L11_lipogenesis
... – Forms thioesters which are, themselves, quite ‘high energy’ bonds – Most common carrier of fatty acids and acetates ...
... – Forms thioesters which are, themselves, quite ‘high energy’ bonds – Most common carrier of fatty acids and acetates ...
lect5
... CPS is the key regulatory step of the urea cycle other N compounds are excreted in the urine carbon skeletons can be recycled or oxidised ...
... CPS is the key regulatory step of the urea cycle other N compounds are excreted in the urine carbon skeletons can be recycled or oxidised ...
Effects of oxygen on the growth and metabolism of Actinomyces
... the closely related species A. naeslundii, the citric acid cycle enzymes have been demonstrated [5], yet the hnk to oxidative catabolism in Actinomyces species has not been made. Taken together the above strongly suggests that A. viscosus adjusts its metabolism to the amount of oxygen available in t ...
... the closely related species A. naeslundii, the citric acid cycle enzymes have been demonstrated [5], yet the hnk to oxidative catabolism in Actinomyces species has not been made. Taken together the above strongly suggests that A. viscosus adjusts its metabolism to the amount of oxygen available in t ...
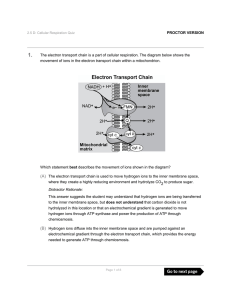
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... (D) What effect will the movement of negatively charged ions through the inner mitochondrial membrane have on the production of water? Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain results in water molecules, ...
... (D) What effect will the movement of negatively charged ions through the inner mitochondrial membrane have on the production of water? Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain results in water molecules, ...
Slide 1
... – Variable biomass inputs (C3 vs. C4 plants) – Some of the carbon incorporated into SOM by these critters has an atmospheric, not SOM source. – Atmospheric C is heavier. Atmospheric CO2 in the soil is 4.4 ‰ heavier than CO2 metabolized by decomposition (Wedin, ...
... – Variable biomass inputs (C3 vs. C4 plants) – Some of the carbon incorporated into SOM by these critters has an atmospheric, not SOM source. – Atmospheric C is heavier. Atmospheric CO2 in the soil is 4.4 ‰ heavier than CO2 metabolized by decomposition (Wedin, ...
Biology 20 Ch 3 Practice Test
... methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen. There was no atmospheric oxygen because it was chemically combined in Earth’s crust in compounds such as iron oxide. Scientists speculate that without life on earth, the composition of the atmosphere would be about 98% carbon dioxide. What bi ...
... methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen. There was no atmospheric oxygen because it was chemically combined in Earth’s crust in compounds such as iron oxide. Scientists speculate that without life on earth, the composition of the atmosphere would be about 98% carbon dioxide. What bi ...
1. Introduction - UBC ECE - University of British Columbia
... respectively. The simulation was performed in an aqueous medium. The AMBER99 force field port6 in GROMACS was used, and the TIP3P water model7 was implemented. The Lennard-Jones potential parameters for the carbon nanotube were manually modified in the AMBER99 port, and the parameter values were tak ...
... respectively. The simulation was performed in an aqueous medium. The AMBER99 force field port6 in GROMACS was used, and the TIP3P water model7 was implemented. The Lennard-Jones potential parameters for the carbon nanotube were manually modified in the AMBER99 port, and the parameter values were tak ...
CHAPTER 4 DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON, SULPHUR, NITROGEN
... 4.5). It was seen that all the curves were familian maxiwellian velocity distribution curves first rising to a maximum and then decreasing to zero at a well defined N and O atom. This upper limit of the N and O atom, which varies, with the different frequency of N and O atom. A few N and O atom hav ...
... 4.5). It was seen that all the curves were familian maxiwellian velocity distribution curves first rising to a maximum and then decreasing to zero at a well defined N and O atom. This upper limit of the N and O atom, which varies, with the different frequency of N and O atom. A few N and O atom hav ...
First Homework Assignment
... reducing sugars and the beta linkages would be hydrolyzed by a beta-galactosidase. Similarly, connecting glucose as a glucopyranoside to galactose also gives 8 possible types of linkage. These are all reducing sugars and the alpha type of linkage would be cut by an alpha glucosidase. Finally, the tw ...
... reducing sugars and the beta linkages would be hydrolyzed by a beta-galactosidase. Similarly, connecting glucose as a glucopyranoside to galactose also gives 8 possible types of linkage. These are all reducing sugars and the alpha type of linkage would be cut by an alpha glucosidase. Finally, the tw ...
Probe into the Financing Mechanism for Chinese Forestry Carbon Sequestration Market
... fund. China Petrochemical Corporation donated RMB 0.3 billion Yuan to the fund at the initial period for the activities of afforestation, forest management and construction of energy forest base that are aimed at absorbing CO2 in the atmosphere. It is estimated that 5 million to 10 million tons of f ...
... fund. China Petrochemical Corporation donated RMB 0.3 billion Yuan to the fund at the initial period for the activities of afforestation, forest management and construction of energy forest base that are aimed at absorbing CO2 in the atmosphere. It is estimated that 5 million to 10 million tons of f ...
Carbon
... and further uptake of CO2 • Malic acid is transported to the chloroplast and decarboxylated to release CO2 • This enters the Calvin cycle as it can not escape the leaf – Pyruvate is converted to starch in the chloroplast – regenerates carbon ...
... and further uptake of CO2 • Malic acid is transported to the chloroplast and decarboxylated to release CO2 • This enters the Calvin cycle as it can not escape the leaf – Pyruvate is converted to starch in the chloroplast – regenerates carbon ...
Chemistry - Higher tier - Paper 2 - Sample assessment material
... 7. There is a NR (No Response) option. Award NR (No Response) if there is nothing written at all in the answer space OR if there is a comment which does not in any way relate to the question (e.g. ‘can’t do’, ‘don’t know’) OR if there is a mark (e.g. a dash, a question mark) which isn’t an attempt a ...
... 7. There is a NR (No Response) option. Award NR (No Response) if there is nothing written at all in the answer space OR if there is a comment which does not in any way relate to the question (e.g. ‘can’t do’, ‘don’t know’) OR if there is a mark (e.g. a dash, a question mark) which isn’t an attempt a ...
File
... 9) Explain why 2 pyruvates are formed from one glucose molecule instead of only one pyruvate. 10) Name the organelle where aerobic respiration occurs? 11) During aerobic respiration, carbon dioxide (CO2) i ...
... 9) Explain why 2 pyruvates are formed from one glucose molecule instead of only one pyruvate. 10) Name the organelle where aerobic respiration occurs? 11) During aerobic respiration, carbon dioxide (CO2) i ...
Pyruvate Oxidation
... Coenzyme A attaches to acetate, forming acetyl-coenzyme A All nutrients, whether protein, lipid or carbohydrate, are converted to acetyl-CoA and then channelled toward fat production or ATP production, depending on the organism’s immediate energy needs ...
... Coenzyme A attaches to acetate, forming acetyl-coenzyme A All nutrients, whether protein, lipid or carbohydrate, are converted to acetyl-CoA and then channelled toward fat production or ATP production, depending on the organism’s immediate energy needs ...
Reactions
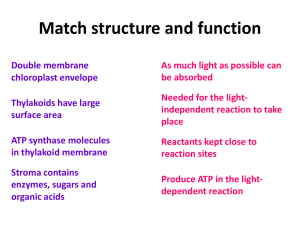
... • The serine is then used to make other organic molecules • All these conversions cost the plant energy and results in the net lost of CO2 from the plant • 75% of the carbon lost during the oxygenation of Rubisco is ...
... • The serine is then used to make other organic molecules • All these conversions cost the plant energy and results in the net lost of CO2 from the plant • 75% of the carbon lost during the oxygenation of Rubisco is ...
Computer modeling: Hyperchem tutorial
... (Make sure drawing tool is selected. R-click on the atom if you want to delete it) 4. Repeat (2) and choose oxygen instead of carbon. Move the cursor to the carbon centre and drag the mouse from the carbon centre to an empty workspace. (A single bond is created between carbon atom and oxygen atom.) ...
... (Make sure drawing tool is selected. R-click on the atom if you want to delete it) 4. Repeat (2) and choose oxygen instead of carbon. Move the cursor to the carbon centre and drag the mouse from the carbon centre to an empty workspace. (A single bond is created between carbon atom and oxygen atom.) ...
this profile of Mike Russell
... right for what happens in cells today. “We the chief was mistaken. helped to inform his ideas. recognized that some types of mineralizaWhile he was on the Solomons, Russell tion had a lot in common with the chemiworked with the Australian geologist Richard A child’s discovery cal processes of life,” ...
... right for what happens in cells today. “We the chief was mistaken. helped to inform his ideas. recognized that some types of mineralizaWhile he was on the Solomons, Russell tion had a lot in common with the chemiworked with the Australian geologist Richard A child’s discovery cal processes of life,” ...
Slide 1
... B – introduce C4 plants, enriched in 13C C – Cropping – removes new, low 13C material, leading to surface ...
... B – introduce C4 plants, enriched in 13C C – Cropping – removes new, low 13C material, leading to surface ...
carbohydrates
... • Glycoside: a carbohydrate in which the -‐OH of the anomeric carbon is replaced by -‐OR • those derived from furanoses are furanosides; those derived from pyranoses are pyranosides • glycosidic bond: the ...
... • Glycoside: a carbohydrate in which the -‐OH of the anomeric carbon is replaced by -‐OR • those derived from furanoses are furanosides; those derived from pyranoses are pyranosides • glycosidic bond: the ...
Biology Chapter 4
... processes The chemical energy used for most cell processes Energy is released when a phosphate group is removed ...
... processes The chemical energy used for most cell processes Energy is released when a phosphate group is removed ...
Towards the atomic level protein sequence analysis
... been developed to study carbon distribution profile [8] and carbon analysis program [9]. However a correct and comprehensive understanding of carbon atom and functionality of protein still needs to be establish. There are many studies which have identified the effect of the distribution of carbon at ...
... been developed to study carbon distribution profile [8] and carbon analysis program [9]. However a correct and comprehensive understanding of carbon atom and functionality of protein still needs to be establish. There are many studies which have identified the effect of the distribution of carbon at ...
The Role of Forest and Soil Carbon Sequestrations on Climate
... al., 2009). As a leading tree based system especially in the tropics, agroforestry, afforestation and reforestation has been suggested as one of the most appropriate land management systems for mitigating atmospheric CO2 (Dixon, 1995; Albrecht and Kandji, 2003; Montagnini and Nair, 2004). Globally f ...
... al., 2009). As a leading tree based system especially in the tropics, agroforestry, afforestation and reforestation has been suggested as one of the most appropriate land management systems for mitigating atmospheric CO2 (Dixon, 1995; Albrecht and Kandji, 2003; Montagnini and Nair, 2004). Globally f ...
Chapter 2 3EPchanges
... c. What is the importance of carbon in forming macromolecules and/or organic compounds? d. Define and draw out the processes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis with an example of a macromolecule or organic compound. e. Compare/contrast the four organic molecules by completing the comparison cha ...
... c. What is the importance of carbon in forming macromolecules and/or organic compounds? d. Define and draw out the processes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis with an example of a macromolecule or organic compound. e. Compare/contrast the four organic molecules by completing the comparison cha ...