Validation of OMI L2 Sulfur Dioxide retrievals over volcanic
... coincident SO2 measurements. The only constraint is that, due to interference from water vapor in the 7.3 µm waveband used to retrieve SO2 column abundance from AIRS measurements, AIRS usually only detects volcanic SO2 in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) or above. We have assembl ...
... coincident SO2 measurements. The only constraint is that, due to interference from water vapor in the 7.3 µm waveband used to retrieve SO2 column abundance from AIRS measurements, AIRS usually only detects volcanic SO2 in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) or above. We have assembl ...
The Critical Zone What is a caldera? The Valles Caldera
... 9. Now zoom out to a scale of 500ft and move south. The white features (shown right) you see are debris fans made of sediment that has flowed down from burned ridges during rain events due to the lack of vegetation. A study found that erosion in the aftermath of fire is responsible for at least 90% ...
... 9. Now zoom out to a scale of 500ft and move south. The white features (shown right) you see are debris fans made of sediment that has flowed down from burned ridges during rain events due to the lack of vegetation. A study found that erosion in the aftermath of fire is responsible for at least 90% ...
Igneous rocks
... of fragments ejected during a volcanic eruption Varieties – Tuff – ash-sized fragments – Volcanic breccia – particles larger than ash ...
... of fragments ejected during a volcanic eruption Varieties – Tuff – ash-sized fragments – Volcanic breccia – particles larger than ash ...
6.16 Landforms from Volcanoes
... These volcanoes have a conduit system inside them that channels magma from deep within the Earth to the surface. They can have clusters of vents, with lava breaking through walls, or issuing from fissures on the sides of the mountain. With all this material coming out, they can grow thousands of met ...
... These volcanoes have a conduit system inside them that channels magma from deep within the Earth to the surface. They can have clusters of vents, with lava breaking through walls, or issuing from fissures on the sides of the mountain. With all this material coming out, they can grow thousands of met ...
Volcanic Tsunamis - Earth and Space Sciences
... hydromagmatic explosions. The energy of these explosions may also be minimized because of high water-to-magma ratios during the submarine eruptions. The volcano currently rises about 500 m above the surrounding sea floor, and has been increasing in height by ca. 4 m/yr. If Kick 'em Jenny volcano co ...
... hydromagmatic explosions. The energy of these explosions may also be minimized because of high water-to-magma ratios during the submarine eruptions. The volcano currently rises about 500 m above the surrounding sea floor, and has been increasing in height by ca. 4 m/yr. If Kick 'em Jenny volcano co ...
Chapter 4 - Igneous Rocks
... – Dark silicates and calcium-rich feldspar – Termed mafic (magnesium and ferrum, for iron) in composition – Higher dense than granitic rocks – Comprise the ocean floor and many ...
... – Dark silicates and calcium-rich feldspar – Termed mafic (magnesium and ferrum, for iron) in composition – Higher dense than granitic rocks – Comprise the ocean floor and many ...
Igneous Rocks: Born of Fire
... – Associated with explosive volcanic activity – Named for Andes mountains ...
... – Associated with explosive volcanic activity – Named for Andes mountains ...
Prof. Manoochehr Shirzaei Physical
... The products of volcanic eruption come in three forms: Lava flows—molten rock that moves over the ground Pyroclastic debris—fragments blown out of a volcano Volcanic gases—expelled vapor and aerosols ...
... The products of volcanic eruption come in three forms: Lava flows—molten rock that moves over the ground Pyroclastic debris—fragments blown out of a volcano Volcanic gases—expelled vapor and aerosols ...
Origin and Evolution of the Western Snake River Plain
... flows may be assigned to one formation and their vents assigned to another (Jenks and Bonnichsen, 1989, 1990; Jenks and others, 1993). In keeping with the practice of Bonnichsen and coworkers (Jenks and Bonnichsen, 1989, 1990; Jenks and others, 1993), we have abandoned the units “Bruneau formation” ...
... flows may be assigned to one formation and their vents assigned to another (Jenks and Bonnichsen, 1989, 1990; Jenks and others, 1993). In keeping with the practice of Bonnichsen and coworkers (Jenks and Bonnichsen, 1989, 1990; Jenks and others, 1993), we have abandoned the units “Bruneau formation” ...
Composition of Magma
... Pressure increases with depth because of the weight of overlying rocks. As pressure increases, the temperature at which a substance melts also increases, which explains why most of the rocks in Earth’s lower crust and upper mantle do not melt. ...
... Pressure increases with depth because of the weight of overlying rocks. As pressure increases, the temperature at which a substance melts also increases, which explains why most of the rocks in Earth’s lower crust and upper mantle do not melt. ...
Earth: Portrait of a Planet 3rd edition
... Earth: Portrait of a Planet, 3rd edition, by Stephen Marshak ...
... Earth: Portrait of a Planet, 3rd edition, by Stephen Marshak ...
Geomorphic Comparison of Volcanoes on Earth
... were calculated to examine correlations between inferred extension directions and volcano asymmetry. Our goal is to create a database of the Earth volcanoes for comparison to those on other solar system bodies, such as Mars, Venus, and Io. Martian and terrestrial volcanoes may be compared to identi ...
... were calculated to examine correlations between inferred extension directions and volcano asymmetry. Our goal is to create a database of the Earth volcanoes for comparison to those on other solar system bodies, such as Mars, Venus, and Io. Martian and terrestrial volcanoes may be compared to identi ...
Volume II: Hazard Annex Volcanic Eruption
... relatively weak eruptions, causing the worst volcanic disaster in the recorded history of the United States.”194 Damage to the built environment within the immediate hazard vicinity in Washington included twenty-seven bridges, about two hundred homes, more than 185 miles of highways and roads, and f ...
... relatively weak eruptions, causing the worst volcanic disaster in the recorded history of the United States.”194 Damage to the built environment within the immediate hazard vicinity in Washington included twenty-seven bridges, about two hundred homes, more than 185 miles of highways and roads, and f ...
Volcanoes and volcanic hazards
... Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards Eruptions, Landforms, and Materials Vulcanian eruptions • More explosive than Strombolian and, as a result, can generate billowing clouds of ash up to 10 km. • Produce pyroclastic flows. • Hot volcanic fragments (tephra), buoyed by heat and volcanic gases, flow ...
... Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards Eruptions, Landforms, and Materials Vulcanian eruptions • More explosive than Strombolian and, as a result, can generate billowing clouds of ash up to 10 km. • Produce pyroclastic flows. • Hot volcanic fragments (tephra), buoyed by heat and volcanic gases, flow ...
Volcanobackground
... a. How do volcanoes form? b. What are the four primary types of volcanoes? Name and describe each type in detail. Encourage students to sketch the shape of each type and note its plate tectonic setting (i.e., over hot spots, spreading centers, or subduction zones). c. Where do volcanoes form? d. Roc ...
... a. How do volcanoes form? b. What are the four primary types of volcanoes? Name and describe each type in detail. Encourage students to sketch the shape of each type and note its plate tectonic setting (i.e., over hot spots, spreading centers, or subduction zones). c. Where do volcanoes form? d. Roc ...
Lava is the molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption
... and ash over time. They range in shape from shield volcanoes with broad, shallow slopes formed from predominantly effusive eruptions of relatively fluid basaltic lava flows, to steeply-sided stratovolcanoes (also known as composite volcanoes) made of alternating layers of ash and more viscous lava f ...
... and ash over time. They range in shape from shield volcanoes with broad, shallow slopes formed from predominantly effusive eruptions of relatively fluid basaltic lava flows, to steeply-sided stratovolcanoes (also known as composite volcanoes) made of alternating layers of ash and more viscous lava f ...
H.Albert et al.
... Seismic, deformation, and gas activity (unrest) typically precedes volcanic eruptions. Tracking the changes of this activity with monitoring data is increasingly possible to successfully ...
... Seismic, deformation, and gas activity (unrest) typically precedes volcanic eruptions. Tracking the changes of this activity with monitoring data is increasingly possible to successfully ...
uLearn Activity Guides and Resources
... The uLearn library contains a great many informative resources to help introduce tectonics, how they work, how they affect the landscape and what impact they have on people. This is just a small selection of the resources available on this subject. There are too many to easily list in one place, bu ...
... The uLearn library contains a great many informative resources to help introduce tectonics, how they work, how they affect the landscape and what impact they have on people. This is just a small selection of the resources available on this subject. There are too many to easily list in one place, bu ...
bubbles - Nevada Mining Association
... the lava was hot worked their way out and left open channels rather than closed bubbles. The relative viscosity of the material determines whether gases escape quietly. The lavas in Hawaii can be viewed in safety because they are not very viscous due to their chemical composition, even though they ...
... the lava was hot worked their way out and left open channels rather than closed bubbles. The relative viscosity of the material determines whether gases escape quietly. The lavas in Hawaii can be viewed in safety because they are not very viscous due to their chemical composition, even though they ...
Ch05 Volcanism
... Mafic lava—very hot, low silica, and low viscosity Basalt flows are often thin and fluid. ...
... Mafic lava—very hot, low silica, and low viscosity Basalt flows are often thin and fluid. ...
Ch. 18 Earth Science B
... Types of Magma Basaltic magma When rock in the upper mantle melts, basaltic magma typically forms. Basaltic magma contains less than 50 percent silica. Its low silica content produces low-viscosity magma. The resulting volcano is characterized by quiet eruptions. ...
... Types of Magma Basaltic magma When rock in the upper mantle melts, basaltic magma typically forms. Basaltic magma contains less than 50 percent silica. Its low silica content produces low-viscosity magma. The resulting volcano is characterized by quiet eruptions. ...
Scientists are monitoring volcanic activity at Yellowstone and if it
... chamber is about 5 miles below the surface of the crust and is about 45 miles across and has a maximum thickness of about 8 miles. The fact that this hot spot is located under continental crust makes a huge difference to its eruptions. Where the other hot spots, like Hawaii, tend to have nonexplosiv ...
... chamber is about 5 miles below the surface of the crust and is about 45 miles across and has a maximum thickness of about 8 miles. The fact that this hot spot is located under continental crust makes a huge difference to its eruptions. Where the other hot spots, like Hawaii, tend to have nonexplosiv ...
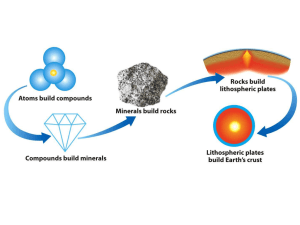
Minerals
... •Earth’s crust is 4/5 igneous rock. •Every igneous rock begins life as magma. •As magma migrates toward the surface, some of it chills and hardens underground into various types of igneous rocks. •Magma that makes it to the surface erupts in either flowing or explosive volcanoes, generating lava or ...
... •Earth’s crust is 4/5 igneous rock. •Every igneous rock begins life as magma. •As magma migrates toward the surface, some of it chills and hardens underground into various types of igneous rocks. •Magma that makes it to the surface erupts in either flowing or explosive volcanoes, generating lava or ...
Level Mountain

Level Mountain is a massive shield volcano in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just southeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about 50 km (31 mi) north of Mount Edziza. It lies on the Nahlin Plateau, comprising a series of buttes and ridges. The shield is lightly glaciated, as compared to the Coast Mountains just to the west. The only named summit of Level Mountain is Meszah Peak on the north side of the shield with an elevation of 2,190 m (7,185 ft), making it the highest point of Level Mountain. Immediately to the west, however, are the Heart Peaks, a related volcanic range just east of the Sheslay River, which is the edge of the Nahlin Plateau.Level Mountain rises above adjacent forested lowlands and undulating alpine areas surround the steeper central peaks. Streams that originate from these peaks drain across the Nahlin Plateau.