Types of Volcanoes
... • Occur when basaltic magma flows onto the surface of the earth through large cracks called fissures. – When the magma cools, it covers large areas with thick igneous rock. – Accounts for largest volume of erupted volcainc material on Earth. ...
... • Occur when basaltic magma flows onto the surface of the earth through large cracks called fissures. – When the magma cools, it covers large areas with thick igneous rock. – Accounts for largest volume of erupted volcainc material on Earth. ...
lava flows
... rapidly cooled rock fragments called pyroclasts – Size range from dust (ash) to boulders (blocks and volcanic bombs) ...
... rapidly cooled rock fragments called pyroclasts – Size range from dust (ash) to boulders (blocks and volcanic bombs) ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
Earth Science - Mr.E Science
... – Magma Chamber -magma collected inside a volcano pocket – Pipe - a long tube that connects the magma chamber to Earth's surface. – Vent - an opening through which the magma leaves the volcano – Crater - a bowl-shaped area around a volcano's central vent. – Pyroclastic Flow -an explosive fast-moving ...
... – Magma Chamber -magma collected inside a volcano pocket – Pipe - a long tube that connects the magma chamber to Earth's surface. – Vent - an opening through which the magma leaves the volcano – Crater - a bowl-shaped area around a volcano's central vent. – Pyroclastic Flow -an explosive fast-moving ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steep slopes. ...
... pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steep slopes. ...
The 1996 Surtseyan Type Eruption in Karymskoye Intracaldera Lake
... On January 2-3, 1996 a surtseyan type eruption with a discharge rate of basaltic magma of ~10 millions kg/s occurred in Karymskoe caldera lake. Initial water depth above the eruption vent was ~50 m. Characteristics of the deposits together with analyses of videotape of several explosions have allowe ...
... On January 2-3, 1996 a surtseyan type eruption with a discharge rate of basaltic magma of ~10 millions kg/s occurred in Karymskoe caldera lake. Initial water depth above the eruption vent was ~50 m. Characteristics of the deposits together with analyses of videotape of several explosions have allowe ...
What do we expect in a volcanic eruption?
... • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
... • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
No Slide Title
... The area surrounding the Pacific Plate which contains almost 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. ...
... The area surrounding the Pacific Plate which contains almost 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. ...
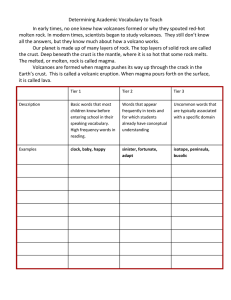
Vocabulary Handouts
... molten rock. In modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes. They still don’t know all the answers, but they know much about how a volcano works. Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep beneath the crust is the mantle, where it is s ...
... molten rock. In modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes. They still don’t know all the answers, but they know much about how a volcano works. Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep beneath the crust is the mantle, where it is s ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... • eruption is mostly lava rather than pyroclastic material • eruptions are not explosive (unless water gets into vents) • lava pours out of vents or as fountains ...
... • eruption is mostly lava rather than pyroclastic material • eruptions are not explosive (unless water gets into vents) • lava pours out of vents or as fountains ...
Informational Sheet for Teachers igneous rock sedimentary rock
... sedimentary rock Sedimentary rock is rock that has formed from sediment, like sand, mud, small pieces of rocks. Over long periods of time, these small pieces of debris are compressed (squeezed) as they are buried under more and more layers of sediment that piles up on top of it. Eventually, they are ...
... sedimentary rock Sedimentary rock is rock that has formed from sediment, like sand, mud, small pieces of rocks. Over long periods of time, these small pieces of debris are compressed (squeezed) as they are buried under more and more layers of sediment that piles up on top of it. Eventually, they are ...
What is like living near a volcano?
... • Countries such as Iceland make extensive use of geothermal power, with approximately two thirds of Iceland's electricity coming from steam powered ...
... • Countries such as Iceland make extensive use of geothermal power, with approximately two thirds of Iceland's electricity coming from steam powered ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Opening at the summit of a volcano – Crater - steep-walled depression at the summit, generally less than 1 km diameter – Caldera - a summit depression typically greater than 1 km diameter, produced by collapse following a massive eruption ...
... • Opening at the summit of a volcano – Crater - steep-walled depression at the summit, generally less than 1 km diameter – Caldera - a summit depression typically greater than 1 km diameter, produced by collapse following a massive eruption ...
Active
... Bottom: Interferogram measures areas of differential change due to ground swelling upward. Maximum displacement is in center and pattern is concentric, suggesting a pending volcanic eruption ...
... Bottom: Interferogram measures areas of differential change due to ground swelling upward. Maximum displacement is in center and pattern is concentric, suggesting a pending volcanic eruption ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volcanic debris mixed with water/melting ice or snow Pyroclastic Fall Deposits – material falls from vertical eruption, well sorted, bla ...
... Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volcanic debris mixed with water/melting ice or snow Pyroclastic Fall Deposits – material falls from vertical eruption, well sorted, bla ...
Volcanic Hazards
... • Volcanic eruption style Depending on lava’s viscosity and amount of dissolved gas content Viscosity: Liquid’s resistance to flow — Determined by silica content (lava composition) and lava temperature Quiet flow (low-viscosity basalt flow) to violent explosion (high-viscosity lava eruption) ...
... • Volcanic eruption style Depending on lava’s viscosity and amount of dissolved gas content Viscosity: Liquid’s resistance to flow — Determined by silica content (lava composition) and lava temperature Quiet flow (low-viscosity basalt flow) to violent explosion (high-viscosity lava eruption) ...
Volcanoes - BrainPOP
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
Volcanoes
... • Lahars are mud flows that often occur after eruptions. • Nuée ardentes are mobile dense clouds of incandescent ash that can move downhill at speeds up to 100 , km/hr. Mt Pelee destroyed St. Pierre on the island of Martinique, West Indies in 1902 ...
... • Lahars are mud flows that often occur after eruptions. • Nuée ardentes are mobile dense clouds of incandescent ash that can move downhill at speeds up to 100 , km/hr. Mt Pelee destroyed St. Pierre on the island of Martinique, West Indies in 1902 ...
Formation of volcanic features| sample answer
... Volcanic features found on the earths surface (external features) are caused by lava emerging from the mantle through the crust and cools when it reaches the surface. These features include; lava plateau, craters and calderas, volcanic plugs and the main feature; volcanic cones. Volcanic cones are e ...
... Volcanic features found on the earths surface (external features) are caused by lava emerging from the mantle through the crust and cools when it reaches the surface. These features include; lava plateau, craters and calderas, volcanic plugs and the main feature; volcanic cones. Volcanic cones are e ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... and basaltic lava flows (quieter than granitic but more violent than basaltic). Gas filled lava – This lava cools to form hole filled rock that has the appearance of a sponge or loaf of bread. This rock type is typically light in weight. Pumice and scoria are examples of this type of igneous rock. ...
... and basaltic lava flows (quieter than granitic but more violent than basaltic). Gas filled lava – This lava cools to form hole filled rock that has the appearance of a sponge or loaf of bread. This rock type is typically light in weight. Pumice and scoria are examples of this type of igneous rock. ...
chapter 9 vocabulary terms
... Mantle Plume (p. 279) – A mass of hotter than normal mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity. These plumes of solid yet mobile material may originate as deep as the core-mantle boundary. ...
... Mantle Plume (p. 279) – A mass of hotter than normal mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity. These plumes of solid yet mobile material may originate as deep as the core-mantle boundary. ...
Put your text here… - Social Circle City Schools
... ● Sill- When magma squeezes between horizontal layers of rock ...
... ● Sill- When magma squeezes between horizontal layers of rock ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4 - sir
... Gases expand within a magma as it nears Earth’s surface due to decreasing pressure. The violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma. ...
... Gases expand within a magma as it nears Earth’s surface due to decreasing pressure. The violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma. ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.