* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18- Volcanoes - Independence High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
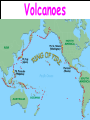
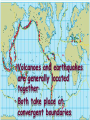
Chapter 10- Volcanoes Lecture notes Shield Volcanoes • Broad, gently sloping sides • Basaltic lava • Small amounts of gases and silica Cinder Cone Volcano • Material ejected high into the air falls back to Earth • Steep sides • More water and silica than shield • Large volume of gases • More explosive than shield Composite Volcano • Volcanic fragments alternate with lava • Large amounts of silica, water, and gases • Dangerous to humans and environment • Violently explosive Vesuvius – Sorrento (Italy) Plutons • Intrusive igneous rock bodies – Batholiths- largest plutons, irregularly shaped masses, course grained – Stocks- smaller than batholiths – Laccoliths- mushroom shaped – Sill- forms parallel to layers of rock – Dike- cuts across layers of rocks Magma Formation • 3 Factors Effect Magma Formation – Temperature • 800 – 1200c° for rock to melt and form magma • Temperature increases with depth – Pressure • Pressure increases with depth • Increased pressure raises a rock’s melting point • Raised melting point prevents all rock from melting Magma Formation -Water – Water molecules occupy pore space within rocks – Water lowers the melting point of a rock – The more water, the lower the melting point Magma Types • Basaltic – – – – – – – rocks in upper mantle melt low silica low viscosity quiet eruptions very hot (1000-1250°C) fast moving lava melted basalt Magma Types • Andesitic – oceanic crust or oceanic sediment – 60% silica (high) – intermediate viscosity – intermediate eruptions – melted andesite Magma Types • Rhyolitic – molten material rises and mixes with overlying silica and water rich continental crust – high viscosity – very explosive eruptions – highest silica content – thick, slow moving lava – melted granite Volcanoes • 80% of volcanoes found along convergent boundaries – Circum-Pacific Belt- along western coastlines of N. and S. Am. • Divergent plates move apart, magma forced upward – Ocean ridges (mid-Atlantic) – Iceland Hot Spot Volcanoes • Located away from plate boundary • Magma plume rises from core • Plume melts the crust •Islands are formed by escaping magma •Usually forms arcs as a result of moving plates • Volcanoes and earthquakes are generally located together • Both take place at convergent boundaries