* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
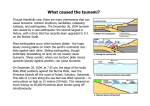
Geologic Disasters Earthquakes Most violent and sudden of the geologic disasters Occur most often along the edge of tectonic plates Most deaths and injuries occur because of buildings collapsing Afterward, injured people may die due to lack of medical aid, food, water and shelter, as well as fires or disease Earthquakes cause more damage and deaths in LDCs because o cities are more crowded (high population density) o lower building standards o no plans or few services ready for disaster relief o less money for disaster relief Volcanoes Volcanoes cause fewer deaths than many other natural disasters. Generally some activity (earth trembles, smoke, ash) occurs before an eruption to warn people to leave. Sometimes the eruption is violent and sudden – these eruptions are the most dangerous. Most deaths in sudden eruptions are caused by pyroclastic flow – clouds of superheated gas. Deaths afterward occur due to fires started by the eruption or famine due to loss of crops. Damage due to large amounts of ash and cinders, fires, or lava flows. Can cause world-wide effects: cooler weather and acid rain. The heat of volcanic activity (geothermal energy) can be used to provide electricity and heat (Iceland does this.) Landslides Occur in areas where natural slopes exist (river valleys, hills, mountains). May be called rockslides, landslides, mudslides, etc. A “triggering event” causes rock or soil to move rapidly down the slope. Triggering events can include: o earthquakes o heavy rainfall o loss of natural vegetation (plant and forest cover) o mining or road construction Damage property and structure by fast speed of movement and weight of soil or rock. Deaths caused by being buried or crushed. Avalanches Occur where snow and ice accumulate on slopes. Can be triggered by human activity or natural causes, such as temperature change. Are less frequent and affect smaller areas than other types of slides. Tsunamis Tsunamis are caused by slides, earthquakes or volcanoes on the ocean floor. Waves do not seem very large on the open water, but the height increases as they approach land. Waves up to 30m high and speeds over 200 km/hour Volcanoes http://gsc.nrcan.gc.ca/volcanoes/images/fig31_e.gif Landslides http://www.satimagingcorp.com/media/images/natural-hazards-5.jpg Tsunamis www.indiana.edu/~pepp/earthquakes/images/sumatra12_26_04/tsunami_traveltime_local.jpeg Tsunami (at the coast) Propagation Generation (occurs offshore) http://users.skynet.be/envirconsult/tsunami/propagation_tsunami.gif