PART 1: ATOMIC NUMBER - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Is the noble gas with the second highest atomic number ____________________ ...
... Is the noble gas with the second highest atomic number ____________________ ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
Regions of the Periodic Table
... noble gases: elements in group VIIIA of the periodic table. 8 valence electrons (except for He which has 2)—full valence shells do not form ions do not react with other compounds ...
... noble gases: elements in group VIIIA of the periodic table. 8 valence electrons (except for He which has 2)—full valence shells do not form ions do not react with other compounds ...
Periodic Table Worksheet 1. Where are the most active metals
... 3. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? Greater ENC, stronger force of attraction between the nucleus and outmost electrons 4. As you travel down a group, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? The number of energy levels increases, weake ...
... 3. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? Greater ENC, stronger force of attraction between the nucleus and outmost electrons 4. As you travel down a group, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? The number of energy levels increases, weake ...
1 - contentextra
... solution of a strong base (alkali). They can react as both acidic and basic oxides. Aluminium oxide is an example. Aqua-ions A complex ion with water molecules acting as ligands. Transition metals and aluminium form aqua-ions in aqueous solutions. Atomicity The number of atoms in a molecule. Atomic ...
... solution of a strong base (alkali). They can react as both acidic and basic oxides. Aluminium oxide is an example. Aqua-ions A complex ion with water molecules acting as ligands. Transition metals and aluminium form aqua-ions in aqueous solutions. Atomicity The number of atoms in a molecule. Atomic ...
Ionic Bonding
... Binary Ionic Compounds 1. How were compounds named before the advent of systematic means of chemical nomenclature? 2. State the common names of each of the following chemicals: (a) hydrochloric acid (b) sodium hydrogen carbonate (c) dinitrogen monoxide (d) ethanol 3. How many elements are there in ...
... Binary Ionic Compounds 1. How were compounds named before the advent of systematic means of chemical nomenclature? 2. State the common names of each of the following chemicals: (a) hydrochloric acid (b) sodium hydrogen carbonate (c) dinitrogen monoxide (d) ethanol 3. How many elements are there in ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... 3. Criss-cross the charges (write them now as subscripts) 4. Drop the signs (+ve and -ve) 5. Remove the common factors (usually) 6. Forget about the “1’s” i.e. Sodium oxide ...
... 3. Criss-cross the charges (write them now as subscripts) 4. Drop the signs (+ve and -ve) 5. Remove the common factors (usually) 6. Forget about the “1’s” i.e. Sodium oxide ...
Dimitri Mendeleev- The father of the modern periodic table. Russian
... heavy metals; and only the first four (actinium, thorium, protactinium, and uranium) occur in nature. The other 11 (the transuranium elements) are unstable and are produced only artificially. ...
... heavy metals; and only the first four (actinium, thorium, protactinium, and uranium) occur in nature. The other 11 (the transuranium elements) are unstable and are produced only artificially. ...
2012 chapter 4 study guide
... The organization of the periodic table is based on the properties of the elements and reflects the structure of atoms. As a basis for understanding this concept: 7 a. Students know how to identify regions corresponding to metals, nonmetals, and inert gases. Be able to 7. tell who Mendeleev was and h ...
... The organization of the periodic table is based on the properties of the elements and reflects the structure of atoms. As a basis for understanding this concept: 7 a. Students know how to identify regions corresponding to metals, nonmetals, and inert gases. Be able to 7. tell who Mendeleev was and h ...
IGCSE Revision document
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
PPT Periodic Families from Class
... after the element that makes up 78% of our atmosphere. • This family includes non-metals, metalloids, and metals. • Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when ...
... after the element that makes up 78% of our atmosphere. • This family includes non-metals, metalloids, and metals. • Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when ...
The Periodic Table Memorize which elements are gases and
... 2. Nonmetals – on the right of the stairs & Hydrogens a.) gain electrons to form negative ions ionic radius is larger than atomic radius) b.) the greater the ability to gain electrons the more non-metallic properties c.) have high ionization energies and electronegativities d.) are brittle e.) are ...
... 2. Nonmetals – on the right of the stairs & Hydrogens a.) gain electrons to form negative ions ionic radius is larger than atomic radius) b.) the greater the ability to gain electrons the more non-metallic properties c.) have high ionization energies and electronegativities d.) are brittle e.) are ...
- sartep.com
... 6 .Which diagram to the right is the Lewis electron dot diagram for phosphorous? a. A b. B c. C d. D 7. From left to right across a period, what change is occurring within the atomic nuclei? a. A proton is gained. _ b. An electron is gained. c. A neutron is lost. d. The electron cloud size is decrea ...
... 6 .Which diagram to the right is the Lewis electron dot diagram for phosphorous? a. A b. B c. C d. D 7. From left to right across a period, what change is occurring within the atomic nuclei? a. A proton is gained. _ b. An electron is gained. c. A neutron is lost. d. The electron cloud size is decrea ...
Preview Sample 1
... 13. The average mass of an atom is determined by A. taking a weighted average of all isotopic masses B. averaging the masses of each isotope C. taking a weighted average of all stable isotopic masses D. adding the isotopic masses and dividing by the number of isotopes ...
... 13. The average mass of an atom is determined by A. taking a weighted average of all isotopic masses B. averaging the masses of each isotope C. taking a weighted average of all stable isotopic masses D. adding the isotopic masses and dividing by the number of isotopes ...
Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... Polar covalent compounds are those in which the shared electron pairs are closer to one atom than to the other, making one part of the molecule relatively negative and another part relatively positive. ...
... Polar covalent compounds are those in which the shared electron pairs are closer to one atom than to the other, making one part of the molecule relatively negative and another part relatively positive. ...
Alchemy Unit Concepts Review
... 4. What type of chemical bond is found in the following compounds? a. ethylene gas, C2H2(g) b. Copper hydroxide, Cu(OH)2 (aq) Molecular covalent Ionic c. Zinc, Zn (s) d. Phosphorus trifluoride, PF3 (g) Metallic Molecular Covalent e. C(s), graphite Network covalent 5. a) What is an isotope? Isotopes ...
... 4. What type of chemical bond is found in the following compounds? a. ethylene gas, C2H2(g) b. Copper hydroxide, Cu(OH)2 (aq) Molecular covalent Ionic c. Zinc, Zn (s) d. Phosphorus trifluoride, PF3 (g) Metallic Molecular Covalent e. C(s), graphite Network covalent 5. a) What is an isotope? Isotopes ...
9F Reactivity - Parrs Wood High School
... In a displacement reaction a more reactive metal takes the place of a less reactive metal in a compound. ...
... In a displacement reaction a more reactive metal takes the place of a less reactive metal in a compound. ...
The Periodic Table
... Copper, Cu, is a relatively soft metal, and a very good electrical conductor. ...
... Copper, Cu, is a relatively soft metal, and a very good electrical conductor. ...
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
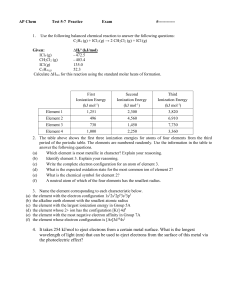
... D) 5s E) 5p 6. Element M reacts with chlorine to form a compound with the formula MCl 2 . Element M is more reactive than magnesium and has a smaller radius than barium. This element is __________. A) Sr B) K C) Na D) Ra E) Be 7. Of the following, which gives the correct order for atomic radius for ...
... D) 5s E) 5p 6. Element M reacts with chlorine to form a compound with the formula MCl 2 . Element M is more reactive than magnesium and has a smaller radius than barium. This element is __________. A) Sr B) K C) Na D) Ra E) Be 7. Of the following, which gives the correct order for atomic radius for ...
HISTORY OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
... IX 1930 Glenn Seaborg – “plucked out” the heaviest Elements (Actinide series & Lanthanide series) X ROY ALEXANDER – designed a three-dimensional Periodic chart (1994) retains the separate Lanthanide and Actinide series. ...
... IX 1930 Glenn Seaborg – “plucked out” the heaviest Elements (Actinide series & Lanthanide series) X ROY ALEXANDER – designed a three-dimensional Periodic chart (1994) retains the separate Lanthanide and Actinide series. ...
Worksheet 3 - contentextra
... Coordination number The number of ligands surrounding a central metal ion, or the number of nearest neighbours an atom, molecule or ion has in a crystal structure. Covalent radius of atom This is half of the inter-nuclear distance between two covalently bonded atoms of the same element. Dative coval ...
... Coordination number The number of ligands surrounding a central metal ion, or the number of nearest neighbours an atom, molecule or ion has in a crystal structure. Covalent radius of atom This is half of the inter-nuclear distance between two covalently bonded atoms of the same element. Dative coval ...