* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diversity of Organisms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
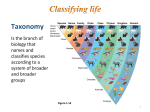
Diversity of Organisms • 5 to 30 million species estimated Axolotl Organisms alive today descended from earlier species • Fossils – Remains of previous forms – Record of life’s history • Life on Earth – Single cell organisms for 3.5 billion years – Abundant multicellular life for 500 million years Evolution • Change is species over time • Organisms alive today descended from older organisms • Evidence is overwhelming Organization of the Living World • System to deal with millions of species • An organism belongs to a unique species Bird’s nest fungi Organization of the Living World • Species designated by a scientific name – Binomial nomenclature – two part name – Developed by Carolus Linnaeus – Example: Homo sapiens • Homo = genus name • sapiens = species name Classification • System to organize life • Classification System – Genus = closely related species – Family = closely related genera Classification System Largest Level • • • • • • • • Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Smallest Level Methods of Classification • Common ancestry is basis for classification • Taxonomy = science of classifying organisms • Systematics – Study of diversity of organisms – Based on evolutionary relationships Domains of Life • Archaea • Bacteria • Eukarya Cell Types of Organisms • Prokaryote – No membrane bound organelles – Genetic material found in a nucleoid • Eukaryote – Membrane bound organelles – Genetic material in a nucleus Archaea • • • • • Originally thought to be bacteria Live in extreme habitats Do not cause disease Prokaryotic Unicellular Bacteria • • • • Found nearly everywhere Some cause disease Prokaryotic Unicellular Eukarya • Unicellular or Multicellular • Eukaryotic cells • Divided into at least four kingdoms – – – – Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Kingdom Protista • Mostly single cell organisms • May actually be up to 20 kingdoms • Gave rise to other eukaryotes Kingdom Fungi • Most are multicellular • Absorptive heterotrophs • Most are saprophites Diversity of Organisms • 5 to 30 million species estimated Axolotl Organisms alive today descended from earlier species • Fossils – Remains of previous forms – Record of life’s history • Life on Earth – Single cell organisms for 3.5 billion years – Abundant multicellular life for 500 million years Evolution • Change is species over time • Organisms alive today descended from older organisms • Evidence is overwhelming Organization of the Living World • System to deal with millions of species • An organism belongs to a unique species Bird’s nest fungi Organization of the Living World • Species designated by a scientific name – Binomial nomenclature – two part name – Developed by Carolus Linnaeus – Example: Homo sapiens • Homo = genus name • sapiens = species name Classification • System to organize life • Classification System – Genus = closely related species – Family = closely related genera Classification System Largest Level • • • • • • • • Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Smallest Level Methods of Classification • Common ancestry is basis for classification • Taxonomy = science of classifying organisms • Systematics – Study of diversity of organisms – Based on evolutionary relationships Domains of Life • Archaea • Bacteria • Eukarya Cell Types of Organisms • Prokaryote – No membrane bound organelles – Genetic material found in a nucleoid • Eukaryote – Membrane bound organelles – Genetic material in a nucleus Archaea • • • • • Originally thought to be bacteria Live in extreme habitats Do not cause disease Prokaryotic Unicellular Bacteria • • • • Found nearly everywhere Some cause disease Prokaryotic Unicellular Eukarya • Unicellular or Multicellular • Eukaryotic cells • Divided into at least four kingdoms – – – – Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Kingdom Protista • Mostly single cell organisms • May actually be up to 20 kingdoms • Gave rise to other eukaryotes Kingdom Fungi • Most are multicellular • Absorptive heterotrophs • Most are saprophites Kingdom Plantae • Multicellular • Photosynthetic autotrophs Kingdom Animalia • Multicellular • Heterotrophs