Lec #6 - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Microbial World - Prokaryotes A. Bacteria 2. Autotrophic Bacteria ...
... Microbial World - Prokaryotes A. Bacteria 2. Autotrophic Bacteria ...
Bacterial Infections
... Why are bacteria so successful? They reproduce quickly They evolve quickly (e.g. antibiotic resistance) They can live in extreme environments (e.g. in hot pools- 90oC) Some can form endospores, which can survive for many years (e.g. anthrax) ...
... Why are bacteria so successful? They reproduce quickly They evolve quickly (e.g. antibiotic resistance) They can live in extreme environments (e.g. in hot pools- 90oC) Some can form endospores, which can survive for many years (e.g. anthrax) ...
bacteria - Cloudfront.net
... • Allow bacteria to stick to host • Some allow conjugation – Exchange of plasmids ...
... • Allow bacteria to stick to host • Some allow conjugation – Exchange of plasmids ...
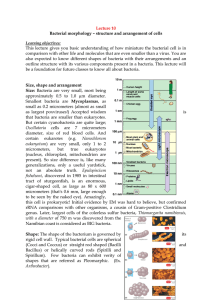
Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of
... Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of cells Learning objectives: ...
... Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of cells Learning objectives: ...
المحاضرة الثالثة عشر Thirteenth lecture
... Different types of diseases are caused by bacteria include: cholera, many sexually diseases األمراض الجنسية, and certain types of food poisoning التسمم الغذائي However, more bacteria are beneficial مفيدة. o Bacteria in our intestines أمعائنا produce important vitamins. o Bacteria recycle ...
... Different types of diseases are caused by bacteria include: cholera, many sexually diseases األمراض الجنسية, and certain types of food poisoning التسمم الغذائي However, more bacteria are beneficial مفيدة. o Bacteria in our intestines أمعائنا produce important vitamins. o Bacteria recycle ...
Microbial Interaction with Human
... numbers in host tissue can occur. Organisms may grow locally at the site of invasion or may spread through the body. ...
... numbers in host tissue can occur. Organisms may grow locally at the site of invasion or may spread through the body. ...
Electron Sources
... 2. As the bacterium grows, the newly replicated chromosomes become separated. 3. The cytoplasmic membrane then invaginates in the center of the bacterium and synthesizes a peptidoglycan septum to separate the two daughter cells Fig.1: Prokaryotic Cell (Bacillus megaterium) ...
... 2. As the bacterium grows, the newly replicated chromosomes become separated. 3. The cytoplasmic membrane then invaginates in the center of the bacterium and synthesizes a peptidoglycan septum to separate the two daughter cells Fig.1: Prokaryotic Cell (Bacillus megaterium) ...
Life in a different time frame
... For years, was thought that the deep sub-seabed (high-pressure, minimal oxygen and low supply of nutrients and energy) was an uninhabitable environments ...
... For years, was thought that the deep sub-seabed (high-pressure, minimal oxygen and low supply of nutrients and energy) was an uninhabitable environments ...
Bacteria
... What are the basic characteristics of bacteria? What are the 2 kingdoms of prokaryotes & what differentiates the 2. 3 basic shapes. Identify the basic structure of a prokaryote as well as the additional structures that can be found in certain species. Understand several impacts of bacterial processe ...
... What are the basic characteristics of bacteria? What are the 2 kingdoms of prokaryotes & what differentiates the 2. 3 basic shapes. Identify the basic structure of a prokaryote as well as the additional structures that can be found in certain species. Understand several impacts of bacterial processe ...
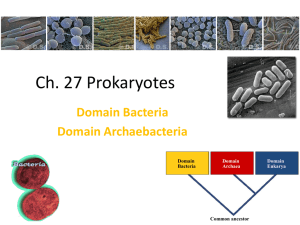
Diversity of Organisms
... Originally thought to be bacteria Live in extreme habitats Do not cause disease Prokaryotic Unicellular ...
... Originally thought to be bacteria Live in extreme habitats Do not cause disease Prokaryotic Unicellular ...
Currenty we have three DOMAINS Who are these organisms
... evidence suggests that the Archaea—an ancient domain of single-celled organisms—are resident within the gut in high numbers, and have direct and indirect effects on the host. In particular, the methanogens are an essential component of luminal intestinal microbial ecosystems. Methanogens oxidize hyd ...
... evidence suggests that the Archaea—an ancient domain of single-celled organisms—are resident within the gut in high numbers, and have direct and indirect effects on the host. In particular, the methanogens are an essential component of luminal intestinal microbial ecosystems. Methanogens oxidize hyd ...
Sterilization & Disinfection
... disinfection, and sanitization 2. Differentiate between bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents 3. Explain the process of pasteurization and lyophilization 4. List several methods used to inhibit the growth of microorganisms 5. Identify several factors that can influence the effectiveness of disinfec ...
... disinfection, and sanitization 2. Differentiate between bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents 3. Explain the process of pasteurization and lyophilization 4. List several methods used to inhibit the growth of microorganisms 5. Identify several factors that can influence the effectiveness of disinfec ...
Fungs
... ulcerating primary lesion in the genitalia but with satellite abscess in the inguinal lymph node with extensive scarring & strictures in the anogenital tract . In active lesions, the diagnosis of lymphogranuloma veneruim is by demostrationof the organism in biopsy sections or smears of exudate. In m ...
... ulcerating primary lesion in the genitalia but with satellite abscess in the inguinal lymph node with extensive scarring & strictures in the anogenital tract . In active lesions, the diagnosis of lymphogranuloma veneruim is by demostrationof the organism in biopsy sections or smears of exudate. In m ...
Bio426Lecture26Apr5
... of nitrogen availability and thus for life support on earth: * some bacteria can convert N2 into ammonia by the process termed nitrogen fixation; these bacteria are either free-living or form symbiotic associations with plants or other organisms (e.g. termites, protozoa) * other bacteria bring about ...
... of nitrogen availability and thus for life support on earth: * some bacteria can convert N2 into ammonia by the process termed nitrogen fixation; these bacteria are either free-living or form symbiotic associations with plants or other organisms (e.g. termites, protozoa) * other bacteria bring about ...
V. Three Domain System
... Genus and species names always written together Ex Homo sapien or Homo sapien,, Canis lupus or Canis lupus Species – organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Genus – group of closely related species ...
... Genus and species names always written together Ex Homo sapien or Homo sapien,, Canis lupus or Canis lupus Species – organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Genus – group of closely related species ...
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
... till spores Injected spores into healthy mice-anthrax Autopsied mice- observed same bacilli ...
... till spores Injected spores into healthy mice-anthrax Autopsied mice- observed same bacilli ...
Microbiology of environment
... water the normative documents or state standards are taken. Microbiologic index of safety of potable water are the following: 1. Common microbial number in one ml of water no more than 100. 2. Number of bacteria of intestinal rod group (coliindex) in 1000 ml of water - no more than 3. 3. Index of fr ...
... water the normative documents or state standards are taken. Microbiologic index of safety of potable water are the following: 1. Common microbial number in one ml of water no more than 100. 2. Number of bacteria of intestinal rod group (coliindex) in 1000 ml of water - no more than 3. 3. Index of fr ...
- European Commission
... plant disease and pests, could be developed as an effective alternative. The research focused on developing a way of applying biocontrol agents to seeds before they are planted. This offers an early non-chemical means of reducing or preventing the devastating effects of disease or pest attack on cro ...
... plant disease and pests, could be developed as an effective alternative. The research focused on developing a way of applying biocontrol agents to seeds before they are planted. This offers an early non-chemical means of reducing or preventing the devastating effects of disease or pest attack on cro ...
7th Grade Microbiology Study Guide
... 6. Some bacteria may have a gelatin capsule, a slime layer, or a flagellum. 7. Bacteria reproduce asexually through fission, and sexually by exchanging genetic material through thin tubes that pass through both bacteria. 8. Some bacteria produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemical reac ...
... 6. Some bacteria may have a gelatin capsule, a slime layer, or a flagellum. 7. Bacteria reproduce asexually through fission, and sexually by exchanging genetic material through thin tubes that pass through both bacteria. 8. Some bacteria produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemical reac ...
MS Word File
... Eukarya=Eukaryotes Evolution through natural selection=framework in which biology is studied Mutations that are beneficial become more common in later generations Changes occur resulting in organisms are well-suited for environment Energy flow through systems-Ecology Sunlight-plants-herbivores-carni ...
... Eukarya=Eukaryotes Evolution through natural selection=framework in which biology is studied Mutations that are beneficial become more common in later generations Changes occur resulting in organisms are well-suited for environment Energy flow through systems-Ecology Sunlight-plants-herbivores-carni ...
Presentation
... 3 Domains with kingdoms within them Organisms are put into domains & kingdoms based on 3 things: Cell type: prokaryotes or eukaryotes Ability to make food: heterotroph or autotroph Number of cells in bodies: unicellular (1 cell) or multicellular (many cells) ...
... 3 Domains with kingdoms within them Organisms are put into domains & kingdoms based on 3 things: Cell type: prokaryotes or eukaryotes Ability to make food: heterotroph or autotroph Number of cells in bodies: unicellular (1 cell) or multicellular (many cells) ...
File
... things in categories that make sense – Helps everyone find what they need – Makes it easier to describe life • For an example…see the next slide! ...
... things in categories that make sense – Helps everyone find what they need – Makes it easier to describe life • For an example…see the next slide! ...
Microorganism

A microorganism (from the Greek: μικρός, mikros, ""small"" and ὀργανισμός, organismós, ""organism"") is a microscopic living organism, which may be single celled or multicellular. The study of microorganisms is called microbiology, a subject that began with the discovery of microorganisms in 1674 by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, using a microscope of his own design.Microorganisms are very diverse and include all the bacteria and archaea and almost all the protozoa. They also include some fungi, algae, and certain animals, such as rotifers. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify viruses (and viroids) as microorganisms, but others consider these as nonliving.Microorganisms live in every part of the biosphere, including soil, hot springs, ""seven miles deep"" in the ocean, ""40 miles high"" in the atmosphere and inside rocks far down within the Earth's crust (see also endolith). Microorganisms, under certain test conditions, have been observed to thrive in the vacuum of outer space. The total amount of soil and subsurface bacterial carbon is estimated as 5 x 1017 g, or the ""weight of the United Kingdom"". The mass of prokaryote microorganisms — which includes bacteria and archaea, but not the nucleated eukaryote microorganisms — may be as much as 0.8 trillion tons of carbon (of the total biosphere mass, estimated at between 1 and 4 trillion tons). On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested microbial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench. the deepest spot in the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microorganisms thrive inside rocks up to 580 m (1,900 ft; 0.36 mi) below the sea floor under 2,590 m (8,500 ft; 1.61 mi) of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States, as well as 2,400 m (7,900 ft; 1.5 mi) beneath the seabed off Japan. On 20 August 2014, scientists confirmed the existence of microorganisms living 800 m (2,600 ft; 0.50 mi) below the ice of Antarctica. According to one researcher,""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Microorganisms are crucial to nutrient recycling in ecosystems as they act as decomposers. As some microorganisms can fix nitrogen, they are a vital part of the nitrogen cycle, and recent studies indicate that airborne microorganisms may play a role in precipitation and weather. Microorganisms are also exploited in biotechnology, both in traditional food and beverage preparation, and in modern technologies based on genetic engineering. A small proportion of microorganisms are pathogenic and cause disease and even death in plants and animals. Microorganisms are often referred to as microbes, but this is usually used in reference to pathogens.