Document
... Since velocity is zero at the surface (no-zero boundary condition), there is a vertical gradient of momentum. ...
... Since velocity is zero at the surface (no-zero boundary condition), there is a vertical gradient of momentum. ...
Non-thermal equilibrium two-phase flow for melt migration and ascent
... fluid within the porous matrix as well as moving of the matrix in an Eulerian grid. The theory can be applied to melts in partially molten rocks, particularly aiming at the transitional regime between melt percolation and flow through dikes, as well as to brine transport in porous rocks. The theory ...
... fluid within the porous matrix as well as moving of the matrix in an Eulerian grid. The theory can be applied to melts in partially molten rocks, particularly aiming at the transitional regime between melt percolation and flow through dikes, as well as to brine transport in porous rocks. The theory ...
Pressure in a fluid
... how the speed of flow in a tube depends on the tube’s size. • how viscous flow and turbulent flow differ from ideal flow. © 2016 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... how the speed of flow in a tube depends on the tube’s size. • how viscous flow and turbulent flow differ from ideal flow. © 2016 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Specification For Insertion Type Magnetic Flowmeter
... Sensor shall operate with a power input of 5 – 26.4 vdc, with a maximum current draw of 15 mA. ...
... Sensor shall operate with a power input of 5 – 26.4 vdc, with a maximum current draw of 15 mA. ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics PP
... Earth’s crust is divided into broken pieces called plates. • Earth’s surface has about a dozen rigid plates • Plates move slowly (a few centimeters per year) ...
... Earth’s crust is divided into broken pieces called plates. • Earth’s surface has about a dozen rigid plates • Plates move slowly (a few centimeters per year) ...
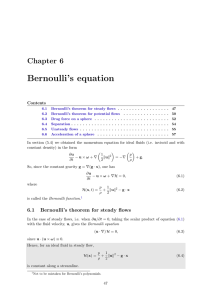
Bernoulli`s equation
... of the body (see Acheson §4.13, p. 150). The way to reduce drag (i.e. resistance) is to reduce separation: • Streamlining: separation occurs because of adverse pressure gradients on the surface of solid bodies. These can be reduced by using more “streamlined” shapes, that avoid diverging streamlines ...
... of the body (see Acheson §4.13, p. 150). The way to reduce drag (i.e. resistance) is to reduce separation: • Streamlining: separation occurs because of adverse pressure gradients on the surface of solid bodies. These can be reduced by using more “streamlined” shapes, that avoid diverging streamlines ...
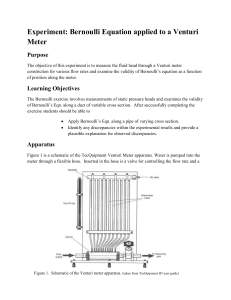
Experiment: Bernoulli Equation applied to a Venturi Meter Purpose
... The Venturi Effect is named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Venturi from the 18th century. He found that the pressure of a moving fluid drops when it passes through a constriction in a pipe. Around the same time, a Dutch-Swiss mathematician, Daniel Bernoulli, showed that the change in velocity ...
... The Venturi Effect is named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Venturi from the 18th century. He found that the pressure of a moving fluid drops when it passes through a constriction in a pipe. Around the same time, a Dutch-Swiss mathematician, Daniel Bernoulli, showed that the change in velocity ...
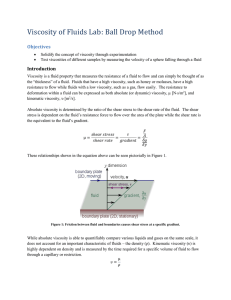
Viscosity of Fluids Lab (Ball Drop Method)
... the “thickness” of a fluid. Fluids that have a high viscosity, such as honey or molasses, have a high resistance to flow while fluids with a low viscosity, such as a gas, flow easily. The resistance to deformation within a fluid can be expressed as both absolute (or dynamic) viscosity, µ [Ns/m2], a ...
... the “thickness” of a fluid. Fluids that have a high viscosity, such as honey or molasses, have a high resistance to flow while fluids with a low viscosity, such as a gas, flow easily. The resistance to deformation within a fluid can be expressed as both absolute (or dynamic) viscosity, µ [Ns/m2], a ...
Upthrust Force
... • A measure of how close-packed the particles are in a substance. EG: gases are much less dense than solids and liquids because their particles are more widespread. ...
... • A measure of how close-packed the particles are in a substance. EG: gases are much less dense than solids and liquids because their particles are more widespread. ...
On fluid flow induced by a rotating magnetic field
... where L and V are typical length and velocity scales of the moving fluid, and p and r~ its permeability and conductivity, respectively. The condition R, B 1 is usually satisfied in astrophysical or geophysical problems on account of the large length scale involved, and many problems have been intens ...
... where L and V are typical length and velocity scales of the moving fluid, and p and r~ its permeability and conductivity, respectively. The condition R, B 1 is usually satisfied in astrophysical or geophysical problems on account of the large length scale involved, and many problems have been intens ...
Summary abstracts and conclusions
... profiles of shear stresses, heat fluxes and gradient coefficients of turbulent diffusivity in various cross sections of the tube have been found. In the conditions of normal heat transfer the flow structure resembles the structure of the one at constant properties, so that simple models of flow and ...
... profiles of shear stresses, heat fluxes and gradient coefficients of turbulent diffusivity in various cross sections of the tube have been found. In the conditions of normal heat transfer the flow structure resembles the structure of the one at constant properties, so that simple models of flow and ...
ent 153_bernoulli equation
... A streamline in a fluid flow is a line tangent to which at any point is in the direction of velocity at that point at that instant. • Streamlines are, therefore, equivalent to an instantaneous snap-shot indicating the directions of velocity in the entire flow field as shown in Fig. 4(a) and (b). • T ...
... A streamline in a fluid flow is a line tangent to which at any point is in the direction of velocity at that point at that instant. • Streamlines are, therefore, equivalent to an instantaneous snap-shot indicating the directions of velocity in the entire flow field as shown in Fig. 4(a) and (b). • T ...
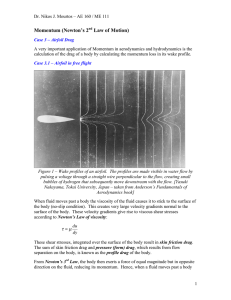
Momentum (Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion)
... where D and L are the drag and lift forces of the airfoil. If the airfoil were included in the control volume, these four forces would all be internal to the control volume and cancel each other out. As a result, none of these forces would appear in Momentum. Streamsurfaces are used for the upper ...
... where D and L are the drag and lift forces of the airfoil. If the airfoil were included in the control volume, these four forces would all be internal to the control volume and cancel each other out. As a result, none of these forces would appear in Momentum. Streamsurfaces are used for the upper ...
THE EQUATIONS OF FLUID DYNAMICS—DRAFT
... We will work solely with the continuum theory of fluids, and thus use conservation principles, supplemented by constitutive assumptions about the nature of the fluids. The conservation principles are common to any material where the continuum hypothesis is valid but different constitutive hypothesiz ...
... We will work solely with the continuum theory of fluids, and thus use conservation principles, supplemented by constitutive assumptions about the nature of the fluids. The conservation principles are common to any material where the continuum hypothesis is valid but different constitutive hypothesiz ...
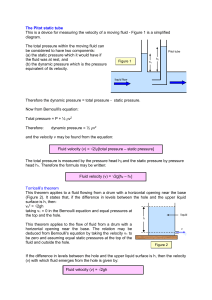
Pitot and Toricelli
... The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a drum with a horizontal opening near the base (Figure 2). It ...
... The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a drum with a horizontal opening near the base (Figure 2). It ...
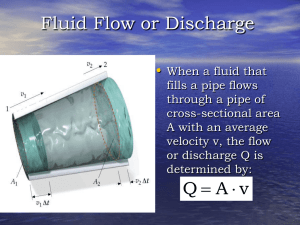
Fluid Dynamics
... column of water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the tube. Gravity pulls on one “packet" of water on the dry end of the tube causing it to move down the tube. As it moves, it creates a small vacuum behind itself. This vacuum pulls the next “packe ...
... column of water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the tube. Gravity pulls on one “packet" of water on the dry end of the tube causing it to move down the tube. As it moves, it creates a small vacuum behind itself. This vacuum pulls the next “packe ...
air or water
... Drag is affected by the following factors: •the shape of an object and how streamlined it is •the density of the fluid (air or water) •the velocity of the object as it moves through the fluid •the cross sectional area of the object in the direction of the motion. ...
... Drag is affected by the following factors: •the shape of an object and how streamlined it is •the density of the fluid (air or water) •the velocity of the object as it moves through the fluid •the cross sectional area of the object in the direction of the motion. ...
Chapter 4 Resistance
... Electrical resistance opposes the flow of electric charge, or current. This resistance is caused by electrons colliding with atoms in the conducting path. Some materials have low resistance, and some have high resistance. For example, a toaster has two wires—a power cord and a heating element. The ...
... Electrical resistance opposes the flow of electric charge, or current. This resistance is caused by electrons colliding with atoms in the conducting path. Some materials have low resistance, and some have high resistance. For example, a toaster has two wires—a power cord and a heating element. The ...
Biofluids - Louisiana Tech University
... • High Values, mean a high kinetic energy relative to its ability to flow. This should cause instability, therefore, we would expect turbulence. • Medium values, mean that the kinetic energy is smoothly related to its ability to flow. This should cause smoothly changing laminar flow. • Low values, m ...
... • High Values, mean a high kinetic energy relative to its ability to flow. This should cause instability, therefore, we would expect turbulence. • Medium values, mean that the kinetic energy is smoothly related to its ability to flow. This should cause smoothly changing laminar flow. • Low values, m ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR 8th GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST “
... -what causes pressure of a gas (particles colliding) -how pressure changes with altitude changes -that Earth’s atmosphere exerts pressure on everything within it -that at sea level, the atmospheric pressure is 101.3kPa -Boyle’s Law (as volume decreases, pressure increases; as volume increases, press ...
... -what causes pressure of a gas (particles colliding) -how pressure changes with altitude changes -that Earth’s atmosphere exerts pressure on everything within it -that at sea level, the atmospheric pressure is 101.3kPa -Boyle’s Law (as volume decreases, pressure increases; as volume increases, press ...
Surficial Processes Take Home Problems
... Problem 5. I used the channel head as an example of a geomorphic threshold. Explain the term geomorphic threshold and come up with another example. Problem 6. A debris flw of thickness h moves down a slope α with a maximum velocity of U. The bulk density ρ is 2200 kg m-3, the shear strength k is 300 ...
... Problem 5. I used the channel head as an example of a geomorphic threshold. Explain the term geomorphic threshold and come up with another example. Problem 6. A debris flw of thickness h moves down a slope α with a maximum velocity of U. The bulk density ρ is 2200 kg m-3, the shear strength k is 300 ...
Enhancing Oil Recovery with Autonomous Inflow
... along the length of the wellbore, which can occur both in homogeneous and heterogeneous formations. In a homogeneous reservoir, the fluid tends to enter the heel at a higher velocity than at the toe, also commonly known as the Heelto-toe effect. Reservoir heterogeneity also contributes to uneven inf ...
... along the length of the wellbore, which can occur both in homogeneous and heterogeneous formations. In a homogeneous reservoir, the fluid tends to enter the heel at a higher velocity than at the toe, also commonly known as the Heelto-toe effect. Reservoir heterogeneity also contributes to uneven inf ...
P - WordPress.com
... Bernoulli’s Equation For flow of an ideal incompressible fluid. The equation is an ideal tool for analysing plumbing systems, hydroelectric generating stations and the flight of aeroplanes. The dependence of pressure on speed follows from the continuity equation. When an incompressible fluid flows ...
... Bernoulli’s Equation For flow of an ideal incompressible fluid. The equation is an ideal tool for analysing plumbing systems, hydroelectric generating stations and the flight of aeroplanes. The dependence of pressure on speed follows from the continuity equation. When an incompressible fluid flows ...
Slide 1
... Fluid Flow No real fluid has all the properties of an ideal fluid, it helps to explain the properties of real fluids. Viscosity refers to the amount of internal friction within a fluid. High viscosity equals a slow flow. Steady flow is when the pressure, viscosity, and density at each point in the ...
... Fluid Flow No real fluid has all the properties of an ideal fluid, it helps to explain the properties of real fluids. Viscosity refers to the amount of internal friction within a fluid. High viscosity equals a slow flow. Steady flow is when the pressure, viscosity, and density at each point in the ...
Aerodynamics Notes 2
... essence "wasted" energy that the ship generates. This wasted energy was not used to propel the boat forward, but rather to generate waves. Figure: (Cortana, 2006) ...
... essence "wasted" energy that the ship generates. This wasted energy was not used to propel the boat forward, but rather to generate waves. Figure: (Cortana, 2006) ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.