* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
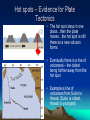
Volcanoes Anatomy of a Volcano • Conduit (pipe) in center • Vent on top • Crater = steep-walled depression Magma • Some magmas have dissolved gasses in them • Gasses rise & cause pressure – Like a soda bottle Viscosity – A substance’s resistance to flow • Determined by – Composition – type of rock (more silica = higher viscosity) • Basaltic Lava = not viscous • Andesitic Lava = very viscous – Temperature – cooler temperatures = higher viscosity – The more viscous the more explosive the eruption Eruptions • The most viscous (cold, silica) gassy lavas have the greatest eruptions Types of Volcanos 1. Shield Volcanoes Are broad, slightly domed structures Produced by fluid basaltic lavas Some form islands in ocean (ex. hawaii & iceland) 2. Cinder Cones Eject lava fragments the size of cinders into the air High in gas-rich basaltic magma small, usually only erupt once (maybe a few times) 3. Composite Cones gas rich magma with andesitic composition (lots of silica) – causes very viscous lavas have explosive eruption Found in the Pacific Ocean called “The Ring of Fire” Hot Spots • A rising mantle plume that melts surface rocks creating volcanoes Hot spots – Evidence for Plate Tectonics • The hot spot stays in one place…then the plate moves…the hot spot is still there so a new volcano forms • Eventually there is a line of volcanoes – the oldest being further away from the hot spot • Example is line of volcanoes from Suiko to Hawaii (Suiko is oldest, Hawaii is youngest)