Culver City H.S. • AP Chemistry Name Period ___ Date ___/___/___
... Draw their orbital diagrams: ...
... Draw their orbital diagrams: ...
Optical Pumping of Rubidium Vapor
... points (6) that we used. More data should have been taken in the low-field regime. When data from higher currents (250mA - 2000mA) was included, the quality of the fit decreased. The accepted values for gF for J = 1/2, L = 0 are .3340 for Rb-85 and .50174 for Rb87. Neither of our measurements lie wi ...
... points (6) that we used. More data should have been taken in the low-field regime. When data from higher currents (250mA - 2000mA) was included, the quality of the fit decreased. The accepted values for gF for J = 1/2, L = 0 are .3340 for Rb-85 and .50174 for Rb87. Neither of our measurements lie wi ...
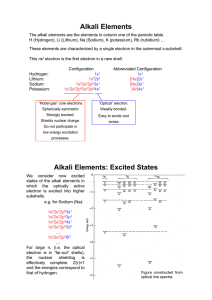
Alkali Elements Alkali Elements: Excited States
... Most of the energetics of these atoms is well described by the Hartree model; however, in detail (e.g. in high-resolution spectroscopy), spin-orbit coupling and the residual coulomb interaction are important. Residual Coulomb Interaction: The Coulomb interaction that is not captured by the effective ...
... Most of the energetics of these atoms is well described by the Hartree model; however, in detail (e.g. in high-resolution spectroscopy), spin-orbit coupling and the residual coulomb interaction are important. Residual Coulomb Interaction: The Coulomb interaction that is not captured by the effective ...
B.Sc. Part - II (Physics) Paper I – Electricity, Magnetism Electrostatics
... field (Time varying electric field ) ,Displacement current , Maxwell’s equations, Electromagnetic waves in free space , Poynting Vector , Theory and working of moving coil ballistic galvanometer . Unit –IV Dielectrics Dielectric constant, polarization, Electronic polarization, Atomic or ionic Polari ...
... field (Time varying electric field ) ,Displacement current , Maxwell’s equations, Electromagnetic waves in free space , Poynting Vector , Theory and working of moving coil ballistic galvanometer . Unit –IV Dielectrics Dielectric constant, polarization, Electronic polarization, Atomic or ionic Polari ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy
... A 1H nucleus is positively charged and its spinning motion generates a magnetic field. In the presence of an external magnetic field, H0, the magnetic field of the hydrogen nucleus can be oriented either with H0 (lower energy) or against H0 (higher energy). These two states are called and spin s ...
... A 1H nucleus is positively charged and its spinning motion generates a magnetic field. In the presence of an external magnetic field, H0, the magnetic field of the hydrogen nucleus can be oriented either with H0 (lower energy) or against H0 (higher energy). These two states are called and spin s ...
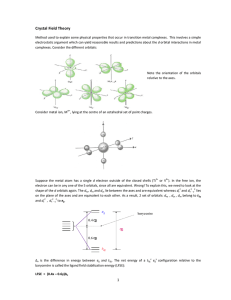
Crystal Field Theory
... Crystal Field Theory Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
... Crystal Field Theory Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
... Certain atomic nuclei should have the properties of spin and magnetic moment. As a consequence, exposure to magnetic field would lead to splitting of their energy levels. Nuclei absorb electromagnetic radiation in a strong magnetic field as a consequence of energy level splitting induced by th ...
... Certain atomic nuclei should have the properties of spin and magnetic moment. As a consequence, exposure to magnetic field would lead to splitting of their energy levels. Nuclei absorb electromagnetic radiation in a strong magnetic field as a consequence of energy level splitting induced by th ...
Atomic Levels
... Searching for high-z star forming galaxies, finding the position of the Lyman limit (also called Lyman limit) :! Star forming galaxies with hot stars that emit UV! Neutral hydrogen around stars absorbs UV at λ< 912 Å! At z=3-4 the Lyman limit is in optical: the galaxy appears brighter in optical (λ> ...
... Searching for high-z star forming galaxies, finding the position of the Lyman limit (also called Lyman limit) :! Star forming galaxies with hot stars that emit UV! Neutral hydrogen around stars absorbs UV at λ< 912 Å! At z=3-4 the Lyman limit is in optical: the galaxy appears brighter in optical (λ> ...
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a technique for studying materials with unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but it is electron spins that are excited instead of the spins of atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes or organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford.