Ch. 14 Test Review
... increases (3) groups (2) periods transition metals ionization energy atomic # noble gases representative electronegativity The periodic table organizes the elements into vertical ____________ and horizontal ____________ in order of increasing _________________. The table is constructed so that eleme ...
... increases (3) groups (2) periods transition metals ionization energy atomic # noble gases representative electronegativity The periodic table organizes the elements into vertical ____________ and horizontal ____________ in order of increasing _________________. The table is constructed so that eleme ...
The Periodic Table
... By looking at the elements that came before and after Ex- you go to school, and there is no mail in the mailbox. You come home and there is. Although you did not see the mailman you can be ...
... By looking at the elements that came before and after Ex- you go to school, and there is no mail in the mailbox. You come home and there is. Although you did not see the mailman you can be ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE ChapterTestA
... 12. WhIch sublevel corresponds to the transition metals in the periodic table? c.d a.s d.f b.p 13. The representative elements are a. inner transition metals. b. transition metals. ...
... 12. WhIch sublevel corresponds to the transition metals in the periodic table? c.d a.s d.f b.p 13. The representative elements are a. inner transition metals. b. transition metals. ...
C1a - Mr Corfe
... RULE: An metal is more reactive if it is further to the left of the periodic table or further down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSITION – is a chemical ...
... RULE: An metal is more reactive if it is further to the left of the periodic table or further down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSITION – is a chemical ...
Periodic Table Notes Fill In
... 9. What do you notice about the properties of metals and nonmetals? _________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 10. What are the properties of metalloids? ________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
... 9. What do you notice about the properties of metals and nonmetals? _________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 10. What are the properties of metalloids? ________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
Date_______________ Elements and facts of the periodic table
... _________________odorless, tasteless, colorless gas; lightest of all elements _______________natural material from which metal can be profitable extracted ________________most reactive metal _________________only metal liquid at room temperature ...
... _________________odorless, tasteless, colorless gas; lightest of all elements _______________natural material from which metal can be profitable extracted ________________most reactive metal _________________only metal liquid at room temperature ...
Review Sheet - Atoms, Elements, Periodic Table Ato
... o A vertical column of the periodic table is called a ________________. o Elements in the same vertical column have very similar _______________. o A horizontal row of the periodic table is called a ________________. ...
... o A vertical column of the periodic table is called a ________________. o Elements in the same vertical column have very similar _______________. o A horizontal row of the periodic table is called a ________________. ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... II elements and their compounds are illustrated. Variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds include both physical and chemical properties. Variation in Physical Properties of the Elements Variation in Atomic and Ionic radii There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii ...
... II elements and their compounds are illustrated. Variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds include both physical and chemical properties. Variation in Physical Properties of the Elements Variation in Atomic and Ionic radii There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii ...
Grouping of Elements in the Periodic Table
... 7. Which elements are most likely to lose electrons and form cations? a) transition metals b) noble gases c) elements in the last two periods d) metals in the first two periods 8. What is another name for semimetals? a) alkaline earth metals b) alkali metals c) transition metals d) metalloids 9. How ...
... 7. Which elements are most likely to lose electrons and form cations? a) transition metals b) noble gases c) elements in the last two periods d) metals in the first two periods 8. What is another name for semimetals? a) alkaline earth metals b) alkali metals c) transition metals d) metalloids 9. How ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... Alkali Metals I- most reactive metals Alkaline Earth Metals II- not as reactive as Alkali Metals Halogens (VII)- most reactive non-metals; “salt formers” Noble Gases (VIII)- colorless, odorless gases; unreactive because they have a full outer shell of electrons Rare-Earth Elements- at bottom of peri ...
... Alkali Metals I- most reactive metals Alkaline Earth Metals II- not as reactive as Alkali Metals Halogens (VII)- most reactive non-metals; “salt formers” Noble Gases (VIII)- colorless, odorless gases; unreactive because they have a full outer shell of electrons Rare-Earth Elements- at bottom of peri ...
CHEM 120 WEEK 11 LECTURES (INORGANIC WEEK 2) Dr. MD
... • Have low densities and melting points. • Also have low ionization energies. • potential reducing agents due to their capacity to form stable cations (M+). ...
... • Have low densities and melting points. • Also have low ionization energies. • potential reducing agents due to their capacity to form stable cations (M+). ...
Elements of the Periodic Table
... but its high cost has kept it from becoming commercially viable allowing it to compete with nitrous oxide. It is 44% more potent as an anesthetic than nitrous oxide. A very common noble gas, as a matter of fact the second most abundant element in the universe is Helium. Helium represents about 24% o ...
... but its high cost has kept it from becoming commercially viable allowing it to compete with nitrous oxide. It is 44% more potent as an anesthetic than nitrous oxide. A very common noble gas, as a matter of fact the second most abundant element in the universe is Helium. Helium represents about 24% o ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... compound to exist, both the cation and anion must be relatively stable. A beryllium cation (Be2+) would only have one shell of electrons (electron configuration 1s2). As such, it would be very small (smaller than helium!) – too small to fully stabilize a +2 charge. So, BeCl2 is a covalent compound w ...
... compound to exist, both the cation and anion must be relatively stable. A beryllium cation (Be2+) would only have one shell of electrons (electron configuration 1s2). As such, it would be very small (smaller than helium!) – too small to fully stabilize a +2 charge. So, BeCl2 is a covalent compound w ...
chapter 4 crossword pre-ap
... 33. The ionization energy __ as you go across a period. 34. The atomic radii __ as you go down a group. Put the following elements in order by the property given. a. decreasing electronegativity: arsenic, bromine, calcium b. increasing atomic radius: arsenic, bromine, calcium c. increasing ionizatio ...
... 33. The ionization energy __ as you go across a period. 34. The atomic radii __ as you go down a group. Put the following elements in order by the property given. a. decreasing electronegativity: arsenic, bromine, calcium b. increasing atomic radius: arsenic, bromine, calcium c. increasing ionizatio ...
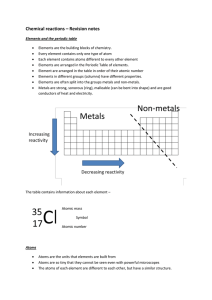
Chemical reactions revision
... Some metals react with water. Bubbles of hydrogen gas are released in this reaction. Heat is ...
... Some metals react with water. Bubbles of hydrogen gas are released in this reaction. Heat is ...
Review Package
... e) Bromine + sodium iodide → iodine + sodium bromide f) Barium nitrate + sodium sulphide → barium sulphide + sodium nitrate g) Lithium carbonate → carbon dioxide + lithium oxide h) Calcium + water → hydrogen + calcium hydroxide i) Sulfur trioxide + water → sulfuric acid ...
... e) Bromine + sodium iodide → iodine + sodium bromide f) Barium nitrate + sodium sulphide → barium sulphide + sodium nitrate g) Lithium carbonate → carbon dioxide + lithium oxide h) Calcium + water → hydrogen + calcium hydroxide i) Sulfur trioxide + water → sulfuric acid ...
34.) Write out the set of four quantum numbers for the last electron
... 6.) What is the mass of 15 nickels? 7.) What is the density of 15 nickels? Unit 2 * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or ...
... 6.) What is the mass of 15 nickels? 7.) What is the density of 15 nickels? Unit 2 * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or ...
Unit 2
... becomes positive which is known as a cation. when an atom gains an electron, it becomes negative which is known as an anion. Cations and anions are attracted to each other and thus come together to form a compound. ...
... becomes positive which is known as a cation. when an atom gains an electron, it becomes negative which is known as an anion. Cations and anions are attracted to each other and thus come together to form a compound. ...
Unit A Remediation Review
... 12. What are five clues that will allow you to conclude that a chemical change has occurred? 13. Describe what occurs in the following reaction types, the general equation and an example for each: a) Formation b) Decomposition c) Single Replacement d) Double Replacement e) Combustion 14. Write a bal ...
... 12. What are five clues that will allow you to conclude that a chemical change has occurred? 13. Describe what occurs in the following reaction types, the general equation and an example for each: a) Formation b) Decomposition c) Single Replacement d) Double Replacement e) Combustion 14. Write a bal ...
NAME: Unit 3 Test Review Arsenic (As), Selenium (Se), and
... 7. The valence electrons determine an elements chemical property and they also determine how an element reacts with other elements. 8. What are the three main subatomic particles of an atom? protons, neutrons, electrons 9. Which group on the periodic table is made of ONLY gases? group 18, noble gase ...
... 7. The valence electrons determine an elements chemical property and they also determine how an element reacts with other elements. 8. What are the three main subatomic particles of an atom? protons, neutrons, electrons 9. Which group on the periodic table is made of ONLY gases? group 18, noble gase ...
Frac Makeup and PPC Treatment
... in the steel industry as ferromanganese. This made by the reduction of iron oxide, Fe2O3, and managanese dioxide, MnO2, in appropriate proportions with carbon (as coke) in a blast furnace. Pure manganese is available through the electrolysis of manganese sulphate, MnSO4, Manganese is a gray-white me ...
... in the steel industry as ferromanganese. This made by the reduction of iron oxide, Fe2O3, and managanese dioxide, MnO2, in appropriate proportions with carbon (as coke) in a blast furnace. Pure manganese is available through the electrolysis of manganese sulphate, MnSO4, Manganese is a gray-white me ...
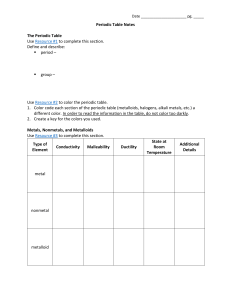
Periodic Table Notes The Periodic Table Use Resource #1
... Periodic Table Notes The Periodic Table Use Resource #1 to complete this section. Define and describe: period – ...
... Periodic Table Notes The Periodic Table Use Resource #1 to complete this section. Define and describe: period – ...
Chemistry Exam Review
... • Elements in the 3rd period (row) all have 3 orbits around the nucleus. • Elements in the 1st column all have 1 electron in their outer (valence) orbit. ...
... • Elements in the 3rd period (row) all have 3 orbits around the nucleus. • Elements in the 1st column all have 1 electron in their outer (valence) orbit. ...