Assigning and Using Oxidation Numbers in Biochemistry Lecture
... The purpose of this article is to illustrate the uses of assigning oxidation numbers to metabolic intermediates and end products in biochemical equations. Oxidation–reduction reactions, reactions in which electrons are transferred, comprise a major class of biochemical processes. For example, why an ...
... The purpose of this article is to illustrate the uses of assigning oxidation numbers to metabolic intermediates and end products in biochemical equations. Oxidation–reduction reactions, reactions in which electrons are transferred, comprise a major class of biochemical processes. For example, why an ...
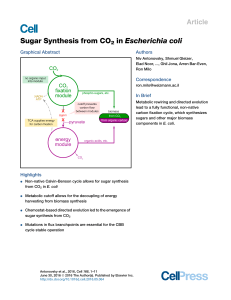
Sugar Synthesis from CO2 in Escherichia coli
... 2008; Parikh et al., 2006; Zhuang and Li, 2013) by employing a fully functional autocatalytic CBB cycle in which, as in autotrophic organisms, CO2, ATP, and reducing power are the only inputs for the synthesis of sugars. We termed this mode of growth, not known to occur in nature, hemiautotrophic gr ...
... 2008; Parikh et al., 2006; Zhuang and Li, 2013) by employing a fully functional autocatalytic CBB cycle in which, as in autotrophic organisms, CO2, ATP, and reducing power are the only inputs for the synthesis of sugars. We termed this mode of growth, not known to occur in nature, hemiautotrophic gr ...
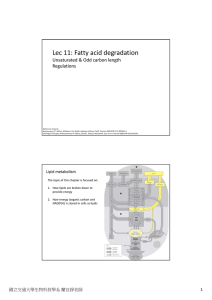
Lec 11: Fatty acid degradation
... Since H2O2 is strong oxidizing agent, it is immediately cleaved to O2 and H2O by catalase. 2. Since peroxisome does not contain ETC, ATP generated is dissipated as heat. For plants, when seeds are germinating, they will use glyoxysome (same as peroxisome) to break the lipid stored in seeds to ...
... Since H2O2 is strong oxidizing agent, it is immediately cleaved to O2 and H2O by catalase. 2. Since peroxisome does not contain ETC, ATP generated is dissipated as heat. For plants, when seeds are germinating, they will use glyoxysome (same as peroxisome) to break the lipid stored in seeds to ...
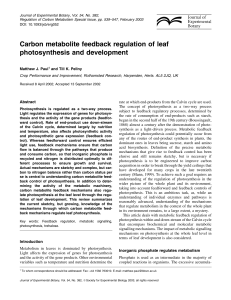
Carbon metabolite feedback regulation of leaf photosynthesis and
... feedback regulation of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, photophosphorylation and CF1-ATPase activity is particularly sensitive to Pi concentration, which can become inhibited if the free Pi concentration falls (Quick and Mills, 1988; Pammenter et al., 1993). In leaves, the rate of endproduct synth ...
... feedback regulation of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, photophosphorylation and CF1-ATPase activity is particularly sensitive to Pi concentration, which can become inhibited if the free Pi concentration falls (Quick and Mills, 1988; Pammenter et al., 1993). In leaves, the rate of endproduct synth ...
Impact of carbon sources on growth and oxalate - The Keep
... Pierson and Rhodes 1992; Briere et al. 2000). To provide insight into the relationship between supplemental carbon source, growth, and oxalogenesis, further studies were conducted with S. sclerotiorum Arg-‐L a ...
... Pierson and Rhodes 1992; Briere et al. 2000). To provide insight into the relationship between supplemental carbon source, growth, and oxalogenesis, further studies were conducted with S. sclerotiorum Arg-‐L a ...
Calvin cycle
... 2. The enzyme G3P dehydrogenase catalyses the reduction of 1,3BPGA by NADPH (which is another product of the light-dependent stage). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (also G3P, GP, TP, PGAL) is produced, and the NADPH itself was oxidized and becomes NADP+. Again, two NADPH are utilized per CO2 fixed. (Sim ...
... 2. The enzyme G3P dehydrogenase catalyses the reduction of 1,3BPGA by NADPH (which is another product of the light-dependent stage). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (also G3P, GP, TP, PGAL) is produced, and the NADPH itself was oxidized and becomes NADP+. Again, two NADPH are utilized per CO2 fixed. (Sim ...
The evolution of photosynthesis.again?
... biological carbon fixation: a carbon-based life form; the presence of inorganic carbon; the availability of reductants; the presence of light; a light-harvesting mechanism to convert the light energy into chemical energy; and carboxylating enzymes. All were present on the early Earth. To provide the ...
... biological carbon fixation: a carbon-based life form; the presence of inorganic carbon; the availability of reductants; the presence of light; a light-harvesting mechanism to convert the light energy into chemical energy; and carboxylating enzymes. All were present on the early Earth. To provide the ...
Chapter 15: Aldehyde and Ketones In this chapter, we discuss the
... In biological systems keto form of aldehyde sugars (aldoses) are converted to ketone sugars (ketoses) via enediol (enol) form as shown below. Therefore D-fructose which is a ketone or keto sugar (ketose) will give a positive test for Benedict's test because of the ability of ketoses to get converted ...
... In biological systems keto form of aldehyde sugars (aldoses) are converted to ketone sugars (ketoses) via enediol (enol) form as shown below. Therefore D-fructose which is a ketone or keto sugar (ketose) will give a positive test for Benedict's test because of the ability of ketoses to get converted ...
Alice and Lewis Carroll
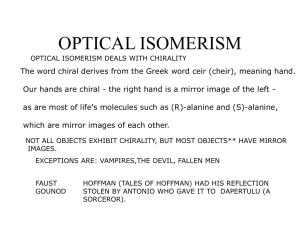
... Use monochromatic light, usually sodium D Movable polarizing filter to measure angle Clockwise = dextrorotatory = d or (+) Counterclockwise = levorotatory = l or (-) Not related to (R) and (S) ...
... Use monochromatic light, usually sodium D Movable polarizing filter to measure angle Clockwise = dextrorotatory = d or (+) Counterclockwise = levorotatory = l or (-) Not related to (R) and (S) ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... THE OXIDATION OF GLUCOSE A. Objectives - Explain the oxidation of an organic molecule such as glucose to carbon dioxide and water by glycolysis and Krebs cycle; discuss the steps that result in ATP production by substrate-level phosphorylation; identify the oxidation steps; know the cost of ATP prod ...
... THE OXIDATION OF GLUCOSE A. Objectives - Explain the oxidation of an organic molecule such as glucose to carbon dioxide and water by glycolysis and Krebs cycle; discuss the steps that result in ATP production by substrate-level phosphorylation; identify the oxidation steps; know the cost of ATP prod ...
01 P⁄g. iniciales (Page 1)
... with the ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco)catalyzed carbon fixation process [15]. However, 16/18S rRNAbased universal phylogenies indicate that chlorophyll-based photosynthesis was a relatively late development in the (eu)bacterial branch [31, 45]. Thus, it is likely that the fir ...
... with the ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco)catalyzed carbon fixation process [15]. However, 16/18S rRNAbased universal phylogenies indicate that chlorophyll-based photosynthesis was a relatively late development in the (eu)bacterial branch [31, 45]. Thus, it is likely that the fir ...
Growth of E. coli BL21 in minimal media with different
... Abstract Escherichia coli strain BL21 is commonly used as a host strain for protein expression and purification. For structural analysis, proteins are frequently isotopically labeled with deuterium (2H), 13C, or 15N by growing E. coli cultures in a medium containing the appropriate isotope. When lar ...
... Abstract Escherichia coli strain BL21 is commonly used as a host strain for protein expression and purification. For structural analysis, proteins are frequently isotopically labeled with deuterium (2H), 13C, or 15N by growing E. coli cultures in a medium containing the appropriate isotope. When lar ...
Source–Sink Relationships
... way the processes of photosynthesis and sucrose synthesis are coordinated. In general, either light and/or the availability of carbon dioxide limit photosynthesis. If these limitations are overcome, then the rate of photosynthesis is largely determined by the capacity of sucrose synthesis to regener ...
... way the processes of photosynthesis and sucrose synthesis are coordinated. In general, either light and/or the availability of carbon dioxide limit photosynthesis. If these limitations are overcome, then the rate of photosynthesis is largely determined by the capacity of sucrose synthesis to regener ...
Mixotrophic and photoheterotrophic metabolism in
... metabolite synthesis under mixotrophic growth. Fig. 1 shows the central metabolic pathways in Cyanothece 51142 (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). The labelling of five amino acids was analysed: histidine (precursors: ribose 5-phosphate and 5,10-methyl-THF), synthesized from the Calvin cycle and pentose p ...
... metabolite synthesis under mixotrophic growth. Fig. 1 shows the central metabolic pathways in Cyanothece 51142 (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). The labelling of five amino acids was analysed: histidine (precursors: ribose 5-phosphate and 5,10-methyl-THF), synthesized from the Calvin cycle and pentose p ...
L20 Medicinal Ch 28.07.2015 Metabolism
... made this reaction of moderate speed? The intermediates that were formed in the reaction are not aromatic; there is a loss of aromaticity in the process (Aromatic system is stable and loss of aromaticity mean loss of stability). This loss gives the intermediate very high energy making the reaction s ...
... made this reaction of moderate speed? The intermediates that were formed in the reaction are not aromatic; there is a loss of aromaticity in the process (Aromatic system is stable and loss of aromaticity mean loss of stability). This loss gives the intermediate very high energy making the reaction s ...
03CAM 2011 - AP Bio Take 5
... PHYSICALLY separate carbon fixation from Calvin cycle different cells to fix carbon vs. where Calvin cycle occurs store carbon in 4C compounds different enzyme to capture CO2 (fix carbon) ...
... PHYSICALLY separate carbon fixation from Calvin cycle different cells to fix carbon vs. where Calvin cycle occurs store carbon in 4C compounds different enzyme to capture CO2 (fix carbon) ...
IB496-April 10 - School of Life Sciences
... understanding of genomic functions, resulting in the inability to link functionally disparate gene expression events. Using the anticancer agent selenite and human lung cancer A549 cells as a model system, we demonstrate that these difficulties can be overcome by a progressive approach which harness ...
... understanding of genomic functions, resulting in the inability to link functionally disparate gene expression events. Using the anticancer agent selenite and human lung cancer A549 cells as a model system, we demonstrate that these difficulties can be overcome by a progressive approach which harness ...
Industrial microbiology Second level
... insights into fermentation and its microbial causes. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. Aerobic respiration: requires oxygen (O2) in order to generate ATP. Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are consumed as reactants, it is the preferred method of pyruvate breakdown in glycoly ...
... insights into fermentation and its microbial causes. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. Aerobic respiration: requires oxygen (O2) in order to generate ATP. Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are consumed as reactants, it is the preferred method of pyruvate breakdown in glycoly ...
Supplement I
... the [U-13C6]-glucose labeling experiment. (a) GCMS fragments from compartmentspecific metabolites have very similar profiles even though they reflect different carbon compositions, indicating that all carbons are similarly labeled. (b) Labeling of different carbons was analyzed by NMR for starch glu ...
... the [U-13C6]-glucose labeling experiment. (a) GCMS fragments from compartmentspecific metabolites have very similar profiles even though they reflect different carbon compositions, indicating that all carbons are similarly labeled. (b) Labeling of different carbons was analyzed by NMR for starch glu ...
Krebs Cycle - ScienceFolks
... After citric acid forms, it goes through a series of reactions that release energy. The energy is captured in molecules of NADH, ATP, and FADH2 , another energy-carrying compound. Carbon dioxide is also released as a waste product of these reactions. ...
... After citric acid forms, it goes through a series of reactions that release energy. The energy is captured in molecules of NADH, ATP, and FADH2 , another energy-carrying compound. Carbon dioxide is also released as a waste product of these reactions. ...
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature Monosaccharides
... mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexose, is found in the furanose ring form, and ribose, an aldopentose, is found in the furanose ring form. The free sugars can exist as a mixt ...
... mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexose, is found in the furanose ring form, and ribose, an aldopentose, is found in the furanose ring form. The free sugars can exist as a mixt ...
Section 2-3: Carbon Compounds (p. 44-48)
... and animals. These foods provide consumers with the materials they need to make their own carbon-base molecules. ...
... and animals. These foods provide consumers with the materials they need to make their own carbon-base molecules. ...
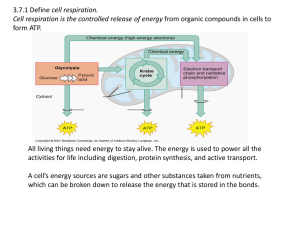
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... volume/number of bubbles of gas produced; by measuring the uptake of carbon dioxide; changes in pH; Do not accept “production of gas”. indirectly: by measuring the increase in biomass; by measuring the production of glucose / starch / other suitable molecule; [3 max] Award [2 max] if only indirect m ...
... volume/number of bubbles of gas produced; by measuring the uptake of carbon dioxide; changes in pH; Do not accept “production of gas”. indirectly: by measuring the increase in biomass; by measuring the production of glucose / starch / other suitable molecule; [3 max] Award [2 max] if only indirect m ...
Two examples of biomarker lipid applica³ons to studies of carbon
... Elemental and compositional changes in vascaular plant biopolymer composition with diagenesis ...
... Elemental and compositional changes in vascaular plant biopolymer composition with diagenesis ...
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature Monosaccharides
... mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexose, is found in the furanose ring form, and ribose, an aldopentose, is found in the furanose ring form. The free sugars can exist as a mixt ...
... mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexose, is found in the furanose ring form, and ribose, an aldopentose, is found in the furanose ring form. The free sugars can exist as a mixt ...