Chapter 8 section 2
... mantle when one plate sinks beneath another. The magma produced when plates melt tends to contain more silica than the magma produced deep inside Earth. This silica traps more water, which turns to steam. Steam produces tremendous pressure in thick, silica-rich magma. When ...
... mantle when one plate sinks beneath another. The magma produced when plates melt tends to contain more silica than the magma produced deep inside Earth. This silica traps more water, which turns to steam. Steam produces tremendous pressure in thick, silica-rich magma. When ...
Explosive eruptions
... • A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface. http://alaskadestination.com/alaska-volcano-images/ ...
... • A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface. http://alaskadestination.com/alaska-volcano-images/ ...
Chapter 7 Volcanoes Notes
... i. Some eruptions of lava form high, level areas ii. Lava flows out of several long cracks in an area, the thin lava flows a long way before cooling and solidifying, and the layers flow on top of each other forming a high plateau iii. Columbia Plateau in Washington, Oregon, and Idaho f. Calderas i. ...
... i. Some eruptions of lava form high, level areas ii. Lava flows out of several long cracks in an area, the thin lava flows a long way before cooling and solidifying, and the layers flow on top of each other forming a high plateau iii. Columbia Plateau in Washington, Oregon, and Idaho f. Calderas i. ...
What is a volcano? - Mr. LaFranca`s Earth Science Class
... • Because the magma is under pressure, sometimes small vent break through the side of the vent making secondary vents. • If these smaller vent go across layers of rock, it is called a dike. • If the vent stops between layers, allowing magma to get sandwiched between layers, it is called a sill. ...
... • Because the magma is under pressure, sometimes small vent break through the side of the vent making secondary vents. • If these smaller vent go across layers of rock, it is called a dike. • If the vent stops between layers, allowing magma to get sandwiched between layers, it is called a sill. ...
Volcanic hazards and Some surprising impacts on human
... (16 mi) high with a 65 km (40 mi) wide caldera at the summit. It is more than 4 times wider than Mauna Loa, the largest volcano on Earth. ...
... (16 mi) high with a 65 km (40 mi) wide caldera at the summit. It is more than 4 times wider than Mauna Loa, the largest volcano on Earth. ...
Answering: What Happens When A Volcano Erupts?
... may cause closing of the air traffic in the airspace around, and above the volcano. With the passage of time, the winds can carry the volcanic gases around a large area. The ash elements obstruct the air traffic, and create breathing complications in the near vicinity. The ash particles produce a la ...
... may cause closing of the air traffic in the airspace around, and above the volcano. With the passage of time, the winds can carry the volcanic gases around a large area. The ash elements obstruct the air traffic, and create breathing complications in the near vicinity. The ash particles produce a la ...
Chapter 9 Volcanoes Test Study Guide: Geology 1P, Mr. Traeger
... § What do viscosity, silica content, and Conditions of Volcano Formation notes and gas content have to do with the explosiveness of a volcano? viscosity lab § How Volcanoes Work website: § What are the types of lava flows? § What are the ash and rock fragments http://www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcano ...
... § What do viscosity, silica content, and Conditions of Volcano Formation notes and gas content have to do with the explosiveness of a volcano? viscosity lab § How Volcanoes Work website: § What are the types of lava flows? § What are the ash and rock fragments http://www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcano ...
No Slide Title
... How would the volcanic ash interfere with plane engines, our lungs, and car engines? ...
... How would the volcanic ash interfere with plane engines, our lungs, and car engines? ...
Hotspots, Shield Volcanoes and Supervolcanoes
... When the steady build up of pressure finally forces a way through to the surface the effect is similar to removing the cork from champagne - the gases suddenly leave the liquid they were dissolved in and blow the liquid out of its container. Once an eruption starts it will accelerate until the whole ...
... When the steady build up of pressure finally forces a way through to the surface the effect is similar to removing the cork from champagne - the gases suddenly leave the liquid they were dissolved in and blow the liquid out of its container. Once an eruption starts it will accelerate until the whole ...
Quiz Three (2:00 to 2:05 PM) - University of South Alabama
... hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth quickly and is still hot (up to 1800 °C) and fluid (low viscosity). Lava erupted at convergent plate boundaries and continental hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth very slowly. It is cooler (as low as 800 °C) and very contaminated by coun ...
... hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth quickly and is still hot (up to 1800 °C) and fluid (low viscosity). Lava erupted at convergent plate boundaries and continental hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth very slowly. It is cooler (as low as 800 °C) and very contaminated by coun ...
Erupting Volcano Model (916k PDF file)
... Composite Volcano - A type of volcano in which the cone is very steep and built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a volcano above the vent; usually bowl-shaped and has steep sides. Dike – Sh ...
... Composite Volcano - A type of volcano in which the cone is very steep and built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a volcano above the vent; usually bowl-shaped and has steep sides. Dike – Sh ...
2430 Volcano GUD v2 - Learning Resources
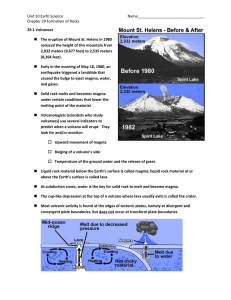
... magma to rise to the surface from deep within Earth’s crust. Sometimes, as in the case of Mount St. Helens in Washington, the eruption can be so powerful that part of the volcano can be blown away, causing the mountain to be reshaped. ...
... magma to rise to the surface from deep within Earth’s crust. Sometimes, as in the case of Mount St. Helens in Washington, the eruption can be so powerful that part of the volcano can be blown away, causing the mountain to be reshaped. ...
6th_Plate_Tectonics
... * Pahoehoe - Lava with a smooth or ropy appearance that can lead to weird shapes. * Block lava - A solid rock chunk greater than 64mm in diameter which was ejected from a volcano or lava flow. * Bomb lava - Also known as volcanic bombs; lava chunk greater than 64mm in diameter which were ejected whi ...
... * Pahoehoe - Lava with a smooth or ropy appearance that can lead to weird shapes. * Block lava - A solid rock chunk greater than 64mm in diameter which was ejected from a volcano or lava flow. * Bomb lava - Also known as volcanic bombs; lava chunk greater than 64mm in diameter which were ejected whi ...
Review for Exam 2
... 3. Describe how each of the following form: shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cones, and lava domes. Be sure to include a discussion of how the type of magma involved plays a role. 4. Give an example of a shield volcano. 5. Give an example of a composite volcano. 6. Suppose you find rock ...
... 3. Describe how each of the following form: shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cones, and lava domes. Be sure to include a discussion of how the type of magma involved plays a role. 4. Give an example of a shield volcano. 5. Give an example of a composite volcano. 6. Suppose you find rock ...
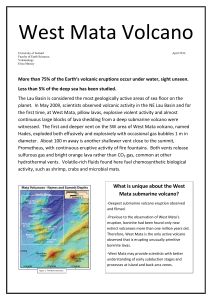
What is unique about the West Mata submarine volcano?
... echelon progression from near the Tonga Arc to the east–west strike-slip portion of the Tonga Trench. These volcanoes seem to form on small tears in the oceanic crust above a much larger tear in the subducting Pacific plate. This rapidly extending basin resides above the subducting slab, reproducing ...
... echelon progression from near the Tonga Arc to the east–west strike-slip portion of the Tonga Trench. These volcanoes seem to form on small tears in the oceanic crust above a much larger tear in the subducting Pacific plate. This rapidly extending basin resides above the subducting slab, reproducing ...
volcano_powerpoint_semi_final[1]
... cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall. Cinder cones are made of pyroclastic material.” ...
... cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall. Cinder cones are made of pyroclastic material.” ...
Study Guide: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
Word format
... B. a huge landslide produced an earthquake that then shook the volcano until it erupted C. a lateral blast occurred first during the eruption, followed by a Plinian column ...
... B. a huge landslide produced an earthquake that then shook the volcano until it erupted C. a lateral blast occurred first during the eruption, followed by a Plinian column ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
... • Flood basalts – Molten lava having flowed long distances within a basalt plateau ...
... • Flood basalts – Molten lava having flowed long distances within a basalt plateau ...
Volcanic Terms - Hamilton Field Naturalists Club
... Aa lava: A relatively stiff type of basalt lava, resulting from the cooling and de-gassing of more fluid lava (pahoehoe, q.v.). It forms a fragmented jagged surface. The name derives from a Hawaiian word for pain. Ash: see Volcanic ash and tephra. Basalt: The name of the rock that forms the bulk of ...
... Aa lava: A relatively stiff type of basalt lava, resulting from the cooling and de-gassing of more fluid lava (pahoehoe, q.v.). It forms a fragmented jagged surface. The name derives from a Hawaiian word for pain. Ash: see Volcanic ash and tephra. Basalt: The name of the rock that forms the bulk of ...
Chapter 29 Notes
... Geothermal energy is the useful product of volcanic activity. Geothermal energy is energy derived from the heat and steam associated with magma close enough to the earth’s surface ...
... Geothermal energy is the useful product of volcanic activity. Geothermal energy is energy derived from the heat and steam associated with magma close enough to the earth’s surface ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Characteristics of a quiet eruption: A volcano erupts quietly if its magma is hot or low in silica. The gases in the magma bubble out gently. The lava oozes quietly from the vent and can flow for many kilometers. Characteristics of an explosive eruption: A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is ...
... Characteristics of a quiet eruption: A volcano erupts quietly if its magma is hot or low in silica. The gases in the magma bubble out gently. The lava oozes quietly from the vent and can flow for many kilometers. Characteristics of an explosive eruption: A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is ...
Chapter 13 Section 2
... iron and that is generally dark in color • Felsic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in feldspar and silica and that is generally light in color • Mafic rock commonly makes up the oceanic crust, whereas felsic rock is more common in continental crust. ...
... iron and that is generally dark in color • Felsic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in feldspar and silica and that is generally light in color • Mafic rock commonly makes up the oceanic crust, whereas felsic rock is more common in continental crust. ...
Level Mountain

Level Mountain is a massive shield volcano in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just southeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about 50 km (31 mi) north of Mount Edziza. It lies on the Nahlin Plateau, comprising a series of buttes and ridges. The shield is lightly glaciated, as compared to the Coast Mountains just to the west. The only named summit of Level Mountain is Meszah Peak on the north side of the shield with an elevation of 2,190 m (7,185 ft), making it the highest point of Level Mountain. Immediately to the west, however, are the Heart Peaks, a related volcanic range just east of the Sheslay River, which is the edge of the Nahlin Plateau.Level Mountain rises above adjacent forested lowlands and undulating alpine areas surround the steeper central peaks. Streams that originate from these peaks drain across the Nahlin Plateau.












![volcano_powerpoint_semi_final[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008391810_1-82225bd21215d0f1bbc6c0c61491a93b-300x300.png)