File
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
Volcano - Muskegon Area ISD
... • Continental volcanoes with felsic lava have cooler and thicker lava so traps gases (H2O and CO2) big explosions ...
... • Continental volcanoes with felsic lava have cooler and thicker lava so traps gases (H2O and CO2) big explosions ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... to lower the average global temperature of Earth. • In 1991, after the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, the amount of sunlight to reach Earth’s surface decreased by 2-4%. • This decrease caused the average global temperature of Earth to decrease by several tenths of a degree for severa ...
... to lower the average global temperature of Earth. • In 1991, after the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, the amount of sunlight to reach Earth’s surface decreased by 2-4%. • This decrease caused the average global temperature of Earth to decrease by several tenths of a degree for severa ...
Volcanoes - City of Redwood City
... A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth’s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive products—layers of lava, ashflows, and ash. When pressure from gases within the molten rock becomes too ...
... A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth’s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive products—layers of lava, ashflows, and ash. When pressure from gases within the molten rock becomes too ...
Volcano types and projectiles
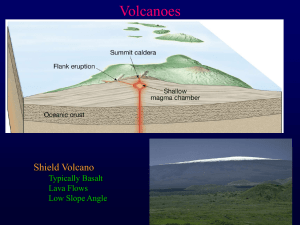
... Shield volcanoes cover a wide area and result from quiet eruptions. Mafic lava forms a gradually sloped cone. Cinder cones cover smaller areas but are higher and steeper, made from solid fragments ejected from a volcano. Composite cones/Stratovolcanoes are formed from both types of eruptions, usuall ...
... Shield volcanoes cover a wide area and result from quiet eruptions. Mafic lava forms a gradually sloped cone. Cinder cones cover smaller areas but are higher and steeper, made from solid fragments ejected from a volcano. Composite cones/Stratovolcanoes are formed from both types of eruptions, usuall ...
volcanoes stations
... 13. After looking at the samples, sketch the crystal sizes of each in the boxes below. Based on the picture of where each of these formed, fill in the blanks below for each sample with (cooled) quickly or slowly or quickly and slowly, large or small or large and small (crystals). Texture information ...
... 13. After looking at the samples, sketch the crystal sizes of each in the boxes below. Based on the picture of where each of these formed, fill in the blanks below for each sample with (cooled) quickly or slowly or quickly and slowly, large or small or large and small (crystals). Texture information ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity - sir
... associated with plumes of heat in the mantle form localized volcanic regions in the overriding plate called a hot spot produces basaltic magma sources in oceanic crust (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) produces granitic magma sources in ...
... associated with plumes of heat in the mantle form localized volcanic regions in the overriding plate called a hot spot produces basaltic magma sources in oceanic crust (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) produces granitic magma sources in ...
Slide 1
... Small crystals form when the molten rock cools quickly- this happens when the lava flows over the Earth’s surface Larger crystals are formed when the molten rock cools slowly- this happens when the magma is trapped underground. From the rocks you have seen today, which do you think came from undergr ...
... Small crystals form when the molten rock cools quickly- this happens when the lava flows over the Earth’s surface Larger crystals are formed when the molten rock cools slowly- this happens when the magma is trapped underground. From the rocks you have seen today, which do you think came from undergr ...
Igneous Extrusive Powerpoint Notes
... from volcanic eruption • Hydrosphere produced by condensation of volcanic water vapor • Biosphere both positively and negatively influenced by volcanism – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – Violent eruptions can destroy nearly all life in their paths – Large amounts of ash and vol ...
... from volcanic eruption • Hydrosphere produced by condensation of volcanic water vapor • Biosphere both positively and negatively influenced by volcanism – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – Violent eruptions can destroy nearly all life in their paths – Large amounts of ash and vol ...
Volcanoes
... silica) – causes very viscous lavas have explosive eruption Found in the Pacific Ocean called “The Ring of Fire” ...
... silica) – causes very viscous lavas have explosive eruption Found in the Pacific Ocean called “The Ring of Fire” ...
Notes -
... starts from Northern California and stretches to northern Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The subduction zone has created large earthquakes, including the Cascadia earthquake, which took place at the evening of January 26, 1700 by a magnitude 8.7 - 9.2 megathrust earthquake. Unlike in most subdu ...
... starts from Northern California and stretches to northern Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The subduction zone has created large earthquakes, including the Cascadia earthquake, which took place at the evening of January 26, 1700 by a magnitude 8.7 - 9.2 megathrust earthquake. Unlike in most subdu ...
Icelandic Geology - Fuchs Foundation: Inspiring teachers
... -Write a paragraph explaining how Iceland was formed. -If you can (this bit is hard!), write down what you think Iceland will be like in 1 million years. ...
... -Write a paragraph explaining how Iceland was formed. -If you can (this bit is hard!), write down what you think Iceland will be like in 1 million years. ...
20150210090647
... • The majority of Volcanoes on earth are located around the edge of the Pacific Plate, which is the tectonic plate that holds the Pacific ocean. • The outer boundary of this plate is nicknamed the Ring of Fire because of the number of Earthquakes and Volcanoes that occur there. ...
... • The majority of Volcanoes on earth are located around the edge of the Pacific Plate, which is the tectonic plate that holds the Pacific ocean. • The outer boundary of this plate is nicknamed the Ring of Fire because of the number of Earthquakes and Volcanoes that occur there. ...
The Origin and Petrogenesis of Mount Hasan (Small Mt. Hasan) and
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
Volcanoes
... • Atmosphere originally created from gases released by magmas • Hydrosphere produced by condensation of volcanic water vapor; chlorine and sulfate in oceans from dissolved gases • Biosphere both positively and negatively influenced by volcanism – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – ...
... • Atmosphere originally created from gases released by magmas • Hydrosphere produced by condensation of volcanic water vapor; chlorine and sulfate in oceans from dissolved gases • Biosphere both positively and negatively influenced by volcanism – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – ...
Analysis of Distribution of Volcanoes around the Korean Peninsula
... Since the scale and disaster characteristics of volcanic eruptions are determined by their geological features, it is important not only to grasp the current states of the volcanoes in neighboring countries around the Korean Peninsula, but also to analyze the tectonic settings, tectonic regions, geo ...
... Since the scale and disaster characteristics of volcanic eruptions are determined by their geological features, it is important not only to grasp the current states of the volcanoes in neighboring countries around the Korean Peninsula, but also to analyze the tectonic settings, tectonic regions, geo ...
Topic 8 Volcanoes
... from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. ...
... from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
plosky tolbachik volcano in kamchatka erupts after 40 years
... hundreds of miles (km) from the nearest residential areas. ...
... hundreds of miles (km) from the nearest residential areas. ...
GEOGRAPHY Chap – 7 VOLCANOES STD. 8 Q1. What is a volcano
... form a depression. This is called a crater. Sometimes lakes are formed on those depressions called Caldera lakes. Q5. What is a geyser? How are they different from hot springs? Ans. Geysers are fountains of superheated steam and hot water that is usually emitted with an explosion, at intervals trigg ...
... form a depression. This is called a crater. Sometimes lakes are formed on those depressions called Caldera lakes. Q5. What is a geyser? How are they different from hot springs? Ans. Geysers are fountains of superheated steam and hot water that is usually emitted with an explosion, at intervals trigg ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.