another study guide
... hemisphere. But they recognize a word faster and more accurately when it is flashed to the left hemisphere. If a word is flashed to your right hemisphere, perception takes a fraction of a second longer-the length of time it takes to send the information through the corpus callosum to the more verbal ...
... hemisphere. But they recognize a word faster and more accurately when it is flashed to the left hemisphere. If a word is flashed to your right hemisphere, perception takes a fraction of a second longer-the length of time it takes to send the information through the corpus callosum to the more verbal ...
Chapter 3
... 4 important parts: hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, amygdala The hypothalamus regulates motivation and emotion. The thalamus primarily relays sensory information to the cerebrum, the part of the brain that allows humans to think and store information. The hippocampus is involved in memory ...
... 4 important parts: hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, amygdala The hypothalamus regulates motivation and emotion. The thalamus primarily relays sensory information to the cerebrum, the part of the brain that allows humans to think and store information. The hippocampus is involved in memory ...
Basic Brain Facts - The Practice of Parenting
... • By the age of three, we have 1,000 trillion (a quadrillion) connections between neurons. • By the age of three, the connections that are the weakest start to get pruned. This allows the brain to operate more efficiently. The strongest connections, those associated with emotion and repetition, remain ...
... • By the age of three, we have 1,000 trillion (a quadrillion) connections between neurons. • By the age of three, the connections that are the weakest start to get pruned. This allows the brain to operate more efficiently. The strongest connections, those associated with emotion and repetition, remain ...
EQ2.5 - major divisions of the nervous system
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
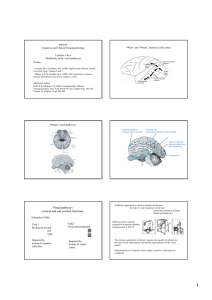
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... The visual brain areas of monkeys and humans are remarkably similar the coordination of saccadic movements, pursuit eye movements, grasping with the hand and body locomotion is computationally complex if carried out by a single central system - As such different specialised circuits may have evolved ...
... The visual brain areas of monkeys and humans are remarkably similar the coordination of saccadic movements, pursuit eye movements, grasping with the hand and body locomotion is computationally complex if carried out by a single central system - As such different specialised circuits may have evolved ...
C2 - The Biological Perspective
... Sensory Neurons carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
... Sensory Neurons carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
Control and Coordination
... ★ Synapse is the connections between neurons. Synapse is a functional region between two neurons where information from one neuron is transmitted or relayed to another neuron. ...
... ★ Synapse is the connections between neurons. Synapse is a functional region between two neurons where information from one neuron is transmitted or relayed to another neuron. ...
Inside the Teen Brain
... facial expressions, in part because the prefrontal cortex is not yet lending the limbic system a hand. Teenagers are not adept readers of social signals, such as facial expressions, even if they seem to do nothing but socialize. "You have to actually learn how to read emotions," says Yurgelun-Todd. ...
... facial expressions, in part because the prefrontal cortex is not yet lending the limbic system a hand. Teenagers are not adept readers of social signals, such as facial expressions, even if they seem to do nothing but socialize. "You have to actually learn how to read emotions," says Yurgelun-Todd. ...
Sample
... (subjects cannot be randomly assigned to either condition). Cause is difficult to surmise in quasiexperimental designs due to the fact that subjects are not randomly assigned to groups, opening up the possibility that factors other than the manipulated ones may be correlated with the experimental gr ...
... (subjects cannot be randomly assigned to either condition). Cause is difficult to surmise in quasiexperimental designs due to the fact that subjects are not randomly assigned to groups, opening up the possibility that factors other than the manipulated ones may be correlated with the experimental gr ...
Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
Major lobes - Ohio University
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
Topic 14 - Center for Complex Systems and Brain Sciences
... access to information Most cognitive processing is unconscious. We are only conscious of the content of the mind, not what generates that content. The question of whether consciousness is required for cognitive processing has been investigated in patients with blindsight. Blindsight is the phenomeno ...
... access to information Most cognitive processing is unconscious. We are only conscious of the content of the mind, not what generates that content. The question of whether consciousness is required for cognitive processing has been investigated in patients with blindsight. Blindsight is the phenomeno ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Directional Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the front, mid, and back areas of the brain) a. Front: Motor b. Mid: Sensory c. Back: Visual Ventricles: A series of hollow, interconnected chambers that are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF ...
... Directional Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the front, mid, and back areas of the brain) a. Front: Motor b. Mid: Sensory c. Back: Visual Ventricles: A series of hollow, interconnected chambers that are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF ...
Autonomic Nervous System - Cedar Bluffs Public Schools
... not be able to say what it is See something funny, laugh but not be able to tell others what was seen ...
... not be able to say what it is See something funny, laugh but not be able to tell others what was seen ...
File
... and motor functions, others, known as association areas serve mainly to shape information into something meaningful on which we can act. The association areas in the frontal lobes could be called the brain’s executive center. It is where we solve problems and make plans and decisions. Language abili ...
... and motor functions, others, known as association areas serve mainly to shape information into something meaningful on which we can act. The association areas in the frontal lobes could be called the brain’s executive center. It is where we solve problems and make plans and decisions. Language abili ...
The Brain
... One symptom which often occurs in stroke victims are speech problems Paul Broca studied the brains of such patients after they died He found a region of the frontal lobe damaged Now called the Broca’s area or region Some patients can recover after a stroke. What does this show? The brain is flexib ...
... One symptom which often occurs in stroke victims are speech problems Paul Broca studied the brains of such patients after they died He found a region of the frontal lobe damaged Now called the Broca’s area or region Some patients can recover after a stroke. What does this show? The brain is flexib ...
nervous system B
... • The left brain controls the right half of the body; the right brain controls the left half of the body. • However, “right brain” or “left brain” functions such as math, language, etc. produce activity on both sides of the brain, and processing of these may be different in different people (males v ...
... • The left brain controls the right half of the body; the right brain controls the left half of the body. • However, “right brain” or “left brain” functions such as math, language, etc. produce activity on both sides of the brain, and processing of these may be different in different people (males v ...
Chapter 31.2: Parts of the brain
... • The control point of the central nervous system is the brain – Each of the major areas of the brain- the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem- are responsible for processing and relaying information – Most of the neurons that enter and leave the brain do so in a large cluster of neurons and other ...
... • The control point of the central nervous system is the brain – Each of the major areas of the brain- the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem- are responsible for processing and relaying information – Most of the neurons that enter and leave the brain do so in a large cluster of neurons and other ...
... • Brain scans, such as CAT, MRI or PET scans, provide a more detailed images of the brain. • They can detect activity through changes in blood flow or uptake of glucose and can allow localisation of function to be identified by showing which areas are most active whilst carrying out a particular fun ...
Chapter 11: Sex differences in spatial intelligence
... Various lines of research support the notion that we have a specialised brain region for processing faces. Neurons in monkeys appear to be selectively responsive to faces, patients with prosopagnosia are unable to recognise familiar faces (but can recognise other objects and can identify features of ...
... Various lines of research support the notion that we have a specialised brain region for processing faces. Neurons in monkeys appear to be selectively responsive to faces, patients with prosopagnosia are unable to recognise familiar faces (but can recognise other objects and can identify features of ...
Damage to the frontal lobes can lead to
... Technology that allows us to see brain at work – EEG –charts brain’s electrical brain waves E for electricity! Output is a graph of lines registering different brain wave patterns – PET—shows where brain activity is occurring by showing where glucose is being consumed after person given radioactive ...
... Technology that allows us to see brain at work – EEG –charts brain’s electrical brain waves E for electricity! Output is a graph of lines registering different brain wave patterns – PET—shows where brain activity is occurring by showing where glucose is being consumed after person given radioactive ...
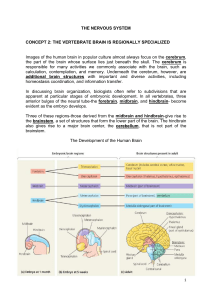
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... Emotional experiences are often stored as memories that can be recalled by similar circumstances. In the case of fear, emotional memory is stored separately from the memory system that supports explicit recall of events. The focus of emotional memory is the amygdala, which is located in the temporal ...
... Emotional experiences are often stored as memories that can be recalled by similar circumstances. In the case of fear, emotional memory is stored separately from the memory system that supports explicit recall of events. The focus of emotional memory is the amygdala, which is located in the temporal ...