful. All the greatest Aztec warriors wanted to marry her. But Iztaccíhuatl loved only one warrior. His name was Popocatépetl. Popocatépetl was the greatest of all the Aztec warriors and the leader of th ...
... named Iztaccíhuatl. Iztaccíhuatl was a wonderful young woman. She was smart, kind, and very beautiful. All the greatest Aztec warriors wanted to marry her. But Iztaccíhuatl loved only one warrior. His name was Popocatépetl. Popocatépetl was the greatest of all the Aztec warriors and the leader of th ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... Volcanic Ash 1. Volcanic ash forms when gases in stiff magma expand rapidly. ...
... Volcanic Ash 1. Volcanic ash forms when gases in stiff magma expand rapidly. ...
Shield Volcano
... • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate around the vent. (Describ ...
... • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate around the vent. (Describ ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
Geologic Overview of the Clackamas Basin
... • Composite volcanoes erupting ash and pumice • Young basalt flows and cinder cones cover large areas • Glacial deposits are present near peaks ...
... • Composite volcanoes erupting ash and pumice • Young basalt flows and cinder cones cover large areas • Glacial deposits are present near peaks ...
File
... • Instead of forming mountains, some eruptions of lava form high, level areas called lava plateaus. First, lava flows out of several long cracks in an area. The thin, runny lava travels far before cooling and solidifying. Again and again, floods of lava flow on top of earlier floods. After millions ...
... • Instead of forming mountains, some eruptions of lava form high, level areas called lava plateaus. First, lava flows out of several long cracks in an area. The thin, runny lava travels far before cooling and solidifying. Again and again, floods of lava flow on top of earlier floods. After millions ...
Section 10-4
... • Dike – forms when magma is squeezed into a vertical crack that cuts across rock layers and solidifies underground • Sill – forms when magma is squeezed into a horizontal crack between rock layers and solidifies underground ...
... • Dike – forms when magma is squeezed into a vertical crack that cuts across rock layers and solidifies underground • Sill – forms when magma is squeezed into a horizontal crack between rock layers and solidifies underground ...
Igneous Rocks (Volcanic or Plutonic) Sedimentary Rocks (Clastic or
... - Identified according to their grain size, include two main types; (i) Inorganic - Rocks from chemicals. - Composed of minerals that have been precipitated from water (sea water, fresh water or ground water). (ii) Organic - Rocks from living things. - Composed of fragments of materials from living ...
... - Identified according to their grain size, include two main types; (i) Inorganic - Rocks from chemicals. - Composed of minerals that have been precipitated from water (sea water, fresh water or ground water). (ii) Organic - Rocks from living things. - Composed of fragments of materials from living ...
Major Rock Categories
... Major Rock Categories Rocks are divided into three main categories according to how they were formed: igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic processes. Rocks differ in their texture, mineral and chemical composition, and bedding characteristics depending on which of these three processes that formed th ...
... Major Rock Categories Rocks are divided into three main categories according to how they were formed: igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic processes. Rocks differ in their texture, mineral and chemical composition, and bedding characteristics depending on which of these three processes that formed th ...
C:\Users\Vico\Documents\Vic Data\Courses\Volcanology\Syllabus
... and the genesis of volcanic rocks. After completing the course, students should be able to meet a number of important objectives, the most salient of which are: 1. Employ rock whole-rock geochemistry and analyze data sets in classifying volcanic rocks, and be able to identify the gross tectomagmatic ...
... and the genesis of volcanic rocks. After completing the course, students should be able to meet a number of important objectives, the most salient of which are: 1. Employ rock whole-rock geochemistry and analyze data sets in classifying volcanic rocks, and be able to identify the gross tectomagmatic ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.