Characterization of AtAAP1 function in amino acid uptake by the root
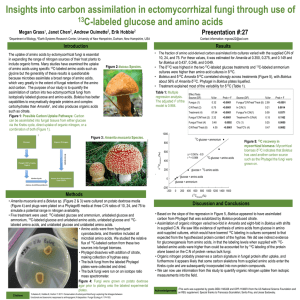
... for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of protein versus bulk fungi. • Organic nitrogen probably preserves a carbon signature in fungal p ...
... for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of protein versus bulk fungi. • Organic nitrogen probably preserves a carbon signature in fungal p ...
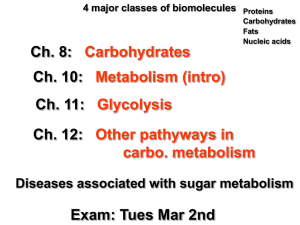
2–3 Carbon Compounds
... Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with the electrons from other atoms to form strong covalent bonds. Living organisms are made of molecules that consist of carbon (C) and other elements (H, ...
... Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with the electrons from other atoms to form strong covalent bonds. Living organisms are made of molecules that consist of carbon (C) and other elements (H, ...
Grade 11 Unit 8 - Amazon Web Services
... electrons which hold them together are very important in accounting for the properties of compounds. Structural formulas and wood models representing molecules can be used to account for the physical and chemical properties of compounds. ...
... electrons which hold them together are very important in accounting for the properties of compounds. Structural formulas and wood models representing molecules can be used to account for the physical and chemical properties of compounds. ...
PPT
... • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
... • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
Biology_Chapter 8_Cellular_Respiration
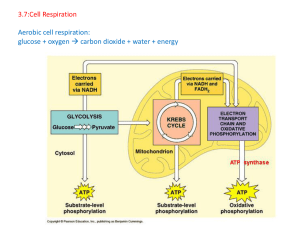
... produces 3NADH, 1FADH2, and 2CO2 • Therefore, For each Glucose molecule, the Krebs Cycle produces 6NADH, 2FADH2, 4CO2, and 2ATP ...
... produces 3NADH, 1FADH2, and 2CO2 • Therefore, For each Glucose molecule, the Krebs Cycle produces 6NADH, 2FADH2, 4CO2, and 2ATP ...
2 H
... • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
... • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
File - SBI
... 8. Why isn't anaerobic respiration effective for larger organisms? a. The energy yield is too small b. It causes too much glucose to be burned up c. It results in products that may be toxic to the organism d. NAD+ is lost over time because it can't be regenerated e. Only d is false 9. More ATP is pr ...
... 8. Why isn't anaerobic respiration effective for larger organisms? a. The energy yield is too small b. It causes too much glucose to be burned up c. It results in products that may be toxic to the organism d. NAD+ is lost over time because it can't be regenerated e. Only d is false 9. More ATP is pr ...
Biology
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with the electrons from other atoms to form ...
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with the electrons from other atoms to form ...
Chapter 8 - Inorganic carbon chemistry
... of ice caps and consequent flooding in low-lying areas of the Earth. There will also be changes in the weather patterns which would affect agriculture worldwide. These problems have been recognised by nations worldwide. Recent agreements under the Kyoto Accord between nations mean that there will be ...
... of ice caps and consequent flooding in low-lying areas of the Earth. There will also be changes in the weather patterns which would affect agriculture worldwide. These problems have been recognised by nations worldwide. Recent agreements under the Kyoto Accord between nations mean that there will be ...
Lesson Overview
... In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms “organic,” believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. We now understand that the principles governing the chemistry of living and nonliving things are the same, but the term “organic chem ...
... In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms “organic,” believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. We now understand that the principles governing the chemistry of living and nonliving things are the same, but the term “organic chem ...
Biocompatibility of synthetic and bio-material fusion
... The choice of a carrier molecule is important in targetted drug delivery because it significantly affects pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drugs. Materials like lipids, natural and synthetic polymers, carbohydrates, surfactants and dendrimers are used as drug carriers 1–3. The drug conjugate ...
... The choice of a carrier molecule is important in targetted drug delivery because it significantly affects pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drugs. Materials like lipids, natural and synthetic polymers, carbohydrates, surfactants and dendrimers are used as drug carriers 1–3. The drug conjugate ...
Multiple Choice Review- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... a. The addition of electrons to a molecule b. The addition of protons to a molecule c. The loss of electrons from a molecule d. The loss of protons from a molecule 2. What molecules are necessary for aerobic cellular respiration? a. Glucose and Oxygen b. Glucose and Carbon Dioxide c. Carbon Dioxide ...
... a. The addition of electrons to a molecule b. The addition of protons to a molecule c. The loss of electrons from a molecule d. The loss of protons from a molecule 2. What molecules are necessary for aerobic cellular respiration? a. Glucose and Oxygen b. Glucose and Carbon Dioxide c. Carbon Dioxide ...
Lesson Overview
... low, glycogen is broken down into glucose, which is then released into the blood, -The glycogen stored in your muscles supplies the energy for muscle contraction. ...
... low, glycogen is broken down into glucose, which is then released into the blood, -The glycogen stored in your muscles supplies the energy for muscle contraction. ...
Slide ()
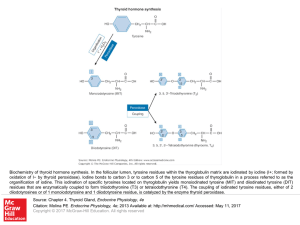
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
Unit Two “Energy Acquisition”
... the cytoplasm of cells, and does not require Oxygen (occurs in the Cytoplasm) – B) Acetyl-CoA formation and Krebs Cycle: production of large amounts of ATP that takes place in the Mitochondria, and does require Oxygen (occurs in the Mitochondria) – C) Electron Transport Chain: NADH and FADH2 release ...
... the cytoplasm of cells, and does not require Oxygen (occurs in the Cytoplasm) – B) Acetyl-CoA formation and Krebs Cycle: production of large amounts of ATP that takes place in the Mitochondria, and does require Oxygen (occurs in the Mitochondria) – C) Electron Transport Chain: NADH and FADH2 release ...
2011-teacher_20110323_1416x
... – As rocks wear down, phosphate is released – It is released into streams and rivers and eventually makes its way to the ocean and is used by marine organisms – On land it is absorbed by plants and passes up through the food chain ...
... – As rocks wear down, phosphate is released – It is released into streams and rivers and eventually makes its way to the ocean and is used by marine organisms – On land it is absorbed by plants and passes up through the food chain ...
Lecture 8. Biogeochemical Cycles
... Hence, even relatively small changes in soil carbon storage could have a significant impact on the global carbon balance In the last 7,800 years, the net carbon reservoir in the soil has decreased by 5.0 X 1010 metric tons largely due to conversion of land to agriculture (Lai, 2004). ...
... Hence, even relatively small changes in soil carbon storage could have a significant impact on the global carbon balance In the last 7,800 years, the net carbon reservoir in the soil has decreased by 5.0 X 1010 metric tons largely due to conversion of land to agriculture (Lai, 2004). ...
cycle - realfuture.org
... discussion on microbial diversity. In addition to requiring energy, all known forms of life are carbon-based and require carbon as their primary macronutrient. It is for this reason that life is commonly categorized on the basis of both energy and carbon sources (Figure 1). Phototrophs obtain their ...
... discussion on microbial diversity. In addition to requiring energy, all known forms of life are carbon-based and require carbon as their primary macronutrient. It is for this reason that life is commonly categorized on the basis of both energy and carbon sources (Figure 1). Phototrophs obtain their ...
cycle - realfuture.org
... discussion on microbial diversity. In addition to requiring energy, all known forms of life are carbon-based and require carbon as their primary macronutrient. It is for this reason that life is commonly categorized on the basis of both energy and carbon sources (Figure 1). Phototrophs obtain their ...
... discussion on microbial diversity. In addition to requiring energy, all known forms of life are carbon-based and require carbon as their primary macronutrient. It is for this reason that life is commonly categorized on the basis of both energy and carbon sources (Figure 1). Phototrophs obtain their ...
Cellular Respiration
... One example of respiration in ourselves The lungs absorb oxygen from the air ...
... One example of respiration in ourselves The lungs absorb oxygen from the air ...
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... IB Question: Compare anaerobic cellular respiration and aerobic cellular respiration. [5] Direct comparisons must be made to achieve a mark. anaerobic in the absence of oxygen whereas aerobic in the presence of oxygen; both may produce 2 CO ; both produce ATP; aerobic releases considerably more ATP ...
... IB Question: Compare anaerobic cellular respiration and aerobic cellular respiration. [5] Direct comparisons must be made to achieve a mark. anaerobic in the absence of oxygen whereas aerobic in the presence of oxygen; both may produce 2 CO ; both produce ATP; aerobic releases considerably more ATP ...
The Carbon Cycle: Implications for Climate Change and Congress June 25, 2007
... In short, the oceans, vegetation, and soils cannot consume carbon released from human activities quickly enough to stop CO2 from accumulating in the atmosphere. Humans tap the huge pool of fossil carbon for energy, and affect the global carbon cycle by transferring fossil carbon — which took million ...
... In short, the oceans, vegetation, and soils cannot consume carbon released from human activities quickly enough to stop CO2 from accumulating in the atmosphere. Humans tap the huge pool of fossil carbon for energy, and affect the global carbon cycle by transferring fossil carbon — which took million ...
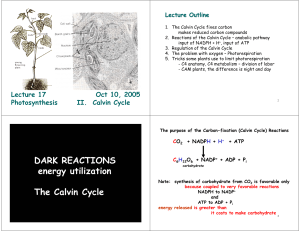
DARK REACTIONS energy utilization The Calvin Cycle
... Costs more energy to do business this way… but has the advantage when CO2 is limiting (when stomates are closed - like on hot days) Who cares as long as the sun is shining ...
... Costs more energy to do business this way… but has the advantage when CO2 is limiting (when stomates are closed - like on hot days) Who cares as long as the sun is shining ...