Answers for Review Questions Exam 3
... of a metal and an acid, water or a base, and finally a metal hydride with water. In the past it was used as a heating fuel. It is also used to form ammonia and primarily as a reactant for many reactions. 21. a.+1 ...
... of a metal and an acid, water or a base, and finally a metal hydride with water. In the past it was used as a heating fuel. It is also used to form ammonia and primarily as a reactant for many reactions. 21. a.+1 ...
Science Review Sheet: Periodic Table Test Name: __________
... 7. List the different properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids. Know how to find them on the periodic table. Also know that metals are to the left of the zigzag line, metalloids touch the zigzag line on both sides (exception Al), and that nonmetals are to the right of the zigzag ...
... 7. List the different properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids. Know how to find them on the periodic table. Also know that metals are to the left of the zigzag line, metalloids touch the zigzag line on both sides (exception Al), and that nonmetals are to the right of the zigzag ...
Chemistry Review - Woodlawn School Wiki
... solution potassium sulfate and a precipitate fell out. Using balanced chemical equations, show work to find out what ion or ions were in my solution. 2) A 1.42-g sample of a pure compound, with formula M2SO4 , was dissolved in a water and treated with an excess of aqueous barium chloride, resulting ...
... solution potassium sulfate and a precipitate fell out. Using balanced chemical equations, show work to find out what ion or ions were in my solution. 2) A 1.42-g sample of a pure compound, with formula M2SO4 , was dissolved in a water and treated with an excess of aqueous barium chloride, resulting ...
Packet
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
Unit 4 Review - Davis
... Modern Periodic Law – The properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. The statement that the physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular pattern when they are arranged in order of increasing atomic number is known as the periodic law. Octet Ru ...
... Modern Periodic Law – The properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. The statement that the physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular pattern when they are arranged in order of increasing atomic number is known as the periodic law. Octet Ru ...
2.2 Periodic Chart
... (1- in charge), then it becomes a +1 ion. A charged atom or group of atoms is called an ion. The ion charge is the electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons to become more stable. ...
... (1- in charge), then it becomes a +1 ion. A charged atom or group of atoms is called an ion. The ion charge is the electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons to become more stable. ...
Who`s in this family?
... They have 7 valence electrons (Halogens react with most metals to produce salts • They have a wide range of physical properties: • Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temp. • Bromine is a liquid • Iodine is a solids • Fun Facts: • The word halogen comes from Greek and means “salt ...
... They have 7 valence electrons (Halogens react with most metals to produce salts • They have a wide range of physical properties: • Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temp. • Bromine is a liquid • Iodine is a solids • Fun Facts: • The word halogen comes from Greek and means “salt ...
Chapter 7:
... common with a neighboring group than with the other elements in their group. This kind of relationship is called a diagonal ...
... common with a neighboring group than with the other elements in their group. This kind of relationship is called a diagonal ...
General Chemistry I
... How many grams of magnesium oxide will result when 10.0 g of magnesium ribbon is burned in air? 2Mg (s) + O2 (s) ...
... How many grams of magnesium oxide will result when 10.0 g of magnesium ribbon is burned in air? 2Mg (s) + O2 (s) ...
The Periodic Table
... • Why does atomic radius DECREASE as you move up a group? • Losing layers of e• Why does atomic radius DECREASE as you move across a period? • Increasing the # of p+ holds the e- in tighter ...
... • Why does atomic radius DECREASE as you move up a group? • Losing layers of e• Why does atomic radius DECREASE as you move across a period? • Increasing the # of p+ holds the e- in tighter ...
Chapter 12 The Periodic Table
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
20151023082664
... How are sounds of musical notes related to the periodic table How is the modern periodic table arranged How are elements related in groups Why is the gram measurement unit not useful for element mass What is the convenient way to compare masses of atoms Know the different ways to classify ele ...
... How are sounds of musical notes related to the periodic table How is the modern periodic table arranged How are elements related in groups Why is the gram measurement unit not useful for element mass What is the convenient way to compare masses of atoms Know the different ways to classify ele ...
Final Exam Review
... level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have? 1. Select the correct electron configuration for silicon, atomic number 14. A. 1s2 2s2 2p2 3s2 3p2 3d2 4s2 B. 1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2 3p4 C. 1s2 2s6 2p6 D. 1s2 2s2 2 ...
... level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have? 1. Select the correct electron configuration for silicon, atomic number 14. A. 1s2 2s2 2p2 3s2 3p2 3d2 4s2 B. 1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2 3p4 C. 1s2 2s6 2p6 D. 1s2 2s2 2 ...
GO 3_3 The Periodic Table
... They react when exposed to air or water As you move down the group, reactivity increases. Lithium ...
... They react when exposed to air or water As you move down the group, reactivity increases. Lithium ...
Basics of the Periodic Table
... *Directions: Use the Periodic Table in your textbook to answer the following questions. Read carefully! ...
... *Directions: Use the Periodic Table in your textbook to answer the following questions. Read carefully! ...
6-Getting to Know the Periodic Table
... a. Which element has 27 protons in its nucleus? ___________________________ b. How many neutrons does Phosphorous have? _________ c. What is the family name of Calcium? __________ d. How many orbitals does an atom of Polonium have? _________ e. How many valance electrons does a bromine atom contain? ...
... a. Which element has 27 protons in its nucleus? ___________________________ b. How many neutrons does Phosphorous have? _________ c. What is the family name of Calcium? __________ d. How many orbitals does an atom of Polonium have? _________ e. How many valance electrons does a bromine atom contain? ...
Periodic Table and Atomic Structure Summary
... Alkali metals react violently with water. When they react with water they form alkaline solutions, this is why they are called the Alkali Metals. e.g. sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen (an alkali) Group 7 – The Halogens The halogens and their compounds have many uses. Fluorine compounds a ...
... Alkali metals react violently with water. When they react with water they form alkaline solutions, this is why they are called the Alkali Metals. e.g. sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen (an alkali) Group 7 – The Halogens The halogens and their compounds have many uses. Fluorine compounds a ...
ChLM Final Review Name: Period: Base Knowledge 1. Classify the
... 16. On the Periodic Table, which type of elements make cations? Which type make anions? 17. List three metals. 18. List three nonmetals. 19. List two halogens. How many valence electrons do the halogens have? ...
... 16. On the Periodic Table, which type of elements make cations? Which type make anions? 17. List three metals. 18. List three nonmetals. 19. List two halogens. How many valence electrons do the halogens have? ...
20161025131513
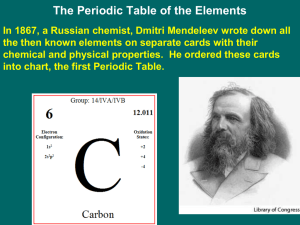
... o # of known elements at his timeo what inspired his approach to the periodic tableo made a “deck of cards” o what patterns did he noticeo what was his final arrangement of the periodic tableo what was missing in his tableo how did he predict undiscovered elementso was he the first to make a periodi ...
... o # of known elements at his timeo what inspired his approach to the periodic tableo made a “deck of cards” o what patterns did he noticeo what was his final arrangement of the periodic tableo what was missing in his tableo how did he predict undiscovered elementso was he the first to make a periodi ...
Document
... 17. The subatomic particle that plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element is the a. proton. c. electron. b. neutron. d. photon. 18. Which of the following atoms would you expect to have the largest atomic radius? a. I c. Ca b. K d. Rb 19. From left to ...
... 17. The subatomic particle that plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element is the a. proton. c. electron. b. neutron. d. photon. 18. Which of the following atoms would you expect to have the largest atomic radius? a. I c. Ca b. K d. Rb 19. From left to ...
File
... TUESDAY: Atoms, Elements, Compounds, & Mixtures (worth 33 percent) True or False: Identify if the following statements are true or false. 1. __________________: Atoms are smallest form of matter. 2. __________________: Electrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. 3. __________________: When two ...
... TUESDAY: Atoms, Elements, Compounds, & Mixtures (worth 33 percent) True or False: Identify if the following statements are true or false. 1. __________________: Atoms are smallest form of matter. 2. __________________: Electrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. 3. __________________: When two ...
Notes Chapter 5 “The Periodic Law” Section 1 Dmitri Mendeleev
... S block – groups 1 and 2 – group 1(alkali metals- end in s1, not found in nature as free elements. Always found in compounds. React strongly with water. Soft silvery appearance can be cut with a knife, will have a +1 charge). Group 2( alkaline earth metals, end in s2, harder, denser, and stronger th ...
... S block – groups 1 and 2 – group 1(alkali metals- end in s1, not found in nature as free elements. Always found in compounds. React strongly with water. Soft silvery appearance can be cut with a knife, will have a +1 charge). Group 2( alkaline earth metals, end in s2, harder, denser, and stronger th ...