Ancient Greek Civilization
... constructed stone roads/bridges, built highly advanced drainage systems and aqueducts (royal family had showers and toilets that could be flushed) • The Minoans were either conquered by or succeed by the Mycenaeans ...
... constructed stone roads/bridges, built highly advanced drainage systems and aqueducts (royal family had showers and toilets that could be flushed) • The Minoans were either conquered by or succeed by the Mycenaeans ...
regional latin forum 2007
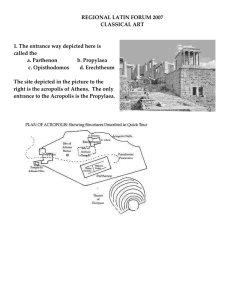
... temple built for the Greek goddess Athena built in the 5th century BC on the Acropolis of Athens. It is the most important surviving building of Classical Greece, generally considered to be the culmination of the development of the Doric order. The Parthenon replaced an older temple of Athena, calle ...
... temple built for the Greek goddess Athena built in the 5th century BC on the Acropolis of Athens. It is the most important surviving building of Classical Greece, generally considered to be the culmination of the development of the Doric order. The Parthenon replaced an older temple of Athena, calle ...
Greekworldstudybuddy - Kent City School District
... Q: Alexander the Great enjoyed Greek culture and ideas. What did he do in his empire that reflects his admiration for their culture? (how did he show that he liked their culture/art?) A: 1) He built cities modeled after Greek cities. 2) Built theaters and temples like those in Greece. 3) Encouraged ...
... Q: Alexander the Great enjoyed Greek culture and ideas. What did he do in his empire that reflects his admiration for their culture? (how did he show that he liked their culture/art?) A: 1) He built cities modeled after Greek cities. 2) Built theaters and temples like those in Greece. 3) Encouraged ...
Ancient Greece
... who has seized control, often by illegal means. Tyrannies in Greece first arose during the mid 600s BCE. Many tyrants only ruled for short periods of time. ...
... who has seized control, often by illegal means. Tyrannies in Greece first arose during the mid 600s BCE. Many tyrants only ruled for short periods of time. ...
Classical Greek Culture Learning Station Information Sheets
... the center of Greek temples were walled rooms that housed both the statues of deities and treasuries in which gifts to the gods and goddesses were safe-guarded. These central rooms were surrounded by a screen of columns that made Greek temples open structures rather than closed ones. Although the co ...
... the center of Greek temples were walled rooms that housed both the statues of deities and treasuries in which gifts to the gods and goddesses were safe-guarded. These central rooms were surrounded by a screen of columns that made Greek temples open structures rather than closed ones. Although the co ...
Document
... *Deep harbors allowed them to become merchants and traders. Exported wine, olive oil, pottery, and cloth. *A land of high mountain ranges enclosing fertile valleys which were isolated because transportation over the mountains was tough. This led the Greeks to organize my independent city-states. *Ci ...
... *Deep harbors allowed them to become merchants and traders. Exported wine, olive oil, pottery, and cloth. *A land of high mountain ranges enclosing fertile valleys which were isolated because transportation over the mountains was tough. This led the Greeks to organize my independent city-states. *Ci ...
Test Seven: Ancient Greece Study Guide
... 1. Which geographical barrier influenced the isolation of Greek communities and the development of many independent city-states? 2. Which ancient Greek civilization emerged on the island of Crete? 3. True or False: The Minoan civilization developed BEFORE and influenced the emergence of the Mycenaea ...
... 1. Which geographical barrier influenced the isolation of Greek communities and the development of many independent city-states? 2. Which ancient Greek civilization emerged on the island of Crete? 3. True or False: The Minoan civilization developed BEFORE and influenced the emergence of the Mycenaea ...
Chapter 29
... direct the rebuilding of the city. Pericles promoted constructing many public and religious buildings, including the Parthenon [Parthenon: the temple built on the acropolis above Athens, honoring the goddess Athena] , the most famous temple in Athens. Pericles believed that Athens was a model—in cul ...
... direct the rebuilding of the city. Pericles promoted constructing many public and religious buildings, including the Parthenon [Parthenon: the temple built on the acropolis above Athens, honoring the goddess Athena] , the most famous temple in Athens. Pericles believed that Athens was a model—in cul ...
REVIEW GAME
... • 31. This bronze statue stood more than 100 feet high. It appears to have been the tallest statue in the Hellenistic world. ...
... • 31. This bronze statue stood more than 100 feet high. It appears to have been the tallest statue in the Hellenistic world. ...
Chapter 11 The Ancient Greeks
... Was located on the Peloponnesus Peninsula and small islands of the Aegean Sea Climate: mild winters, hot summers. Mountains & Water kept regions isolated from each other, that is why there were many individual city-states Due to closeness of sea, Greeks traveled and others traveled to Greece ...
... Was located on the Peloponnesus Peninsula and small islands of the Aegean Sea Climate: mild winters, hot summers. Mountains & Water kept regions isolated from each other, that is why there were many individual city-states Due to closeness of sea, Greeks traveled and others traveled to Greece ...
Ancient Greek architecture

The architecture of Ancient Greece is the architecture produced by the Greek-speaking people (Hellenic people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland and Peloponnesus, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC.Ancient Greek architecture is best known from its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, mostly as ruins but many substantially intact. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 350 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (propylon), the public square (agora) surrounded by storied colonnade (stoa), the town council building (bouleuterion), the public monument, the monumental tomb (mausoleum) and the stadium.Ancient Greek architecture is distinguished by its highly formalised characteristics, both of structure and decoration. This is particularly so in the case of temples where each building appears to have been conceived as a sculptural entity within the landscape, most often raised on high ground so that the elegance of its proportions and the effects of light on its surfaces might be viewed from all angles. Nikolaus Pevsner refers to ""the plastic shape of the [Greek] temple.....placed before us with a physical presence more intense, more alive than that of any later building"".The formal vocabulary of Ancient Greek architecture, in particular the division of architectural style into three defined orders: the Doric Order, the Ionic Order and the Corinthian Order, was to have profound effect on Western architecture of later periods. The architecture of Ancient Rome grew out of that of Greece and maintained its influence in Italy unbroken until the present day. From the Renaissance, revivals of Classicism have kept alive not only the precise forms and ordered details of Greek architecture, but also its concept of architectural beauty based on balance and proportion. The successive styles of Neoclassical architecture and Greek Revival architecture followed and adapted Ancient Greek styles closely. Several issues related to interpretation, restoration or/and reconstruction of Ancient Greek architectural monuments are often assisted by new technologies, including 3D and virtual or augmented reality environments.