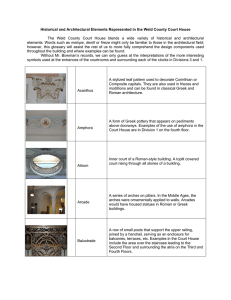
The Golden Age of Pericles, Achievements and Contributions of
... •Comedy – dramas filled with humor and poked fun at customs or respected people, written mainly by Aristophanes ...
... •Comedy – dramas filled with humor and poked fun at customs or respected people, written mainly by Aristophanes ...
Chapter 6 Greece*s Golden and Hellenistic Age
... 2. Spent 3 years as a hostage in Thebes where he learned about Greek culture and military techniques 3. He admired Greek ways 4. He organized a well-disciplined army 5. Some Greeks saw him as a savior. ...
... 2. Spent 3 years as a hostage in Thebes where he learned about Greek culture and military techniques 3. He admired Greek ways 4. He organized a well-disciplined army 5. Some Greeks saw him as a savior. ...
Athenian Agora Archaic through Hellenistic Greek 600 BCE – 150
... piece of jewelry from a jewelry box handed to her by standing servant ...
... piece of jewelry from a jewelry box handed to her by standing servant ...
The functions and rituals of these two temples are mostly different.
... Kingdom Egypt) and on the right is the Parthenon, in Athens, Greece (c. 450 BCE, Classical Greece). They are similar in that they are monumental temples designed for limited access and featuring large, stone columns and painted decorations. In addition, both buildings were the focus of religious rit ...
... Kingdom Egypt) and on the right is the Parthenon, in Athens, Greece (c. 450 BCE, Classical Greece). They are similar in that they are monumental temples designed for limited access and featuring large, stone columns and painted decorations. In addition, both buildings were the focus of religious rit ...
ANCIENT GREECE
... The region declined for hundreds of years after the Mycenaeans. Around 750 BC, the Greek City state, or polis, starts to develop. Cities were built on two levels, with an acropolis on the top level. The Acropolis The acropolis of each city had temples to the Greek gods and goddesses. The G ...
... The region declined for hundreds of years after the Mycenaeans. Around 750 BC, the Greek City state, or polis, starts to develop. Cities were built on two levels, with an acropolis on the top level. The Acropolis The acropolis of each city had temples to the Greek gods and goddesses. The G ...
Ancient Greece Notes
... o Trade food, soil was not good for growing crops o Strong navies to aid/support trade o Volcano erupted nearby, tidal wave destroyed Crete. Mycenaeans o Society on the mainland, Southern Greece o Conquered weak Minoans 1400BC o Groups and clans of warriors o Built fort-like cities 800-700BC Greeks ...
... o Trade food, soil was not good for growing crops o Strong navies to aid/support trade o Volcano erupted nearby, tidal wave destroyed Crete. Mycenaeans o Society on the mainland, Southern Greece o Conquered weak Minoans 1400BC o Groups and clans of warriors o Built fort-like cities 800-700BC Greeks ...
• Section 4: The Glory that Was Greece • LEQ: How did Greek
... • Showed human beings in their most perfect, graceful form Think about it… • Can you think of an example of architecture in the US that was heavily influenced by the Greek style of architecture? Greek Literature One of the Greeks greatest contributions to literature was the Greek tragedy: plays that ...
... • Showed human beings in their most perfect, graceful form Think about it… • Can you think of an example of architecture in the US that was heavily influenced by the Greek style of architecture? Greek Literature One of the Greeks greatest contributions to literature was the Greek tragedy: plays that ...
Laura Cook, Ibtissam Gad, and Angela Li
... commonly found in mainland Greece, stands sturdy and formal with a plain capital, or the top of the column. The Doric column also did not sit on a base, or a platform at the bottom of the column. The Parthenon, built in the 5th century BC, contains Doric columns. The Ionic style had a more elegant c ...
... commonly found in mainland Greece, stands sturdy and formal with a plain capital, or the top of the column. The Doric column also did not sit on a base, or a platform at the bottom of the column. The Parthenon, built in the 5th century BC, contains Doric columns. The Ionic style had a more elegant c ...
Unit 6ана Classical Greece
... Developed Socratic method: learning about beliefs and ideas by asking questions ...
... Developed Socratic method: learning about beliefs and ideas by asking questions ...
Ancient Greek architecture

The architecture of Ancient Greece is the architecture produced by the Greek-speaking people (Hellenic people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland and Peloponnesus, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC.Ancient Greek architecture is best known from its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, mostly as ruins but many substantially intact. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 350 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (propylon), the public square (agora) surrounded by storied colonnade (stoa), the town council building (bouleuterion), the public monument, the monumental tomb (mausoleum) and the stadium.Ancient Greek architecture is distinguished by its highly formalised characteristics, both of structure and decoration. This is particularly so in the case of temples where each building appears to have been conceived as a sculptural entity within the landscape, most often raised on high ground so that the elegance of its proportions and the effects of light on its surfaces might be viewed from all angles. Nikolaus Pevsner refers to ""the plastic shape of the [Greek] temple.....placed before us with a physical presence more intense, more alive than that of any later building"".The formal vocabulary of Ancient Greek architecture, in particular the division of architectural style into three defined orders: the Doric Order, the Ionic Order and the Corinthian Order, was to have profound effect on Western architecture of later periods. The architecture of Ancient Rome grew out of that of Greece and maintained its influence in Italy unbroken until the present day. From the Renaissance, revivals of Classicism have kept alive not only the precise forms and ordered details of Greek architecture, but also its concept of architectural beauty based on balance and proportion. The successive styles of Neoclassical architecture and Greek Revival architecture followed and adapted Ancient Greek styles closely. Several issues related to interpretation, restoration or/and reconstruction of Ancient Greek architectural monuments are often assisted by new technologies, including 3D and virtual or augmented reality environments.