Veterinary Bacteriology and Virology 101
... The outer layer is comprised of Lipid A, which is toxic to most animals and causes fever, diarrhea, and in extreme cases, septic shock ...
... The outer layer is comprised of Lipid A, which is toxic to most animals and causes fever, diarrhea, and in extreme cases, septic shock ...
Future Microbiology article on
... A study demonstrates the use of silver to enhance antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative pathogens. A significant amount of research has been conducted regarding the development of effective antimicrobial treatments. This appears especially true in terms of combating difficult-to-treat Gram-ne ...
... A study demonstrates the use of silver to enhance antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative pathogens. A significant amount of research has been conducted regarding the development of effective antimicrobial treatments. This appears especially true in terms of combating difficult-to-treat Gram-ne ...
File
... Can bacteria survive without a cell wall? If so how? Can you treat them with penicillin, why or why not? What does PPLO stand for? Define the following terms. What group do they most commonly describe? ...
... Can bacteria survive without a cell wall? If so how? Can you treat them with penicillin, why or why not? What does PPLO stand for? Define the following terms. What group do they most commonly describe? ...
Microorganisms Microorganisms (microbes) are small living
... Biogas is a renewable fuel made using methane gas produced from waste materials by bacteria. It is used to produce electricity. Gasohol is another use for the alcohol produced by yeast. It is used as a fuel for vehicles. Microbes and breaking down waste: Sewage treatment- In treatment works the main ...
... Biogas is a renewable fuel made using methane gas produced from waste materials by bacteria. It is used to produce electricity. Gasohol is another use for the alcohol produced by yeast. It is used as a fuel for vehicles. Microbes and breaking down waste: Sewage treatment- In treatment works the main ...
LARYNGITIS
... For most cases, resting the voice for a few days is all that is needed. • Use a cool-mist, ultrasonic humidifier to increase air moisture and ease the constricted feeling in the throat. Clean humidifier daily. • Hot, steamy showers also help. • Avoid smoking and secondary cigarette smoke. MEDICATION ...
... For most cases, resting the voice for a few days is all that is needed. • Use a cool-mist, ultrasonic humidifier to increase air moisture and ease the constricted feeling in the throat. Clean humidifier daily. • Hot, steamy showers also help. • Avoid smoking and secondary cigarette smoke. MEDICATION ...
A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA
... A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA genome surrounded by a capsid (protein coat). Viruses are sub-cellular particles that cannot metabolize on their own. In the past, biologists considered them to be nonliving particles; but some now view them as life forms. Viruses may ...
... A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA genome surrounded by a capsid (protein coat). Viruses are sub-cellular particles that cannot metabolize on their own. In the past, biologists considered them to be nonliving particles; but some now view them as life forms. Viruses may ...
NUTRACEUTICALS: Let Food be Your Medicine
... disease, and to the digestion and absorption of food and nutrients. • Each person's mix of bacteria varies. Interactions between a person and the microorganisms in his body, and among the microorganisms themselves, can be crucial to the person's health and well-being. • This bacterial "balancing act ...
... disease, and to the digestion and absorption of food and nutrients. • Each person's mix of bacteria varies. Interactions between a person and the microorganisms in his body, and among the microorganisms themselves, can be crucial to the person's health and well-being. • This bacterial "balancing act ...
Antibiotic resistant bacteria
... to treat people with bacterial infections (does not treat viral infections) ...
... to treat people with bacterial infections (does not treat viral infections) ...
Gram-Negative Bacteria - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting peptidoglycan, which is present in a thick layer in Gram-positive bacteria ...
... Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting peptidoglycan, which is present in a thick layer in Gram-positive bacteria ...
biology of prokaryotes
... 5. Critical Thinking Why are broad-spectrum antibiotics often used to treat infections caused by unidentified pathogens? What is the danger associated with overusing such antibiotics? ________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________ ...
... 5. Critical Thinking Why are broad-spectrum antibiotics often used to treat infections caused by unidentified pathogens? What is the danger associated with overusing such antibiotics? ________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________ ...
Study Guide
... 5. Critical Thinking Why are broad-spectrum antibiotics often used to treat infections caused by unidentified pathogens? What is the danger associated with overusing such antibiotics? ________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________ ...
... 5. Critical Thinking Why are broad-spectrum antibiotics often used to treat infections caused by unidentified pathogens? What is the danger associated with overusing such antibiotics? ________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________ ...
Modelling microbial growth
... It takes 20 minutes for one E. coli bacterium to divide to make two bacteria. Assuming there is nothing to limit their growth, how many bacteria would there be after eight hours? More than 16 million! ...
... It takes 20 minutes for one E. coli bacterium to divide to make two bacteria. Assuming there is nothing to limit their growth, how many bacteria would there be after eight hours? More than 16 million! ...
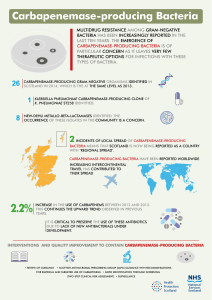
Infographic: Carbapenemase
... KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE CARBAPENEMASE-PRODUCING CLONE OF K. PNEUMONIAE ST258 IDENTIFIED. ...
... KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE CARBAPENEMASE-PRODUCING CLONE OF K. PNEUMONIAE ST258 IDENTIFIED. ...
Guidelines for a Palliative Approach in Residential Aged Care
... • Minimization of interventions that can cause loss of dignity • Comfort for the resident ...
... • Minimization of interventions that can cause loss of dignity • Comfort for the resident ...
Infection Control
... Divide into two new cells – mitosis Inactive (spore forming stage)-form spherical spores with tough outer covering for protection-cannot be harmed by disinfectants When conditions are favorable they grow and reproduce. ...
... Divide into two new cells – mitosis Inactive (spore forming stage)-form spherical spores with tough outer covering for protection-cannot be harmed by disinfectants When conditions are favorable they grow and reproduce. ...
Culturing Bacteria
... Chemoheterotrophs: most common form, they obtain energy by feeding on organic material and breaking that down. (just like us) ...
... Chemoheterotrophs: most common form, they obtain energy by feeding on organic material and breaking that down. (just like us) ...
Bacteria A NATURALLY-OCCURRING PHENOMENON
... that “someone dumped paint or a rust-colored substance” or that there is an unnatural colored oil-like sheen in moist areas or in a water body. Some oil-like films, coatings, and slimes, although they may look bad, are natural phenomena. These phenomena are caused by single- celled organisms called ...
... that “someone dumped paint or a rust-colored substance” or that there is an unnatural colored oil-like sheen in moist areas or in a water body. Some oil-like films, coatings, and slimes, although they may look bad, are natural phenomena. These phenomena are caused by single- celled organisms called ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
... Looks ill, still abdominal pain severe diarrhea (~2000 cc of stool/day), weight loss (6-7 kg), BMI 19, hypoalbuminemia (2.7 g/dL) ...
... Looks ill, still abdominal pain severe diarrhea (~2000 cc of stool/day), weight loss (6-7 kg), BMI 19, hypoalbuminemia (2.7 g/dL) ...
A photosensory two-component system regulates
... Caulobacter crescentus • Gram-negative, oligotrophic bacterium • Dimorphic lifecycle • One circular chromosome containing ~3,700 genes ...
... Caulobacter crescentus • Gram-negative, oligotrophic bacterium • Dimorphic lifecycle • One circular chromosome containing ~3,700 genes ...
Bacteria in your life HW
... 6. What kind of medicine is used to treat bacterial infections? Why? ...
... 6. What kind of medicine is used to treat bacterial infections? Why? ...
Ch. 19 – Bacteria Notes
... Boil it, peel it, cook it, or FORGET IT! Transmitted by ingestion of food or water contaminated with feces of infected people. Typhoid Mary – 36 years quarantined!), Botulism (home canned foods or bad seal on canned foods.) ...
... Boil it, peel it, cook it, or FORGET IT! Transmitted by ingestion of food or water contaminated with feces of infected people. Typhoid Mary – 36 years quarantined!), Botulism (home canned foods or bad seal on canned foods.) ...
Blaine Fritz: Cell Biology & Neuroscience
... CDC reactor according to ASTM Method E2562. The mature biofilm was exposed to chlorine (buffered water for controls) and neutralized. The biofilm was removed from the surface, disaggregated, and serially diluted. Samples from the dilution tubes were plated in duplicate on Petrifilm Aerobic Count pla ...
... CDC reactor according to ASTM Method E2562. The mature biofilm was exposed to chlorine (buffered water for controls) and neutralized. The biofilm was removed from the surface, disaggregated, and serially diluted. Samples from the dilution tubes were plated in duplicate on Petrifilm Aerobic Count pla ...
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth

Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), also termed bacterial overgrowth, or small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SBBOS), is a disorder of excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine. Unlike the colon (or large bowel), which is rich with bacteria, the small bowel usually has fewer than 104 organisms per millilitre. Patients with bacterial overgrowth typically develop symptoms including nausea, bloating, vomiting, diarrhea, malnutrition, weight loss and malabsorption which is caused by a number of mechanisms.The diagnosis of bacterial overgrowth is made by a number of techniques, with the gold standard diagnosis being an aspirate from the jejunum that grows in excess of 105 bacteria per millilitre. Risk factors for the development of bacterial overgrowth include dysmotility, anatomical disturbances in the bowel, including fistulae, diverticula and blind loops created after surgery, and resection of the ileo-cecal valve, gastroenteritis induced alterations to the small intestine as well as the use of certain medications, including proton pump inhibitors. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome is treated with an elemental diet or else antibiotics, which may be given in a cyclic fashion to prevent tolerance to the antibiotics sometimes followed by prokinetic drugs to prevent recurrence if dysmotility is a suspected cause.