phy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... A gas is easily compressed and usually treated as such - it changes volume with pressure. A given mass of liquid occupies a given volume and will occupy the container it is in and form a free surface on top(if the container is of a larger volume). A gas has no fixed volume, it changes volume and exp ...
... A gas is easily compressed and usually treated as such - it changes volume with pressure. A given mass of liquid occupies a given volume and will occupy the container it is in and form a free surface on top(if the container is of a larger volume). A gas has no fixed volume, it changes volume and exp ...
Progress Review
... To test the air flow distribution across the surface of the core, the pressure distribution should be modelled. Using data from the spreadsheet will show the required cooling and heat transfer; the simulation will not show this as typical data can be given from the spreadsheet. The simulation will o ...
... To test the air flow distribution across the surface of the core, the pressure distribution should be modelled. Using data from the spreadsheet will show the required cooling and heat transfer; the simulation will not show this as typical data can be given from the spreadsheet. The simulation will o ...
Télécharger le sujet de stage - Laboratoire de Physique des Solides
... Instability or a flux argument – which controls sedimentation in capillaries? Particles that are heavier than the solvent in which they are suspended in sediment, they flow down to the bottom of the recipient. This can be a nuisance, but it is a useful way to separate material in industrial processe ...
... Instability or a flux argument – which controls sedimentation in capillaries? Particles that are heavier than the solvent in which they are suspended in sediment, they flow down to the bottom of the recipient. This can be a nuisance, but it is a useful way to separate material in industrial processe ...
Regional Vascular Systems
... (CPP) / cerebrovascular resistance (CVR). The CPP is normally MAP - CVP, however in pathological states where there is raised ICP a starling resistor model is set up. In this setting ICP>CVP and therefore the CPP = MAP -ICP. Extrinsic nerve and hormonal control have little influence on CBF. The cere ...
... (CPP) / cerebrovascular resistance (CVR). The CPP is normally MAP - CVP, however in pathological states where there is raised ICP a starling resistor model is set up. In this setting ICP>CVP and therefore the CPP = MAP -ICP. Extrinsic nerve and hormonal control have little influence on CBF. The cere ...
Timothy J. Pedley
... ‘bumblebees cannot fly’, but that was according to the steady-state aerodynamics that is applicable to fixed-wing aircraft with long wings. In fact, their wings are three-dimensional, and the beating is by no means approximately steady. The three dimensionality combined with the unsteadiness generat ...
... ‘bumblebees cannot fly’, but that was according to the steady-state aerodynamics that is applicable to fixed-wing aircraft with long wings. In fact, their wings are three-dimensional, and the beating is by no means approximately steady. The three dimensionality combined with the unsteadiness generat ...
No Slide Title - Cobb Learning
... A fluid is any substance that flows and conforms to the boundaries of its container. A fluid could be a gas or a liquid. An ideal fluid is assumed to be incompressible (so that its density does not change), to flow at a steady rate, to be non-viscous (no friction between the fluid and the container ...
... A fluid is any substance that flows and conforms to the boundaries of its container. A fluid could be a gas or a liquid. An ideal fluid is assumed to be incompressible (so that its density does not change), to flow at a steady rate, to be non-viscous (no friction between the fluid and the container ...
Chapter 11 in Review - Garnet Valley School District
... • Buoyant force is an upward force caused by pressure from displaced fluids and makes the object seem lighter. • When an object is placed in a fluid, it displaces a volume of fluid equal to it’s own volume. • By comparing densities, you can determine whether an object sinks or floats. • Density = ma ...
... • Buoyant force is an upward force caused by pressure from displaced fluids and makes the object seem lighter. • When an object is placed in a fluid, it displaces a volume of fluid equal to it’s own volume. • By comparing densities, you can determine whether an object sinks or floats. • Density = ma ...
Fluid Mechanics Primer
... the influence of a constant force δFx. • The oil next to the block sticks to the block and moves at velocity δu. The surface beneath the oil is stationary and the oil there sticks to that surface and has velocity zero. • No-slip boundary condition--The condition of zero velocity at a boundary is k ...
... the influence of a constant force δFx. • The oil next to the block sticks to the block and moves at velocity δu. The surface beneath the oil is stationary and the oil there sticks to that surface and has velocity zero. • No-slip boundary condition--The condition of zero velocity at a boundary is k ...
Fluid Mechanics II
... Solution procedure of VK integral 1- Obtain U from Bernoulli’s equation out of BL and potential flow 2- Guess the velocity profile within the BL 3- Compute the shear stress (Newtonian fluid) , displacement and momentum ...
... Solution procedure of VK integral 1- Obtain U from Bernoulli’s equation out of BL and potential flow 2- Guess the velocity profile within the BL 3- Compute the shear stress (Newtonian fluid) , displacement and momentum ...
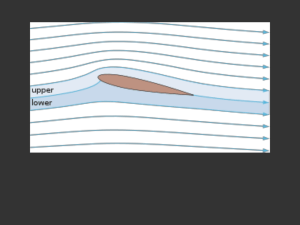
The lift of a wing is proportional to the amount of air diverted down
... and another on the upper surface near the trailing edge. The dividing line between the upper and lower streamtubes mentioned above intersects the body at the stagnation points. Since the flow speed is zero at these points, by Bernoulli's principle the static pressure at these points is at a maximum. ...
... and another on the upper surface near the trailing edge. The dividing line between the upper and lower streamtubes mentioned above intersects the body at the stagnation points. Since the flow speed is zero at these points, by Bernoulli's principle the static pressure at these points is at a maximum. ...
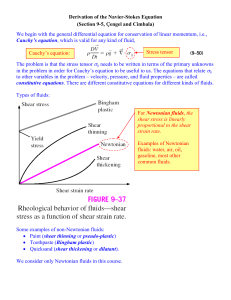
Derivation_of_NS_equation.pdf
... Now we plug this expression for the stress tensor ij into Cauchy’s equation. The result is the famous Navier-Stokes equation, shown here for incompressible flow. ...
... Now we plug this expression for the stress tensor ij into Cauchy’s equation. The result is the famous Navier-Stokes equation, shown here for incompressible flow. ...
Transport Phenomena 3
... than with the microscopic or molecular behavior. • In most cases is convenient to think as a continuous distribution of matter or a continuum. • Validity of this concept is seem to be dependent upon the type of information desired rather than the nature of the fluid. ...
... than with the microscopic or molecular behavior. • In most cases is convenient to think as a continuous distribution of matter or a continuum. • Validity of this concept is seem to be dependent upon the type of information desired rather than the nature of the fluid. ...
Fluid Mechanics Concepts
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
1 - vnhsphysics
... (5) v2 = [(15 m/s)2 – 2(9.8 m/s2)(3 m)]1/2 (6) v2 = 12.9 m/s (7) Second Equation: A1v1 = A2v2 (8) A2 = A1v1 / v2 (9) A1 = r2 (10) A2 = (r2)v1 / v2 (11) A2 = (0.04 m)2(15 m/s) / (12.9 m/s) (12) A2 = 5.84 x 10-3 m2 BERNOULLI’S PRINCIPLE Bernoulli’s principle states that swiftly moving fluids exert ...
... (5) v2 = [(15 m/s)2 – 2(9.8 m/s2)(3 m)]1/2 (6) v2 = 12.9 m/s (7) Second Equation: A1v1 = A2v2 (8) A2 = A1v1 / v2 (9) A1 = r2 (10) A2 = (r2)v1 / v2 (11) A2 = (0.04 m)2(15 m/s) / (12.9 m/s) (12) A2 = 5.84 x 10-3 m2 BERNOULLI’S PRINCIPLE Bernoulli’s principle states that swiftly moving fluids exert ...
Provedení, principy činnosti a základy výpočtu pro výměníky tepla
... floater, the wider is the gap, therefore the lower are velocities and viscous friction. This flowmeter can be used not only for liquids, but also for gases (or inviscid fluids). In this case the fluid forces are not viscous, but inertial and can be derived from Bernoulli’s equation. What do you thin ...
... floater, the wider is the gap, therefore the lower are velocities and viscous friction. This flowmeter can be used not only for liquids, but also for gases (or inviscid fluids). In this case the fluid forces are not viscous, but inertial and can be derived from Bernoulli’s equation. What do you thin ...
1D channel flows I
... Channel flows in the Earth occur when a fluid flows within a channel, between two solid “walls” hch ...
... Channel flows in the Earth occur when a fluid flows within a channel, between two solid “walls” hch ...
The Difference Between Data Rate and Data
... If the data density is high, this problem can be avoided simply by sampling at uniform time increments. The velocity sampled will be the most recent measurement of the signal processor. While it may be shifted slightly in time, the answer will be correct if the data density is high. Not only the mea ...
... If the data density is high, this problem can be avoided simply by sampling at uniform time increments. The velocity sampled will be the most recent measurement of the signal processor. While it may be shifted slightly in time, the answer will be correct if the data density is high. Not only the mea ...
Quality of Service Challenges for IP Networks
... direction of flow from the entry point into the pipe. An optimum is reached at 0.6m down the flow line. This region may be described as a segment the fluid must flow before the parabolic curve is properly and completely built up. Within this region, the flow can be said to be fairly turbulent possib ...
... direction of flow from the entry point into the pipe. An optimum is reached at 0.6m down the flow line. This region may be described as a segment the fluid must flow before the parabolic curve is properly and completely built up. Within this region, the flow can be said to be fairly turbulent possib ...
Slide 1 - UT Arlington`s Aerodynamics Research Center
... aerodynamics and propulsion has yielded few feasible applications, mainly because their power consumption would require generators far too large to fit onto an aerospace vehicle •Electromagnetic flow control utilizes the Lorentz body force, which is created from the cross product of the current and ...
... aerodynamics and propulsion has yielded few feasible applications, mainly because their power consumption would require generators far too large to fit onto an aerospace vehicle •Electromagnetic flow control utilizes the Lorentz body force, which is created from the cross product of the current and ...
congestion calculator
... There are three inputs required in the worksheets: The existing number of lanes The existing speed limit The hourly vehicle flow at the site (for a typical weekday or typical weekend day as appropriate) This is for all lanes combined (i.e. the carriageway flow) The hourly vehicle flow should b ...
... There are three inputs required in the worksheets: The existing number of lanes The existing speed limit The hourly vehicle flow at the site (for a typical weekday or typical weekend day as appropriate) This is for all lanes combined (i.e. the carriageway flow) The hourly vehicle flow should b ...
Section_11_Similarit..
... There are several other non-dimensional parameters that appear in the literature that are combinations of Se and S . For example, Pr S / Se / ( / 0 ) is called the magnetic Prandtl number. It measures the relative effects of viscous and resistive diffusion. Similarly, H SSe is called the H ...
... There are several other non-dimensional parameters that appear in the literature that are combinations of Se and S . For example, Pr S / Se / ( / 0 ) is called the magnetic Prandtl number. It measures the relative effects of viscous and resistive diffusion. Similarly, H SSe is called the H ...
ICNS 132 : Fluid Mechanics
... magnitude F1 is applied to a small piston of surface area A1. The pressure is transmitted through an incompressible liquid to a larger piston of surface area A2. Because the pressure must be the same on both sides, P = F1/A1 = F2/A2. Therefore, the force F2 is greater than the force F1 by a factor A ...
... magnitude F1 is applied to a small piston of surface area A1. The pressure is transmitted through an incompressible liquid to a larger piston of surface area A2. Because the pressure must be the same on both sides, P = F1/A1 = F2/A2. Therefore, the force F2 is greater than the force F1 by a factor A ...
Chapter 13: Fluids Mechanics
... This photograph was taken in a water tunnel using hydrogen bubbles to visualize the flow pattern around a cylinder. The flow was started from rest, and at this instant the pattern shows the development of a complex wake structure on the downstream side of the cylinder. Four characteristics of an id ...
... This photograph was taken in a water tunnel using hydrogen bubbles to visualize the flow pattern around a cylinder. The flow was started from rest, and at this instant the pattern shows the development of a complex wake structure on the downstream side of the cylinder. Four characteristics of an id ...
Physics--Chapter 9: Fluid Mechanics
... smaller "pad" results in a larger force to a large lift An equational relationship for how hydraulic systems work ...
... smaller "pad" results in a larger force to a large lift An equational relationship for how hydraulic systems work ...
Product Data Sheet: Damcos DPI-B - direct hydraulic open/closed
... shift. When the valve reaches its end position, the flow switch will close. ...
... shift. When the valve reaches its end position, the flow switch will close. ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.