0325 Greece Cause and Effect
... 2. Why do you think Pericles would call Athens the “school of Greece”? ...
... 2. Why do you think Pericles would call Athens the “school of Greece”? ...
3_Classical_Civilizations
... - Everyone should use good moral behavior - Have good educational system – to help have good government officials - Government officials should rule by setting a good example of behavior for the people - Technology: paper, rudder, wheel barrow ...
... - Everyone should use good moral behavior - Have good educational system – to help have good government officials - Government officials should rule by setting a good example of behavior for the people - Technology: paper, rudder, wheel barrow ...
Unit 3 - Waterville Central School
... - Everyone should use good moral behavior - Have good educational system – to help have good government officials - Government officials should rule by setting a good example of behavior for the people - Technology: paper, rudder, wheel barrow ...
... - Everyone should use good moral behavior - Have good educational system – to help have good government officials - Government officials should rule by setting a good example of behavior for the people - Technology: paper, rudder, wheel barrow ...
Ancient Greece Study Guide
... _____ 31. Led to the end of the Minoan civilization _____ 32. Greeks saw themselves as members of this, rather than as Greeks _____ 33. Battle that marked the end of the Persian Wars _____ 34. This groups was strong and well organized _____ 35. A poem set to music _____ 36. Explained why natural or ...
... _____ 31. Led to the end of the Minoan civilization _____ 32. Greeks saw themselves as members of this, rather than as Greeks _____ 33. Battle that marked the end of the Persian Wars _____ 34. This groups was strong and well organized _____ 35. A poem set to music _____ 36. Explained why natural or ...
What can we learn about the Ancient Greeks L1
... • The Ancient Greece empire spread over Europe as far as France in the East. The Greek Empire was most powerful between 2000 BC and 146 BC ...
... • The Ancient Greece empire spread over Europe as far as France in the East. The Greek Empire was most powerful between 2000 BC and 146 BC ...
Golden Age of Athens
... the city could hold thousands of people. Dionysus was the god of theater and wine. Greek plays grew out of the songs and dances that the Greeks performed at harvest time to honor him. As Greek playwrights developed their art, they began to write plays that told stories. The plays included a few main ...
... the city could hold thousands of people. Dionysus was the god of theater and wine. Greek plays grew out of the songs and dances that the Greeks performed at harvest time to honor him. As Greek playwrights developed their art, they began to write plays that told stories. The plays included a few main ...
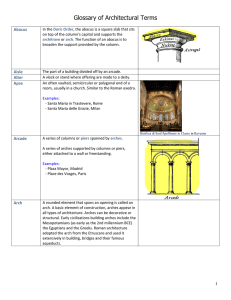
Glossary of Architectural Terms
... the Great Exhibition of 1851. More than 14,000 exhibitors from around the world gathered in the Palace's 990,000 square feet (92,000 m2) of exhibition space to display examples of the latest technology developed in the Industrial Revolution. Designed by Joseph Paxton, the Great Exhibition building w ...
... the Great Exhibition of 1851. More than 14,000 exhibitors from around the world gathered in the Palace's 990,000 square feet (92,000 m2) of exhibition space to display examples of the latest technology developed in the Industrial Revolution. Designed by Joseph Paxton, the Great Exhibition building w ...
Historical Background (all dates BCE)
... Indo-Europeans, Trans-Caucasus, “Aryan” (term adopted from Skr.) Mycenae, Lion’s Gate Heinrich Schliemann Tombs Mask of Agamemnon Trojan War Collapse: so-called Dorian Invasion, starting c. 1200 Cyclopean architecture Isthmus of Corinth (canal built 1893) ...
... Indo-Europeans, Trans-Caucasus, “Aryan” (term adopted from Skr.) Mycenae, Lion’s Gate Heinrich Schliemann Tombs Mask of Agamemnon Trojan War Collapse: so-called Dorian Invasion, starting c. 1200 Cyclopean architecture Isthmus of Corinth (canal built 1893) ...
AP Art History Unit Sheet #5: Greek Art (Chapter 5)
... inherited some practices and forms from Egypt and Mesopotamia, they developed a distinct artistic and architectural identity that had profound impact on every Western culture since their time. Ancient Greek culture spans from ca. 900 BCE to ca. 30 BCE, and is divided into periods—the Geometric and ...
... inherited some practices and forms from Egypt and Mesopotamia, they developed a distinct artistic and architectural identity that had profound impact on every Western culture since their time. Ancient Greek culture spans from ca. 900 BCE to ca. 30 BCE, and is divided into periods—the Geometric and ...
Ancient Greek Games - ps1286-2
... mainland Greece and the colonies in southern This style was found in eastern Greece and the Italy and Sicily. islands. ...
... mainland Greece and the colonies in southern This style was found in eastern Greece and the Italy and Sicily. islands. ...
Bi-Weekly Quiz # 4
... What was considered the greatest contribution to western civilization? What building material, which we rely on today, was not around to be used in Ancient Greece? Why was Socrates put to death? (What was he found guilty of?) What was the main building material in Ancient Greece? What was “The Acade ...
... What was considered the greatest contribution to western civilization? What building material, which we rely on today, was not around to be used in Ancient Greece? Why was Socrates put to death? (What was he found guilty of?) What was the main building material in Ancient Greece? What was “The Acade ...
Ancient Greek Art Presentation
... The Parthenon, built in the fifth century B.C., is perhaps the most well known example of Greek architecture. Dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena, the Parthenon was an example of the Greek ideals of structure and devotion to their faith. Its construction began in 447 BC when the Athenian Empire wa ...
... The Parthenon, built in the fifth century B.C., is perhaps the most well known example of Greek architecture. Dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena, the Parthenon was an example of the Greek ideals of structure and devotion to their faith. Its construction began in 447 BC when the Athenian Empire wa ...
Greek Art - Lee County Schools
... Athens 530 BCE. The figures remained in the orange-red color of the clay, and the surrounding background was turned to black by the firing of the pot. With this, the method of detailing the figures was changed dramatically. Instead of using a sharp tool to incise lines, the painters used a fine brus ...
... Athens 530 BCE. The figures remained in the orange-red color of the clay, and the surrounding background was turned to black by the firing of the pot. With this, the method of detailing the figures was changed dramatically. Instead of using a sharp tool to incise lines, the painters used a fine brus ...
ANCIENT CORINTH Corinth, or Korinth was a city-state
... Founded by Corinthos, a descendant of the god Helios (Sun), in accordance with the Hellenic myth, Corinth was inhabited from at least as early as 6500 BC. In classical times, Corinth rivaled Athens and Thebes in wealth, based on the Isthmian traffic and trade. Until the mid-6th century, was a major ...
... Founded by Corinthos, a descendant of the god Helios (Sun), in accordance with the Hellenic myth, Corinth was inhabited from at least as early as 6500 BC. In classical times, Corinth rivaled Athens and Thebes in wealth, based on the Isthmian traffic and trade. Until the mid-6th century, was a major ...
Ancient Greek architecture

The architecture of Ancient Greece is the architecture produced by the Greek-speaking people (Hellenic people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland and Peloponnesus, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC.Ancient Greek architecture is best known from its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, mostly as ruins but many substantially intact. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 350 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (propylon), the public square (agora) surrounded by storied colonnade (stoa), the town council building (bouleuterion), the public monument, the monumental tomb (mausoleum) and the stadium.Ancient Greek architecture is distinguished by its highly formalised characteristics, both of structure and decoration. This is particularly so in the case of temples where each building appears to have been conceived as a sculptural entity within the landscape, most often raised on high ground so that the elegance of its proportions and the effects of light on its surfaces might be viewed from all angles. Nikolaus Pevsner refers to ""the plastic shape of the [Greek] temple.....placed before us with a physical presence more intense, more alive than that of any later building"".The formal vocabulary of Ancient Greek architecture, in particular the division of architectural style into three defined orders: the Doric Order, the Ionic Order and the Corinthian Order, was to have profound effect on Western architecture of later periods. The architecture of Ancient Rome grew out of that of Greece and maintained its influence in Italy unbroken until the present day. From the Renaissance, revivals of Classicism have kept alive not only the precise forms and ordered details of Greek architecture, but also its concept of architectural beauty based on balance and proportion. The successive styles of Neoclassical architecture and Greek Revival architecture followed and adapted Ancient Greek styles closely. Several issues related to interpretation, restoration or/and reconstruction of Ancient Greek architectural monuments are often assisted by new technologies, including 3D and virtual or augmented reality environments.