Unit 4 Compounds, Naming, Formula Writing
... Ions: atoms or groups of atoms that have a positive or negative charge. Cation: An ion with a positive charge, formed by the loss of electrons, usually metals. Ex. Na+ Anion: An ion with a negative charge, formed by the gain of electrons, usually nonmetals. Ex. ClIonic Compounds: Compounds composed ...
... Ions: atoms or groups of atoms that have a positive or negative charge. Cation: An ion with a positive charge, formed by the loss of electrons, usually metals. Ex. Na+ Anion: An ion with a negative charge, formed by the gain of electrons, usually nonmetals. Ex. ClIonic Compounds: Compounds composed ...
HW 2-1 Review Chap 2 Key
... Use the helium-4 isotope to define atomic number and mass number. Why does a knowledge of atomic number enable us to deduce the number of electrons present in an atom? Helium–4, written 42 He , has atomic number 2 because it has 2 protons (number at lower left) and mass number 4 because it has a tot ...
... Use the helium-4 isotope to define atomic number and mass number. Why does a knowledge of atomic number enable us to deduce the number of electrons present in an atom? Helium–4, written 42 He , has atomic number 2 because it has 2 protons (number at lower left) and mass number 4 because it has a tot ...
New quasiatomic nanoheterostructures: Superatoms and Excitonic
... In [1], in the framework of the modified method of the effective mass, developed a theory superatom of spatially separated electrons and holes (the hole is in the amount of QD, and the electron is localized on the spherical surface interface (QD-matrix)). As a core advocate QDs containing in its vol ...
... In [1], in the framework of the modified method of the effective mass, developed a theory superatom of spatially separated electrons and holes (the hole is in the amount of QD, and the electron is localized on the spherical surface interface (QD-matrix)). As a core advocate QDs containing in its vol ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
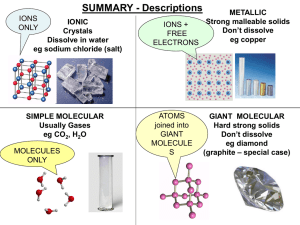
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
Chapter 1_chemh
... Change of state: physical change from one state to another. ●Solid: definite volume definite shape ●Liquid: definite volume indefinite shape ...
... Change of state: physical change from one state to another. ●Solid: definite volume definite shape ●Liquid: definite volume indefinite shape ...
matter and its reactivity. Objects in the universe are composed of
... 3.3a All matter is made up of atoms. Atoms are far too small to see with a light microscope. 3.3c Atoms may join together in well-defined molecules or may be arranged in regular geometric patterns. 3.3d Interactions among atoms and/or molecules result in chemical reactions. 3.3e The atoms of any on ...
... 3.3a All matter is made up of atoms. Atoms are far too small to see with a light microscope. 3.3c Atoms may join together in well-defined molecules or may be arranged in regular geometric patterns. 3.3d Interactions among atoms and/or molecules result in chemical reactions. 3.3e The atoms of any on ...
Electrical Engineering
... electrical function performed by any component that can convert electrical energy into another form of energy ...
... electrical function performed by any component that can convert electrical energy into another form of energy ...
ACA__Beat_sheet_bonding_2016
... What are some properties of metals? What are some properties of nonmetals? In what block (s, p, d, f) are the Lanthanides and Actinides? ...
... What are some properties of metals? What are some properties of nonmetals? In what block (s, p, d, f) are the Lanthanides and Actinides? ...
CHM 111: General Physical Chemistry 3 Units
... empirical gas laws, Ideal Gas Equation of State, qualitative treatment of kinetic theory of gases, real gases and deviations from ideal gas laws; liquid, macroscopic properties of liquids, evaporation, vapor pressure and its variation with temperature, boiling point, heat of vaporization, Clausius-C ...
... empirical gas laws, Ideal Gas Equation of State, qualitative treatment of kinetic theory of gases, real gases and deviations from ideal gas laws; liquid, macroscopic properties of liquids, evaporation, vapor pressure and its variation with temperature, boiling point, heat of vaporization, Clausius-C ...
syllabus - Rutgers MSE
... Crystal Symmetry: Symmetry elements, point group and crystal classes, enumeration of the 32 point groups and crystal classes. Review of the periodic system emphasizing important elements, compounds and minerals of Interest to Materials Engineers. Crystal system and unit cells: Theoretical density, h ...
... Crystal Symmetry: Symmetry elements, point group and crystal classes, enumeration of the 32 point groups and crystal classes. Review of the periodic system emphasizing important elements, compounds and minerals of Interest to Materials Engineers. Crystal system and unit cells: Theoretical density, h ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Dissolved Mixture Suspension Chemical property A liquid changes into a gas through evaporation When ingredients are evenly mixed a solution is formed. When iron turns to rust it is an example of a chemical property. When ingredients can easily be seen such as the ingredients in salad dressing it is ...
... Dissolved Mixture Suspension Chemical property A liquid changes into a gas through evaporation When ingredients are evenly mixed a solution is formed. When iron turns to rust it is an example of a chemical property. When ingredients can easily be seen such as the ingredients in salad dressing it is ...
Study Guide for Ch. 1
... Identify the benefits of the metric system versus classical measurement. Temperature scales and their details. Differentiate between solutions, colloids, and suspensions. Understand the physical properties involved in determining solids, liquids, & gases. Use significant figures in calculations and ...
... Identify the benefits of the metric system versus classical measurement. Temperature scales and their details. Differentiate between solutions, colloids, and suspensions. Understand the physical properties involved in determining solids, liquids, & gases. Use significant figures in calculations and ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... - atomic: arrangement of atoms in a crystal - microscopic: size, shape and orientation of crystals - macroscopic Processing - shaping, treating conditioning etc. to alter form, structure and properties mechanically, thermally or chemically ...
... - atomic: arrangement of atoms in a crystal - microscopic: size, shape and orientation of crystals - macroscopic Processing - shaping, treating conditioning etc. to alter form, structure and properties mechanically, thermally or chemically ...
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary)
... Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary) ...
... Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary) ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.