Estimating Oxygen Saturation of Blood in Vivo with MR
... • The magnetic field exerts a torque on the spinning proton, causing it to precess, similar to a spinning top. • The magnetic moment precesses around the applied field at a rate proportional to the applied static field: the Larmor frequency. ...
... • The magnetic field exerts a torque on the spinning proton, causing it to precess, similar to a spinning top. • The magnetic moment precesses around the applied field at a rate proportional to the applied static field: the Larmor frequency. ...
Lecture 7 - UIC Department of Chemistry
... ■ We will return your graded notebook on the day of the Final. ■ We will not return the Final or Quiz 4, but let you review them in case that your grade is very close to the border line. ...
... ■ We will return your graded notebook on the day of the Final. ■ We will not return the Final or Quiz 4, but let you review them in case that your grade is very close to the border line. ...
Reilly
... In ferromagnetic materials, exchange interaction leads to an alignment of atomic spins. However, this leads to a large external and dipolar magnetic fields which will tend to demagnetize the material. Domains are formed to minimize this effect. ...
... In ferromagnetic materials, exchange interaction leads to an alignment of atomic spins. However, this leads to a large external and dipolar magnetic fields which will tend to demagnetize the material. Domains are formed to minimize this effect. ...
Basic Physical Principles of MRI
... • Spinning particles with mass have angular momentum – Angular momentum resists attempts to change the spin orientation (think of a gyroscope) ...
... • Spinning particles with mass have angular momentum – Angular momentum resists attempts to change the spin orientation (think of a gyroscope) ...
PHYS 212 James Scholar Assignment #4
... called, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging (the name was changed because the average Joe was afraid of anything with the word nuclear, or 'nucular', as George W. would say!). UIUC Chemistry professor Paul Lauterbur (who passed away in March 2007) won the 2003 Nobel Prize in Medicine for his de ...
... called, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging (the name was changed because the average Joe was afraid of anything with the word nuclear, or 'nucular', as George W. would say!). UIUC Chemistry professor Paul Lauterbur (who passed away in March 2007) won the 2003 Nobel Prize in Medicine for his de ...
ABOUT FEASIBILITY OF MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON
... From (1) it follows that the gain of electrons energy depends from and it enables to measure absolute energy of positrons. The basic purpose of this work is consideration of experimental approbation of RA method on lower energies 10 - 70 MeV. The expediency of approbation of RA method on low energ ...
... From (1) it follows that the gain of electrons energy depends from and it enables to measure absolute energy of positrons. The basic purpose of this work is consideration of experimental approbation of RA method on lower energies 10 - 70 MeV. The expediency of approbation of RA method on low energ ...
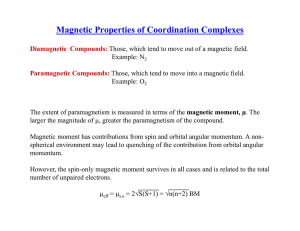
Magnetic Properties of Coordination Complexes √ √ μ
... Total unpaired electrons = 1, S = 1/2 Oxygenated form is low-spin The magnetic moment of Fe3+ and the superoxide radical involves in antiferromagnetic coupling and the oxygenated complex is not paramagnetic ...
... Total unpaired electrons = 1, S = 1/2 Oxygenated form is low-spin The magnetic moment of Fe3+ and the superoxide radical involves in antiferromagnetic coupling and the oxygenated complex is not paramagnetic ...
SPIN WAVES (INCLUDING DIMENSIONALITY
... Magnetism is an effect, that is intimately linked to the spin of the electron. While paramagnetic and diamagnetic substances show no spontaneous magnetic order, ferromagnets, antiferromagnets and ferrimagnets show an ordered configuration of magnetic moments below the critical temperature [1]. The n ...
... Magnetism is an effect, that is intimately linked to the spin of the electron. While paramagnetic and diamagnetic substances show no spontaneous magnetic order, ferromagnets, antiferromagnets and ferrimagnets show an ordered configuration of magnetic moments below the critical temperature [1]. The n ...
Coherent control of a single nuclear spin with an electric field
... with a classical bit. In this regard, the inherent spin of an atomic nucleus with its two (or more) eigenstates is a promising candidate. We have developed a molecular transistor which allows nuclear spin with us to write quantum information onto a single nuclear spin purely by means of an electric ...
... with a classical bit. In this regard, the inherent spin of an atomic nucleus with its two (or more) eigenstates is a promising candidate. We have developed a molecular transistor which allows nuclear spin with us to write quantum information onto a single nuclear spin purely by means of an electric ...
Atomic Structure and Atomic Spectra
... atom place restrictions on the allowed values of m and l. Those restrictions are: 1. For each value of the principal quantum number n, the possible values for the angular momentum quantum number l are l = 0,1,2…..(n-1). 2. For each value of l, there are 2l + 1 possible values of m ranging from -l to ...
... atom place restrictions on the allowed values of m and l. Those restrictions are: 1. For each value of the principal quantum number n, the possible values for the angular momentum quantum number l are l = 0,1,2…..(n-1). 2. For each value of l, there are 2l + 1 possible values of m ranging from -l to ...
Temperature and sample dependence of spin echo in SiC
... • Sample placed directly on the copper cold finger ...
... • Sample placed directly on the copper cold finger ...
Section 5.3 - 1 5.3 Paramagnetism • Paramagnetism originates from
... Furthermore, g may not have the same value in all spatial directions. In other words, the atom or molecule in question may be magnetically anisotropic. Solid state or frozen solution EPR spectroscopy can be used to determine the values of gx, gy and gz. In a room temperature solution (particularly o ...
... Furthermore, g may not have the same value in all spatial directions. In other words, the atom or molecule in question may be magnetically anisotropic. Solid state or frozen solution EPR spectroscopy can be used to determine the values of gx, gy and gz. In a room temperature solution (particularly o ...
Lecture 9.
... Nuclear spin and magnets. All nucleons, that is neutrons and protons, composing any atomic nucleus, have the intrinsic quantum property of spin. The overall spin of the nucleus is determined by the spin quantum number S. If the number of both the protons and neutrons in a given nuclide are even then ...
... Nuclear spin and magnets. All nucleons, that is neutrons and protons, composing any atomic nucleus, have the intrinsic quantum property of spin. The overall spin of the nucleus is determined by the spin quantum number S. If the number of both the protons and neutrons in a given nuclide are even then ...
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a technique for studying materials with unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but it is electron spins that are excited instead of the spins of atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes or organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford.