primary visual cortex - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
How Psychotherapy Changes the Brain
... psychotherapy for 12 months. Of the patients, 8 were classified as having atypical depression. Midbrain serotonin transporter and striatum dopamine(Drug information on dopamine) transporter densities were recorded using SPECT brain imaging with the [123I]nor-β-CIT radioligand before and after psycho ...
... psychotherapy for 12 months. Of the patients, 8 were classified as having atypical depression. Midbrain serotonin transporter and striatum dopamine(Drug information on dopamine) transporter densities were recorded using SPECT brain imaging with the [123I]nor-β-CIT radioligand before and after psycho ...
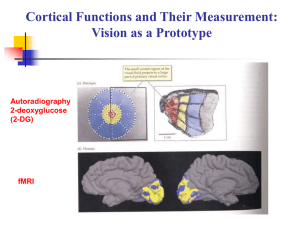
Visual Field and the Human Visual System
... and Fox in St. Louis (green circles). The areas of activation in the extrastriate cortex almost superimpose. ...
... and Fox in St. Louis (green circles). The areas of activation in the extrastriate cortex almost superimpose. ...
PDF - ib psych notes
... 2. Animal research can provide insight into human behaviour. - Animal research are sometimes the only feasible method of executing a research study. - Animal research can be generalised to humans, to some extent, because we are similar. ...
... 2. Animal research can provide insight into human behaviour. - Animal research are sometimes the only feasible method of executing a research study. - Animal research can be generalised to humans, to some extent, because we are similar. ...
Dorsal Column * Medial Lemniscal System (DC-ML)
... Tactile hallucination is subdivided to pleasant and unpleasant tactile hallucinations. ...
... Tactile hallucination is subdivided to pleasant and unpleasant tactile hallucinations. ...
7.2 Student Notes
... Brain obtains energy using _____________________________________, which pass rapidly from the blood to the brain cells. ______________________________ helps to make ATP within the brain. CHO storage in the brain __________________________, so the supply of glucose must be continuous. ...
... Brain obtains energy using _____________________________________, which pass rapidly from the blood to the brain cells. ______________________________ helps to make ATP within the brain. CHO storage in the brain __________________________, so the supply of glucose must be continuous. ...
HPA Axis Activation and Hippocampal Atrophy
... hippocampal pyramidal neurons was first noticed in aging rats. Adrenalectomy performed on middle-aged rat can halt this process, while administration of glucocorticoid for 12 weeks resulted in neuronal loss in hippocampal formation. Chronic social stress can also decrease the amount of hippocampal n ...
... hippocampal pyramidal neurons was first noticed in aging rats. Adrenalectomy performed on middle-aged rat can halt this process, while administration of glucocorticoid for 12 weeks resulted in neuronal loss in hippocampal formation. Chronic social stress can also decrease the amount of hippocampal n ...
Chapter 2
... Depolarization: Depolarization occurs when positive ions enter the neuron, making it more prone to firing an action potential. Hyperpolarization occurs when negative ions enter the neuron, making it less prone to firing an action potential. ...
... Depolarization: Depolarization occurs when positive ions enter the neuron, making it more prone to firing an action potential. Hyperpolarization occurs when negative ions enter the neuron, making it less prone to firing an action potential. ...
Chapter 3
... spoken words Wernicke’s area: responsible for transforming spoken words into thoughts ...
... spoken words Wernicke’s area: responsible for transforming spoken words into thoughts ...
Протокол
... the highest functional level of the nervous system and responsible for uniquely human characteristics, such as intricate hand movements, highly developed speech, symbolic thought, personality, conscience, and self-awareness. These qualities are known to depend on the cortex because, if certain areas ...
... the highest functional level of the nervous system and responsible for uniquely human characteristics, such as intricate hand movements, highly developed speech, symbolic thought, personality, conscience, and self-awareness. These qualities are known to depend on the cortex because, if certain areas ...
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine L15 –Dr. Loai Physiology
... (like sensation information) to the CNS & to receive orders from the CNS. Note: all the nerves you learnt about in the anatomy course are peripheral nerves. 3) Central nervous system mainly we will focus on the nerves that are in the core of the body (inside the spinal cord & the brain) its main ...
... (like sensation information) to the CNS & to receive orders from the CNS. Note: all the nerves you learnt about in the anatomy course are peripheral nerves. 3) Central nervous system mainly we will focus on the nerves that are in the core of the body (inside the spinal cord & the brain) its main ...
Functional Neural Anatomy
... – Association cortex processes information more elaborately than the primary sensory areas do, but they do not link one kind of sensory information with another. Only visual info goes to associative visual cortex; only auditory info goes to associative auditory cortex, etc. – The brain has no single ...
... – Association cortex processes information more elaborately than the primary sensory areas do, but they do not link one kind of sensory information with another. Only visual info goes to associative visual cortex; only auditory info goes to associative auditory cortex, etc. – The brain has no single ...
Nervous System
... Within the gray matter most of the brain is white matter with isolated masses of gray matter called the basal ganglia The white matter is comprised of fibers which form the ascending and descending tracts in the cerebrum and areas in the spinal cord. a. projection tracts - found above and downward l ...
... Within the gray matter most of the brain is white matter with isolated masses of gray matter called the basal ganglia The white matter is comprised of fibers which form the ascending and descending tracts in the cerebrum and areas in the spinal cord. a. projection tracts - found above and downward l ...
Paper
... delivery of an aversive stimulus (electric foot shock). Interestingly, fast spiking cells (putative inhibitory interneurons) and regular spiking cells (putative projection neurons) showed different patterns of responses. Fast spiking cell tended to show transient responses and increased their firing ...
... delivery of an aversive stimulus (electric foot shock). Interestingly, fast spiking cells (putative inhibitory interneurons) and regular spiking cells (putative projection neurons) showed different patterns of responses. Fast spiking cell tended to show transient responses and increased their firing ...
Document
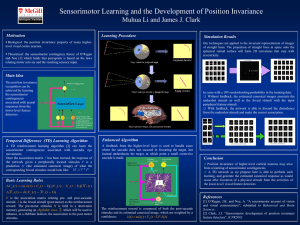
... Theoretical: the sensorimotor contingency theory of O’Regan and Noe [1] which holds that perception is based on the laws relating motor activity and the resulting sensory input. ...
... Theoretical: the sensorimotor contingency theory of O’Regan and Noe [1] which holds that perception is based on the laws relating motor activity and the resulting sensory input. ...
November 1 CNS INTRO
... 5. “Decussation” is when information crosses from one side of the brain or spinal cord to the other. “Projection” is when information is exchanged between brainstem and spinal cord, or deep brain nucleand cortical ribbon. What two major anatomical areas of gray matter in the brain account for each r ...
... 5. “Decussation” is when information crosses from one side of the brain or spinal cord to the other. “Projection” is when information is exchanged between brainstem and spinal cord, or deep brain nucleand cortical ribbon. What two major anatomical areas of gray matter in the brain account for each r ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... 6. Regions of the cerebrum are specialized for different functions The cerebrum is divided into frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal lobes. Frontal lobe. Contains the primary motor cortex. Parietal lobe. Contains the primary somatosensory cortex Integrative Function of the Associat ...
... 6. Regions of the cerebrum are specialized for different functions The cerebrum is divided into frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal lobes. Frontal lobe. Contains the primary motor cortex. Parietal lobe. Contains the primary somatosensory cortex Integrative Function of the Associat ...
Slide 1
... Parietal Lobe - One of the two parietal lobes of the brain located behind the frontal lobe at the top of the brain. Parietal Lobe, Right - Damage to this area can cause visuo-spatial deficits (e.g., the patient may have difficulty finding their way around new, or even familiar, places). Parietal Lob ...
... Parietal Lobe - One of the two parietal lobes of the brain located behind the frontal lobe at the top of the brain. Parietal Lobe, Right - Damage to this area can cause visuo-spatial deficits (e.g., the patient may have difficulty finding their way around new, or even familiar, places). Parietal Lob ...
Anatomy of Brain
... memory and other language functions. Sound processing is controlled by the temporal lobes- in the Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area. The underside (ventral) part high-level visual processing of complex stimuli such as faces (fusiform gyrus) and scenes (parahippocampal gyrus) object perception and r ...
... memory and other language functions. Sound processing is controlled by the temporal lobes- in the Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area. The underside (ventral) part high-level visual processing of complex stimuli such as faces (fusiform gyrus) and scenes (parahippocampal gyrus) object perception and r ...
thoughts - Budokon MD
... These three parts of the brain do not operate independently of one another. They have established numerous interconnections through which they influence one another. The brain’s nerve cells are known as neurons, which make up the organ’s so-called “gray matter.” The neurons transmit and gather elect ...
... These three parts of the brain do not operate independently of one another. They have established numerous interconnections through which they influence one another. The brain’s nerve cells are known as neurons, which make up the organ’s so-called “gray matter.” The neurons transmit and gather elect ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... Know how vs. Know what RAS –reticular activating systemInformation from the sense organs ...
... Know how vs. Know what RAS –reticular activating systemInformation from the sense organs ...