The non newtonian fluids
... - Reopessici flids: are substances which tend to increase their viscosity with the passing of time when subjected to shear forces and such variation of viscosity depends on the speed with which that force is applied. Being formed by a liquid and a solid phase, low speed values, the particles suspend ...
... - Reopessici flids: are substances which tend to increase their viscosity with the passing of time when subjected to shear forces and such variation of viscosity depends on the speed with which that force is applied. Being formed by a liquid and a solid phase, low speed values, the particles suspend ...
Wing / boom Control for Anhydrous Applicators
... anhydrous ammonia coming from the nurse tank. This pump maintains constant pressure of ammonia distributed to knives. Anhydrous ammonia can be applied consistently over a wide variation in tank pressure, even on a very cold day. 2. Orifices are used at the manifold for each line going to an injectio ...
... anhydrous ammonia coming from the nurse tank. This pump maintains constant pressure of ammonia distributed to knives. Anhydrous ammonia can be applied consistently over a wide variation in tank pressure, even on a very cold day. 2. Orifices are used at the manifold for each line going to an injectio ...
Unsteady MHD Couette Flow with Heat Transfer of a Viscoelastic
... finite difference approximation. The Crank-Nicolson implicit method [17] is used at two successive time levels. Finite difference equations relating the variables are obtained by writing the equations at the mid point of the computational cell and then replacing the different terms by their second o ...
... finite difference approximation. The Crank-Nicolson implicit method [17] is used at two successive time levels. Finite difference equations relating the variables are obtained by writing the equations at the mid point of the computational cell and then replacing the different terms by their second o ...
ch14
... An open-tube manometer measures the gauge pressure pg of a gas. It consists of a U-tube containing a liquid, with one end of the tube connected to the vessel whose gauge pressure we wish to measure and the other end open to the atmosphere. If po is the atmospheric pressure, p is the pressure at leve ...
... An open-tube manometer measures the gauge pressure pg of a gas. It consists of a U-tube containing a liquid, with one end of the tube connected to the vessel whose gauge pressure we wish to measure and the other end open to the atmosphere. If po is the atmospheric pressure, p is the pressure at leve ...
10-6 - Physics
... fixed shape, have ability to flow Liquids and gases are called fluids Fluids statics: study of fluids at rest Fluids dynamics: study of fluids in ...
... fixed shape, have ability to flow Liquids and gases are called fluids Fluids statics: study of fluids at rest Fluids dynamics: study of fluids in ...
Chapter 3 Basic of Fluid Flow
... particles to vary from point to point throughout the flow field. The motion of fluids can be predicted using the fundamental laws of physics together with the physical properties of the fluid. The geometry of the motion of fluid particles in space and time is known as the kinematics of the fluid ...
... particles to vary from point to point throughout the flow field. The motion of fluids can be predicted using the fundamental laws of physics together with the physical properties of the fluid. The geometry of the motion of fluid particles in space and time is known as the kinematics of the fluid ...
ENIAC`s Problem 1 Discussion
... nearly the speed of sound, at which point effects having to do with the compressibility of air become important. Above “Mach 1” 2 , the drag force depends approximately linearly on velocity (but unlike Stokes’ law: with a negative y-intercept). All the above formulae hide the fact that at “high” spe ...
... nearly the speed of sound, at which point effects having to do with the compressibility of air become important. Above “Mach 1” 2 , the drag force depends approximately linearly on velocity (but unlike Stokes’ law: with a negative y-intercept). All the above formulae hide the fact that at “high” spe ...
ent 257/4 fluid mechanics
... Two dimensional Flow: When the dependent variables in a fluid flow vary with only two space coordinates, the flow is said to be two dimensional. The flow does not vary along the third coordinate direction Example: The flow around a circular cylinder of infinite length (as shown in Fig. 2c) is two ...
... Two dimensional Flow: When the dependent variables in a fluid flow vary with only two space coordinates, the flow is said to be two dimensional. The flow does not vary along the third coordinate direction Example: The flow around a circular cylinder of infinite length (as shown in Fig. 2c) is two ...
Basic Biomechanics, (5th edition) by Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
... Laminar flow is characterized by smooth, parallel layers of fluid. Basic Biomechanics, 6th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D. ...
... Laminar flow is characterized by smooth, parallel layers of fluid. Basic Biomechanics, 6th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D. ...
Viscosity Lab - Net Start Class
... Background Information: From Glencoe Science laboratory handout the following information was determined: Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to flow. Fluids are liquids and gases. A viscous fluid has a high viscosity: that is, it does not flow easily. A less viscous fluid flows easily. Viscosity ...
... Background Information: From Glencoe Science laboratory handout the following information was determined: Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to flow. Fluids are liquids and gases. A viscous fluid has a high viscosity: that is, it does not flow easily. A less viscous fluid flows easily. Viscosity ...
FLUID FLOW IDEAL FLUID BERNOULLI`S PRINCIPLE
... • Nonviscous – fluid has no internal friction ( η= 0) • Steady flow – the velocity of the fluid at each point is constant in time. BERNOULLI'S EQUATION (conservation of ENERGY) An interesting effect is that, for a fluid (e.g. air) flowing through a pipe with a constriction in it, the fluid pressure ...
... • Nonviscous – fluid has no internal friction ( η= 0) • Steady flow – the velocity of the fluid at each point is constant in time. BERNOULLI'S EQUATION (conservation of ENERGY) An interesting effect is that, for a fluid (e.g. air) flowing through a pipe with a constriction in it, the fluid pressure ...
901 bubblemotion10 05
... not arise. Though Plesset (1949) introduced a variable external driving pressure and surface tension, the effects of surface tension were also introduced and the effects of viscosity were first introduced by Poritsky (1951). His understanding of irrotational viscous stresses is exemplary, unique for ...
... not arise. Though Plesset (1949) introduced a variable external driving pressure and surface tension, the effects of surface tension were also introduced and the effects of viscosity were first introduced by Poritsky (1951). His understanding of irrotational viscous stresses is exemplary, unique for ...
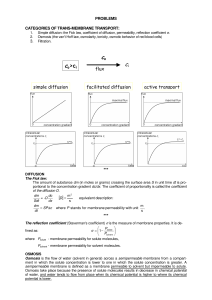
Basics of transmembrane transport of solutes
... Osmosis is the flow of water (solvent in general) across a semipermeable membrane from a compartment in which the solute concentration is lower to one in which the solute concentration is greater. A semipermeable membrane is defined as a membrane permeable to solvent but impermeable to solute. Osmos ...
... Osmosis is the flow of water (solvent in general) across a semipermeable membrane from a compartment in which the solute concentration is lower to one in which the solute concentration is greater. A semipermeable membrane is defined as a membrane permeable to solvent but impermeable to solute. Osmos ...
CVE 240 – Fluid Mechanics
... • Select a control volume. Select coordinate axes. Select an inertial reference frame. • Identify governing equations (scalar vs. vector), and the other equations (Bernoulli, continuity) may also be applied. • Force analysis and diagram • Sketch body forces on the force diagram • Sketch surface forc ...
... • Select a control volume. Select coordinate axes. Select an inertial reference frame. • Identify governing equations (scalar vs. vector), and the other equations (Bernoulli, continuity) may also be applied. • Force analysis and diagram • Sketch body forces on the force diagram • Sketch surface forc ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance, Capacitance and Inductance
... Digital signals • Digital electronic signals usually use one voltage to represent 0, and another to represent 1. • Voltage (potential difference) measured with respect to ground • 0 volts Logic 0 • 5 volts Logic 1 – Often not 5 volts, but 3, or 2.7 or 1.5… – Actual signal is analogue • Interpretati ...
... Digital signals • Digital electronic signals usually use one voltage to represent 0, and another to represent 1. • Voltage (potential difference) measured with respect to ground • 0 volts Logic 0 • 5 volts Logic 1 – Often not 5 volts, but 3, or 2.7 or 1.5… – Actual signal is analogue • Interpretati ...
Chapter 14
... Fig. 14-19 Fluid flows at a steady rate through a length L of a tube, from the input end at the left to the output end at the right. From time t in (a) to time t+Dt in (b), the amount of fluid shown in purple enters the input end and the equal amount shown in green emerges from the output end. ...
... Fig. 14-19 Fluid flows at a steady rate through a length L of a tube, from the input end at the left to the output end at the right. From time t in (a) to time t+Dt in (b), the amount of fluid shown in purple enters the input end and the equal amount shown in green emerges from the output end. ...
AE1110x -‐ Lecture 3b -‐ The boundary layer on a flat plate In
... The friction force on the element dx is tau times the area, which is dx times 1. The total skin friction drag on the plate is The integral from the leading edge to the trailing edge, so ...
... The friction force on the element dx is tau times the area, which is dx times 1. The total skin friction drag on the plate is The integral from the leading edge to the trailing edge, so ...
This can be better explained by demonstrating a steady flow
... across the thickness dr of the body in a manner that a differential force of dp dA acts on the body radially inward. This force, in fact, is the centripetal force responsible for the rotation of the fluid element and thus becomes equal to the centrifugal force under equilibrium conditions in the rad ...
... across the thickness dr of the body in a manner that a differential force of dp dA acts on the body radially inward. This force, in fact, is the centripetal force responsible for the rotation of the fluid element and thus becomes equal to the centrifugal force under equilibrium conditions in the rad ...
Pore-scale study of the fracture influence on fluid
... fracture aperture, inclination, and the geometric center. Then Lattice Boltzmann method is applied to make flow simulation on them and the resultant effects of fracture are investigated. The new issues about association of fracture into pore network model are addressed for the future new pore networ ...
... fracture aperture, inclination, and the geometric center. Then Lattice Boltzmann method is applied to make flow simulation on them and the resultant effects of fracture are investigated. The new issues about association of fracture into pore network model are addressed for the future new pore networ ...
Three-dimensional traveling-wave solutions in
... In order to understand transition mechanisms from laminar state to turbulence for the simplest form of shear motion, plane Couette flow has been studied a great deal both theoretically @1–3# and experimentally @4–9# in the last few years. In experiments, turbulent spots are triggered by injecting a ...
... In order to understand transition mechanisms from laminar state to turbulence for the simplest form of shear motion, plane Couette flow has been studied a great deal both theoretically @1–3# and experimentally @4–9# in the last few years. In experiments, turbulent spots are triggered by injecting a ...
An Aerodynamicist`s View of Lift, Bernoulli, and Newton
... relatively small region of the flow field. This is a standard wind-tunnel experiment that my classes do every semester. Measuring lift by measuring the increase in downward vertical velocity in the flow coming off the trailing edge of the airfoil is conceptually possible. This downward velocity is d ...
... relatively small region of the flow field. This is a standard wind-tunnel experiment that my classes do every semester. Measuring lift by measuring the increase in downward vertical velocity in the flow coming off the trailing edge of the airfoil is conceptually possible. This downward velocity is d ...
the possio integral equation of aeroelasticity: a modern view
... origin so that we have a singular integral equation [9]. Assume that (5) has a solution. Then the solution of the linearised potential equation (1) specialized for ql = l,q2,q3 both zero , is given by: ...
... origin so that we have a singular integral equation [9]. Assume that (5) has a solution. Then the solution of the linearised potential equation (1) specialized for ql = l,q2,q3 both zero , is given by: ...
Numerical Example
... If FLOW is LOW and TIME is LATER ON then CONCENTRATION is C2 convenience, we rename the If FLOW is MODERATE and TIME is EARLY ON then CONCENTRATION is C3 different input If FLOW is MODERATE and TIME is LATER ON then CONCENTRATION is C4 MFs with ...
... If FLOW is LOW and TIME is LATER ON then CONCENTRATION is C2 convenience, we rename the If FLOW is MODERATE and TIME is EARLY ON then CONCENTRATION is C3 different input If FLOW is MODERATE and TIME is LATER ON then CONCENTRATION is C4 MFs with ...
Fluids
... Equation of Continuity If the flow of a fluid is smooth, it is called streamline or laminar flow (a). Above a certain speed, the flow becomes turbulent (b). Turbulent flow has eddies; the viscosity of the fluid is much ...
... Equation of Continuity If the flow of a fluid is smooth, it is called streamline or laminar flow (a). Above a certain speed, the flow becomes turbulent (b). Turbulent flow has eddies; the viscosity of the fluid is much ...
Fluid Dynamics
... water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the tube. Gravity pulls on one “packet" of water on the dry end of the tube causing it to move down the tube. As it moves, it creates a small vacuum behind itself. This vacuum pulls the next “packet” forward ...
... water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the tube. Gravity pulls on one “packet" of water on the dry end of the tube causing it to move down the tube. As it moves, it creates a small vacuum behind itself. This vacuum pulls the next “packet” forward ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.