* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8: Major Elements
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
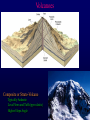
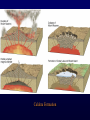
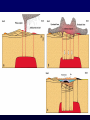
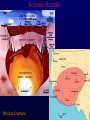
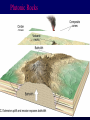
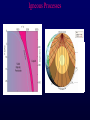
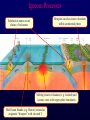
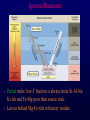
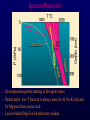
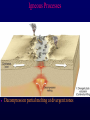
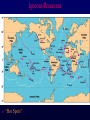
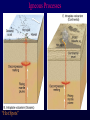
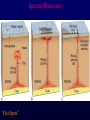
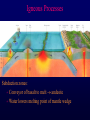
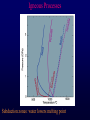
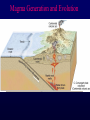
Volcanoes Shield Volcano Typically Basalt Lava Flows Low Slope Angle Volcanoes Composite or Strato-Volcano Typically Andesite Lava Flows and Tuffs (pyroclastic) Higher Slope Angle Volcanoes Cinder or Scoria Cone Typically Basalt Gas-charged spray Not very violent Volcanoes Volcanoes Lava Dome Typically Rhyolite Slow extrusion following violent explosion Volcanoes Spatter Cone Typically Basalt Gas-charged spray Not very violent Returns to ground before solidifies Volcanoes Vent vs. Fissure Volcanoes Plateau Basalt Eruptions Volcanoes Plateau Basalts are Fissure Eruptions Volcanoes Columnar Joints Caldera Formation Volcanic Hazards Lava Flows Basalt flows in Kalapana area, Hawaii Volcanic Hazards Geologists outpace lava in Hawaii! Volcanic Hazards San Juan Parangaricutiro engulfed by basaltic aa from Paricutin, 1944 Lava Flows Basalt from Mt Nyiragongo invades Goma, Congo, 2002 Volcanic Hazards Wind-blown ash deposits Heimay, Iceland 1973 Ash Volcanic Hazards Ash Vertical plinian ash column from Mt. St. Helens, 1980 Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, on June 12, 1991 Ash Volcanic Hazards Volcanic Hazards Pyroclastic Flows Video of pyroclastic flow on Mt. Unzen Soufriere erupts on Montserrat, August 1997 Glowing ash cloud descends Mt St Helens, August 1980 Volcanic Hazards Pyroclastic Flows St. Pierre, Martinique after Nuée Ardente from Mont Pelée, 1902 Volcanic Hazards Rhyolite Eruptions Plutonic Rocks Plutonic Rocks Igneous Processes Igneous Processes Hotspots can also create volcanism within continental plates Subduction zones create chains of volcanoes Melting creates volcanoes (e.g. Iceland) and oceanic crust at divergent plate boundaries Mid-Ocean Islands (e.g. Hawaii) created at enigmatic “hotspots” with elevated T Igneous Processes (and last to melt) More Mafic More Sialic (and first to melt) Partial melts: low-T fraction is always more Si-Al-NaK-rich and Fe-Mg-poor than source rock. Leaves behind Mg-Fe-rich refractory residue Igneous Processes Geotherm Decompression partial melting at divergent zones Partial melts: low-T fraction is always more Si-Al-Na-K-rich and Fe-Mg-poor than source rock. Leaves behind Mg-Fe-rich refractory residue Igneous Processes Decompression partial melting at divergent zones Igneous Processes “Hot Spots” Igneous Processes “Hot Spots” Igneous Processes “Hot Spots” Igneous Processes Subduction zones: Conveyor of basalt to melt andesite Water lowers melting point of mantle wedge Igneous Processes Subduction zones: water lowers melting point Magma Generation and Evolution Magma Generation and Evolution More Mafic (and last to melt) Crystal Fractionation More Sialic (and first to melt)