Experimental Verification of Filter Characteristics Using
... • The purpose of this experiment is to measure the ratio of the electron’s charge to its mass, a quantity referred to as “e/m”. ...
... • The purpose of this experiment is to measure the ratio of the electron’s charge to its mass, a quantity referred to as “e/m”. ...
β - Indico
... of amany single particles it becomes as accurate as a particle is highly inaccurate, strong measurement. ...
... of amany single particles it becomes as accurate as a particle is highly inaccurate, strong measurement. ...
Magnetism - Howard Elementary School
... repel and opposites attract, and the force between is inversely proportional to the distance between them. This means that closer is stronger, and further is weaker. Electric charges are positive or negative, magnetic poles are north or south. One main difference is that magnetic poles cannot be iso ...
... repel and opposites attract, and the force between is inversely proportional to the distance between them. This means that closer is stronger, and further is weaker. Electric charges are positive or negative, magnetic poles are north or south. One main difference is that magnetic poles cannot be iso ...
Technisch-Administrativer Leiter - Max-Born
... We will discuss the probing of proton rearrangements within laser field ionised molecules via HHG using the chirp encoded property of the electron recollisions. The initial experimental confirmation of this technique in H2 and CH4 are presented and discussed. New observations of transient two-centre ...
... We will discuss the probing of proton rearrangements within laser field ionised molecules via HHG using the chirp encoded property of the electron recollisions. The initial experimental confirmation of this technique in H2 and CH4 are presented and discussed. New observations of transient two-centre ...
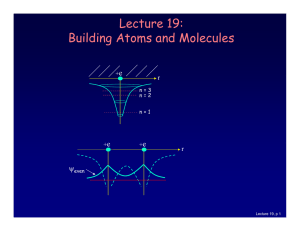
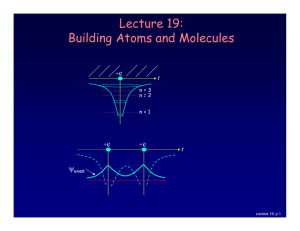
6.1 Nondegenerate Perturbation Theory
... Magnetic moment of the electron It has been said that experiments on the electron require that one attribute to it a magnetic moment, as though it were a ball of charge spinning about its own axis. The relationship between this magnetic moment and the spin angular momentum can be e S using relativi ...
... Magnetic moment of the electron It has been said that experiments on the electron require that one attribute to it a magnetic moment, as though it were a ball of charge spinning about its own axis. The relationship between this magnetic moment and the spin angular momentum can be e S using relativi ...
dyanmics and radiation of anelectrons driven by relativistically
... relativistic Newton equation with the Lorentz force. Approximate expressions for the laser field are used which describe the propagation of a Gaussian beam with a caustic waist. The longitudinal component of the electromagnetic field is also accounted for by the model. The electromagnetic radiation ...
... relativistic Newton equation with the Lorentz force. Approximate expressions for the laser field are used which describe the propagation of a Gaussian beam with a caustic waist. The longitudinal component of the electromagnetic field is also accounted for by the model. The electromagnetic radiation ...
Spectroscopy - Universität Wien
... → Principle similar to that of NMR: No external magnetic field: all spin states are equal (S = 1/2) With strong external field: splitting (S = +1/2 and S = -1/2) (here: EPR spectra are obtained by keeping the microwave frequency constant and varying the magnetic field until resonance is reached) → E ...
... → Principle similar to that of NMR: No external magnetic field: all spin states are equal (S = 1/2) With strong external field: splitting (S = +1/2 and S = -1/2) (here: EPR spectra are obtained by keeping the microwave frequency constant and varying the magnetic field until resonance is reached) → E ...
LABORATORY FACILITIES IN THE
... vapor phase methods in high-temperature furnaces. The flux melt furnace can reach temperatures in excess of 1500 K and can be programmed to raise or lower temperatures at rates of less than 0.5 K per hour. Many solids with high melting temperatures not attainable by other means can be prepared using ...
... vapor phase methods in high-temperature furnaces. The flux melt furnace can reach temperatures in excess of 1500 K and can be programmed to raise or lower temperatures at rates of less than 0.5 K per hour. Many solids with high melting temperatures not attainable by other means can be prepared using ...
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a technique for studying materials with unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but it is electron spins that are excited instead of the spins of atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes or organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford.