Volcanic Tsunamis - Earth and Space Sciences
... likely to become more energetic as it approaches the ocean surface and hydrostatic pressures decrease, and the local tsunami hazard may increase. The documentation of submarine eruptions and a concomitant tsunami hazard at Kick 'em Jenny raises questions about the number, distribution, and eruptive ...
... likely to become more energetic as it approaches the ocean surface and hydrostatic pressures decrease, and the local tsunami hazard may increase. The documentation of submarine eruptions and a concomitant tsunami hazard at Kick 'em Jenny raises questions about the number, distribution, and eruptive ...
Chapter 4 - Igneous Rocks
... – Higher dense than granitic rocks – Comprise the ocean floor and many volcanic islands ...
... – Higher dense than granitic rocks – Comprise the ocean floor and many volcanic islands ...
bubbles - Nevada Mining Association
... the lava was hot worked their way out and left open channels rather than closed bubbles. The relative viscosity of the material determines whether gases escape quietly. The lavas in Hawaii can be viewed in safety because they are not very viscous due to their chemical composition, even though they ...
... the lava was hot worked their way out and left open channels rather than closed bubbles. The relative viscosity of the material determines whether gases escape quietly. The lavas in Hawaii can be viewed in safety because they are not very viscous due to their chemical composition, even though they ...
Volume II: Hazard Annex Volcanic Eruption
... Washington included twenty-seven bridges, about two hundred homes, more than 185 miles of highways and roads, and fifteen miles of railways. Ash from the eruption column and cloud spread across the United States in three days and circled around the Earth in fifteen days. Detectable amounts of ash we ...
... Washington included twenty-seven bridges, about two hundred homes, more than 185 miles of highways and roads, and fifteen miles of railways. Ash from the eruption column and cloud spread across the United States in three days and circled around the Earth in fifteen days. Detectable amounts of ash we ...
Geography Revision - Christ the King College
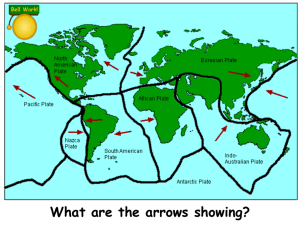
... Explain the 4 different types of plate boundary. Make sure you can create a diagram of each (include ...
... Explain the 4 different types of plate boundary. Make sure you can create a diagram of each (include ...
The Critical Zone What is a caldera? The Valles Caldera
... 9. Now zoom out to a scale of 500ft and move south. The white features (shown right) you see are debris fans made of sediment that has flowed down from burned ridges during rain events due to the lack of vegetation. A study found that erosion in the aftermath of fire is responsible for at least 90% ...
... 9. Now zoom out to a scale of 500ft and move south. The white features (shown right) you see are debris fans made of sediment that has flowed down from burned ridges during rain events due to the lack of vegetation. A study found that erosion in the aftermath of fire is responsible for at least 90% ...
Geomorphic Comparison of Volcanoes on Earth
... therefore have a preferential extension in a given direction due to the magma source not being in a relative fixed position while plate subduction occurs. It is also too early to determine if there are any correlations between plate tectonics and the geomorphologies of these volcanoes. Ideally a glo ...
... therefore have a preferential extension in a given direction due to the magma source not being in a relative fixed position while plate subduction occurs. It is also too early to determine if there are any correlations between plate tectonics and the geomorphologies of these volcanoes. Ideally a glo ...
Earth: Portrait of a Planet 3rd edition
... Pyroclastic flows (or, nuée ardentes - French): 200oC - 450oC avalanches of hot ash that race downslope. Moving up to 300 kph, they incinerate all in their path. Immediately deadly; they kill everything quickly. Many famous examples: Vesuvius, Mt. Pelée, Augustine. ...
... Pyroclastic flows (or, nuée ardentes - French): 200oC - 450oC avalanches of hot ash that race downslope. Moving up to 300 kph, they incinerate all in their path. Immediately deadly; they kill everything quickly. Many famous examples: Vesuvius, Mt. Pelée, Augustine. ...
Volcanoes and volcanic hazards
... • What factors might prevent magma from reaching Earth’s surface? • What reasons can you think of for living near a volcano? Do you think the advantages outweigh the disadvantages? • If you were to heat up a glass beaker full of crushed rock, the beaker would melt before you could finish studying th ...
... • What factors might prevent magma from reaching Earth’s surface? • What reasons can you think of for living near a volcano? Do you think the advantages outweigh the disadvantages? • If you were to heat up a glass beaker full of crushed rock, the beaker would melt before you could finish studying th ...
6.16 Landforms from Volcanoes
... down around the vent. Over time, this builds up a circular or oval-shaped cone, with a bowl-shaped crater at the top. Cinder cone volcanoes rarely grow larger than about 1,000 feet above their surroundings. Composite/Strata Volcanoes Composite volcanoes, or stratovolcanoes, make up some of the world ...
... down around the vent. Over time, this builds up a circular or oval-shaped cone, with a bowl-shaped crater at the top. Cinder cone volcanoes rarely grow larger than about 1,000 feet above their surroundings. Composite/Strata Volcanoes Composite volcanoes, or stratovolcanoes, make up some of the world ...
Prof. Manoochehr Shirzaei Physical
... Move extremely fast (100 to 300 km/hour) on a carpet of air. They are so hot (500 to 1000 °C) they kill every living thing. Flatten buildings and forests, leaving destruction behind. ...
... Move extremely fast (100 to 300 km/hour) on a carpet of air. They are so hot (500 to 1000 °C) they kill every living thing. Flatten buildings and forests, leaving destruction behind. ...
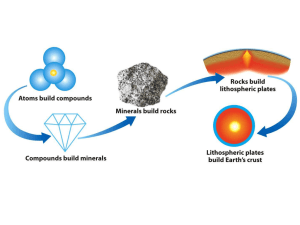
Minerals
... •Earth’s crust is 4/5 igneous rock. •Every igneous rock begins life as magma. •As magma migrates toward the surface, some of it chills and hardens underground into various types of igneous rocks. •Magma that makes it to the surface erupts in either flowing or explosive volcanoes, generating lava or ...
... •Earth’s crust is 4/5 igneous rock. •Every igneous rock begins life as magma. •As magma migrates toward the surface, some of it chills and hardens underground into various types of igneous rocks. •Magma that makes it to the surface erupts in either flowing or explosive volcanoes, generating lava or ...
Composition of Magma
... As magma rises due to plate tectonics and hot spots, it mixes with Earth’s crust. This mixing causes differences in the temperature, silica content, and gas content of magma as it reaches Earth’s surface. These properties of ...
... As magma rises due to plate tectonics and hot spots, it mixes with Earth’s crust. This mixing causes differences in the temperature, silica content, and gas content of magma as it reaches Earth’s surface. These properties of ...
No Slide Title
... 450 feet in some areas, and by late April was estimated to be growing at five feet a day. ...
... 450 feet in some areas, and by late April was estimated to be growing at five feet a day. ...
Quito - Class Notes For Mr. Pantano
... The eruption caused significant disruption of activities, including closing of the international airport. ...
... The eruption caused significant disruption of activities, including closing of the international airport. ...
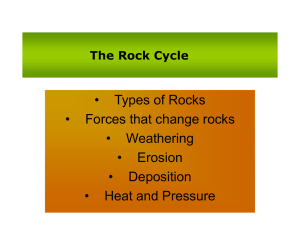
The Rock Cycle
... – Heat (contact with nearby magma changes minerals and grain sizes) – Pressure (from weight of rocks on top causes grains to line up in the same direction = banded rocks) – Chemicals (from magma’s liquids or gases change minerals) ...
... – Heat (contact with nearby magma changes minerals and grain sizes) – Pressure (from weight of rocks on top causes grains to line up in the same direction = banded rocks) – Chemicals (from magma’s liquids or gases change minerals) ...
Scientists are monitoring volcanic activity at Yellowstone and if it
... type of eruption could have on Earth’s climate from the amount of volcanic dust and gases shot into the atmosphere. There is no doubt that when large explosive eruptions occur the whole planet can be impacted through climate change and the cooling of the planet. No one knows for sure how long the “v ...
... type of eruption could have on Earth’s climate from the amount of volcanic dust and gases shot into the atmosphere. There is no doubt that when large explosive eruptions occur the whole planet can be impacted through climate change and the cooling of the planet. No one knows for sure how long the “v ...
Note - ees.nmt.edu
... • Subduction of Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America • Water released from slab aids melting above • Magma travels toward surface, some cools, other erupts • 6-7 of these volcanoes have erupted in last 200 years ...
... • Subduction of Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America • Water released from slab aids melting above • Magma travels toward surface, some cools, other erupts • 6-7 of these volcanoes have erupted in last 200 years ...
Volcanoes
... • The viscosity of magma depends upon its silica content and temperature. • Silica – material found in magma that is formed from the elements oxygen and silicon. – Silica content of magma ranges from 50-70% – The more silica magma contains, the higher its viscosity – Cooled high-viscosity magma form ...
... • The viscosity of magma depends upon its silica content and temperature. • Silica – material found in magma that is formed from the elements oxygen and silicon. – Silica content of magma ranges from 50-70% – The more silica magma contains, the higher its viscosity – Cooled high-viscosity magma form ...
Volcanoes
... • The viscosity of magma depends upon its silica content and temperature. • Silica – material found in magma that is formed from the elements oxygen and silicon. – Silica content of magma ranges from 50-70% – The more silica magma contains, the higher its viscosity – Cooled high-viscosity magma form ...
... • The viscosity of magma depends upon its silica content and temperature. • Silica – material found in magma that is formed from the elements oxygen and silicon. – Silica content of magma ranges from 50-70% – The more silica magma contains, the higher its viscosity – Cooled high-viscosity magma form ...
Volcanoes
... Physical and Chemical Properties • Each substance has a particular set of physical and chemical properties. • These properties can be used to identify a substance or to predict how it will behave • Physical property – any characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changin ...
... Physical and Chemical Properties • Each substance has a particular set of physical and chemical properties. • These properties can be used to identify a substance or to predict how it will behave • Physical property – any characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changin ...
Mt. FUJI
... pure water and amazing scenery, it is also an active volcano with a high possibility of eruption in the future. This "Volcanic Hazard Map" was created based on the results of detailed investigations by The Committee for Hazard Maps of Fuji Volcano and Yamanashi prefecture, and ...
... pure water and amazing scenery, it is also an active volcano with a high possibility of eruption in the future. This "Volcanic Hazard Map" was created based on the results of detailed investigations by The Committee for Hazard Maps of Fuji Volcano and Yamanashi prefecture, and ...
Physical processes taking place at different types of plate margin
... by the energy released using the seismometer. Many people think that 10 is the highest, but this scale is actually openended. The highest recorded earthquakes have not yet exceeded 10. ...
... by the energy released using the seismometer. Many people think that 10 is the highest, but this scale is actually openended. The highest recorded earthquakes have not yet exceeded 10. ...