* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
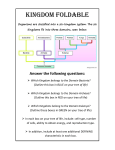
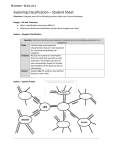
Introduction to Living Things Taxonomy The scientific study of how living things are classified. Response What is it? Give an example. When a plant grows toward light, the plant’s action is a response. Classification Level What is the broadest classification level? DOMAIN Which characteristic could be used to place organisms into kingdoms? A. Their ability to make food or B. Where they live What does an organisms scientific name consist of? A. Kingdom name & Phylum name Or B. Genus name & Species name Which group contains only multicellular heterotrophs? A. animals or B. plants Scientists get information about evolutionary history of species by: A. comparing body structures or B. observing what they eat What is an organism that makes its own food called? A. heterotroph or B. autotroph Which is more abundant in living cells? A. water or B. proteins What happens when two organisms share many classification levels? A. they have more characteristics in common B. it’s easier to tell them apart Redi and Pasteur helped demonstrate that: Living things do not arise from nonliving materials. Spontaneous generation is a mistaken idea because: Living things are produced by other living things. Which kingdoms include unicellular and multicellular organisms? Fungi & Protists Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution had a major impact on classification. Gradual change in species over time is evolution. Which domains include only prokaryotes? Bacteria & Archaea Each genus of organisms contain one or more species. Archaea aren’t classified with bacteria because its chemical makeup is different. If an owl & robin share the same kingdom, phylum, and class, they share more characteristics than an owl and bat that share the same kingdom and phylum. Biologists find taxonomy useful because it gives them information about an organism based on classification. Stable internal conditions held by an organism is homeostasis. Genus is the first word in an organism’s scientific name. Evolutionary history suggests bats and whales have similar characteristics. A taxonomic key consists of paired statements about characteristics of organisms.