Name: Per: _____ Date: ______ Unit 5 Redemption Packet: The
... 15. Which noble gas does not have 8 valence electrons? _______________ 16. How is the atomic radius of an atom determined? _________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 17. a) How does atomic radius change across a period? _______________ ...
... 15. Which noble gas does not have 8 valence electrons? _______________ 16. How is the atomic radius of an atom determined? _________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 17. a) How does atomic radius change across a period? _______________ ...
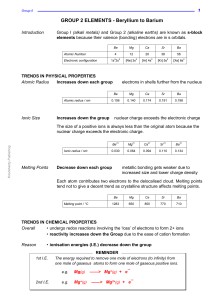
GROUP 2 ELEMENTS - Beryllium to Barium
... Values for Group I are low because the electron has just gone into a new level and is shielded by filled inner levels. This makes them reactive. Group 2 values are higher than their Group I equivalents due to the increased nuclear charge. ...
... Values for Group I are low because the electron has just gone into a new level and is shielded by filled inner levels. This makes them reactive. Group 2 values are higher than their Group I equivalents due to the increased nuclear charge. ...
I CAN write Chemical formulas
... oxidation number (without plus or minus) of one element as the subscript of the other element. 3. Reduce the subscripts (number of atoms) to their simplest form, if needed. WHAT IS THE CHEMICAL FORMULA FOR CALCIUM CHLORIDE? ...
... oxidation number (without plus or minus) of one element as the subscript of the other element. 3. Reduce the subscripts (number of atoms) to their simplest form, if needed. WHAT IS THE CHEMICAL FORMULA FOR CALCIUM CHLORIDE? ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... 12. Which sublevel corresponds to the transition metals in the periodic table? a. s c. d b. p d. f 14. Which of the following elements is a metalloid? a. As c. Br b. Se d. Kr 16. The element iodine, I, is a a. period 5 alkali metal. b. period 4 halogen. ...
... 12. Which sublevel corresponds to the transition metals in the periodic table? a. s c. d b. p d. f 14. Which of the following elements is a metalloid? a. As c. Br b. Se d. Kr 16. The element iodine, I, is a a. period 5 alkali metal. b. period 4 halogen. ...
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name:
... 16. What are the characteristics of each of the following reaction types? a) Synthesis b) Combustion c) Decomposition d) Double replacement e) Single replacement 17. Complete the word equation, write and balance the equation using symbols and indicate the type of the reaction on the left. a. Propane ...
... 16. What are the characteristics of each of the following reaction types? a) Synthesis b) Combustion c) Decomposition d) Double replacement e) Single replacement 17. Complete the word equation, write and balance the equation using symbols and indicate the type of the reaction on the left. a. Propane ...
Metals and non-metals III IMPORTANT POINTS Non-metals
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
chapter-8- alklimetal
... – Seawater is a source of magnesium—there are about 1.3 g of magnesium in each kilogram of seawater. – Metallic magnesium is obtained by ...
... – Seawater is a source of magnesium—there are about 1.3 g of magnesium in each kilogram of seawater. – Metallic magnesium is obtained by ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure – Standard 1 Review
... 1b.1 On the Periodic Table, be able to identify Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Semi-metals). 1c.1-1c.3 On the Periodic Table, be able to identify Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Transition Metals, Chalcogens, Halogens, and Noble Gases. 1c.4 – 1c.5 On the Periodic Table, be able to identify ...
... 1b.1 On the Periodic Table, be able to identify Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Semi-metals). 1c.1-1c.3 On the Periodic Table, be able to identify Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Transition Metals, Chalcogens, Halogens, and Noble Gases. 1c.4 – 1c.5 On the Periodic Table, be able to identify ...
Final Exam Review – Free Response Section Name: 1. A sample of
... Solubility rules: 1. All common compounds of Group I and ammonium ions are soluble. 2. All nitrates, acetates, and chlorates are soluble. 3. All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) 4. All su ...
... Solubility rules: 1. All common compounds of Group I and ammonium ions are soluble. 2. All nitrates, acetates, and chlorates are soluble. 3. All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) 4. All su ...
T - Rev.ch_.1.part2_
... 2) Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following elements. Remember to write the names of the elements. a) I am a noble gas belonging b) I am the lightest halogen. c) I am the smallest of the to the third period. atoms with four valence ...
... 2) Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following elements. Remember to write the names of the elements. a) I am a noble gas belonging b) I am the lightest halogen. c) I am the smallest of the to the third period. atoms with four valence ...
Lab 18
... conduct heat and electricity, Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids. Also, generally the melting points of non-metals are generally lower than metals. And finally compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic in nature as opposed to non-metal’s being nonmetal oxides are acidic oxide. 4. ...
... conduct heat and electricity, Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids. Also, generally the melting points of non-metals are generally lower than metals. And finally compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic in nature as opposed to non-metal’s being nonmetal oxides are acidic oxide. 4. ...
Notes 3-2
... Alloy – a mixture of two or more metals. Ex. Cu + Zn = Brass Metals in the Periodic Table Alkali Metals – metals in Group 1 from lithium to francium. Alkaline Earth Metals – an element in Group 2 of the periodic table. Transition Metals – elements in Groups 3 through 12 on the periodic table. Ex. A ...
... Alloy – a mixture of two or more metals. Ex. Cu + Zn = Brass Metals in the Periodic Table Alkali Metals – metals in Group 1 from lithium to francium. Alkaline Earth Metals – an element in Group 2 of the periodic table. Transition Metals – elements in Groups 3 through 12 on the periodic table. Ex. A ...
SOL Review Station: Equipment, Accuracy, Precision and Lab Safety
... SOL Review Topic 3: Elements, Radioactivity, and the Periodic Table 1. What is formed if you change the following in an atom? a. Protons ...
... SOL Review Topic 3: Elements, Radioactivity, and the Periodic Table 1. What is formed if you change the following in an atom? a. Protons ...
Post-Lab Questions
... magnesium are members of the Group IIA family of elements, the alkaline earth metals. Elements that share similar properties are arranged together in the periodic table within vertical columns called groups or families. The alkaline earth metals—beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and ...
... magnesium are members of the Group IIA family of elements, the alkaline earth metals. Elements that share similar properties are arranged together in the periodic table within vertical columns called groups or families. The alkaline earth metals—beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and ...
ELEMENTS and THEIR PROPERTIES
... 6. Metallic bonding- positively charged metallic ions are surrounded by a cloud of electrons; ions are in sliding layers and electrons are weakly held; readily form ionic bonds with non-metals. ...
... 6. Metallic bonding- positively charged metallic ions are surrounded by a cloud of electrons; ions are in sliding layers and electrons are weakly held; readily form ionic bonds with non-metals. ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
ALKALI EARTH METALS Introduction Properties Beryllium
... The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form ionic compounds. Be forms mostly covalent compounds. The atomic radius increases from top to bottom. The melting point, boiling point and the hardness of the elements decrease top to b ...
... The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form ionic compounds. Be forms mostly covalent compounds. The atomic radius increases from top to bottom. The melting point, boiling point and the hardness of the elements decrease top to b ...
Alkaline earth metals
... All In the second row Don’t occur as free elements Most commonly are found occurring as the carbonates, phosphates silicates, and sulfates Atoms loose 2 electrons Most are insoluble or slightly soluble Very Reactive ...
... All In the second row Don’t occur as free elements Most commonly are found occurring as the carbonates, phosphates silicates, and sulfates Atoms loose 2 electrons Most are insoluble or slightly soluble Very Reactive ...