Coastal Processes and Sediment Transport
... shows the phase variation of Si and 62. Fig. 3 shows the measured maximum thicknesses during half an oscillatory period S\, and <52 in relation to the Shields number W for CASE- 1 ~ 6. The sheet flow layer thickness <$i increases almost linearly with the Shields number, and shows good agreement with ...
... shows the phase variation of Si and 62. Fig. 3 shows the measured maximum thicknesses during half an oscillatory period S\, and <52 in relation to the Shields number W for CASE- 1 ~ 6. The sheet flow layer thickness <$i increases almost linearly with the Shields number, and shows good agreement with ...
Fluids Notes - Net Start Class
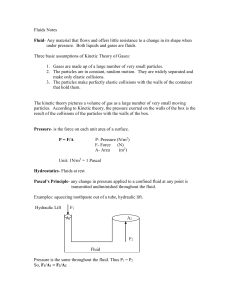
... Fluids Notes Fluid- Any material that flows and offers little resistance to a change in its shape when under pressure. Both liquids and gases are fluids. Three basic assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases: 1. Gases are made up of a large number of very small particles. 2. The particles are in consta ...
... Fluids Notes Fluid- Any material that flows and offers little resistance to a change in its shape when under pressure. Both liquids and gases are fluids. Three basic assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases: 1. Gases are made up of a large number of very small particles. 2. The particles are in consta ...
Fluid Flow - Binus Repository
... The more uniform distribution well above the boundary reflects the fact that fluid momentum is being transferred not only by viscous shear. The chaotic mixing that takes place also transfers momentum through the flow. The movement of fluid up and down in the flow more evenly distributes the velocit ...
... The more uniform distribution well above the boundary reflects the fact that fluid momentum is being transferred not only by viscous shear. The chaotic mixing that takes place also transfers momentum through the flow. The movement of fluid up and down in the flow more evenly distributes the velocit ...
1703-5823-1-SP - AGH University of Science and Technology
... To start with, from the design point of view conventional automotive hydraulic shock absorbers also known as vehicle dampers [1] as of a simple double-tube design with passive deflected disc type valves or preloaded spring valving. Although being a mature technology (the telescopic device's operatin ...
... To start with, from the design point of view conventional automotive hydraulic shock absorbers also known as vehicle dampers [1] as of a simple double-tube design with passive deflected disc type valves or preloaded spring valving. Although being a mature technology (the telescopic device's operatin ...
Swirling Flow Visualisation in a Square Section Test Duct by Particle
... The purpose of this work is to investigate swirling flow in a square section test duct at section 1 and 2 experimentally, one foot and one foot and 7cm from front respectively. The two components of the velocity i.e. velocity field in a plane, vorticity, strain rate, Reynolds shear stress and total ...
... The purpose of this work is to investigate swirling flow in a square section test duct at section 1 and 2 experimentally, one foot and one foot and 7cm from front respectively. The two components of the velocity i.e. velocity field in a plane, vorticity, strain rate, Reynolds shear stress and total ...
Drag and Drag Coefficients
... general the drag cannot be predicted. For spheres and other regular shapes at low fluid velocities, the flow patterns and drag forces can be estimated from published correlations or by numerical calculations using the general momentum balance equations. ...
... general the drag cannot be predicted. For spheres and other regular shapes at low fluid velocities, the flow patterns and drag forces can be estimated from published correlations or by numerical calculations using the general momentum balance equations. ...
Design specifications
... A key feature of the device is that it can work with a wide range of engines. It is expected that the device should be able to handle the mass flow rates of not only small displacement engines, but engines with displacements of up to 5.7L. This brings in two aspects: the Maximum Output flow rate and ...
... A key feature of the device is that it can work with a wide range of engines. It is expected that the device should be able to handle the mass flow rates of not only small displacement engines, but engines with displacements of up to 5.7L. This brings in two aspects: the Maximum Output flow rate and ...
control volume approach and continuity principle
... just B referenced to mass), and in the volume (if we increase the control volume, we probably include more of the total property B ) Notice also that V in the last term has to be the velocity relative to the control surface. ...
... just B referenced to mass), and in the volume (if we increase the control volume, we probably include more of the total property B ) Notice also that V in the last term has to be the velocity relative to the control surface. ...
the fluid mechanics course, CHE 204, Transport Phenomena I
... Now, coming back to the same question; what is a fluid? We can all think of some things which obviously are fluids. For example, air, water, gasoline, lubricating oil and milk. We can also think of some things which obviously are not fluid. For example, steel, diamonds, rubber band and paper. These ...
... Now, coming back to the same question; what is a fluid? We can all think of some things which obviously are fluids. For example, air, water, gasoline, lubricating oil and milk. We can also think of some things which obviously are not fluid. For example, steel, diamonds, rubber band and paper. These ...
How we arrive at a steady state/linear velocity profile, i.e., = constant
... opposite direction (i.e., -x direction) of that exerted at the top of the fluid parcel. The problem is, initially the fluid is not in steady state! However, when the two are equal and opposite throughout the entire fluid, we have reached an equilibrium state whereby there is a force acting (upper pl ...
... opposite direction (i.e., -x direction) of that exerted at the top of the fluid parcel. The problem is, initially the fluid is not in steady state! However, when the two are equal and opposite throughout the entire fluid, we have reached an equilibrium state whereby there is a force acting (upper pl ...
Sediment transport via dam-break flows over sloping
... retaining wall is suddenly released by the removal of the barrier, the resulting flow over a horizontal or sloping bed is referred to as a dam-break flow. When bed resistance is neglected the exact solution, in the case of a stable horizontal bed, may be obtained on the basis of shallow-water theory ...
... retaining wall is suddenly released by the removal of the barrier, the resulting flow over a horizontal or sloping bed is referred to as a dam-break flow. When bed resistance is neglected the exact solution, in the case of a stable horizontal bed, may be obtained on the basis of shallow-water theory ...
Velocity Profiles for Circular Sections and Flow in
... In Example Problem 8.1 we found that the Reynolds number is 708 when glycerine at 25°C flows with an average flow velocity of 3.6 m/s in a pipe having a 150mm inside diameter. Thus the flow is laminar. Compute points on the velocity profile from the pipe wall to the centerline of the pipe in increme ...
... In Example Problem 8.1 we found that the Reynolds number is 708 when glycerine at 25°C flows with an average flow velocity of 3.6 m/s in a pipe having a 150mm inside diameter. Thus the flow is laminar. Compute points on the velocity profile from the pipe wall to the centerline of the pipe in increme ...
Document
... • where the dot over Q and W signifies a time rate and e is the specific energy. It is very difficult to apply the above equations directly to a collection of fluid particles as the fluid moves along in a simple pipe flow as well as in a more complicated flow, such as flow through a turbine. • We co ...
... • where the dot over Q and W signifies a time rate and e is the specific energy. It is very difficult to apply the above equations directly to a collection of fluid particles as the fluid moves along in a simple pipe flow as well as in a more complicated flow, such as flow through a turbine. • We co ...
Fluid Power Formulas in SI Metric Units
... HP = Horsepower PSI = Gauge pressure, lbs/sq. inch GPM = Flow, gallons per minute ...
... HP = Horsepower PSI = Gauge pressure, lbs/sq. inch GPM = Flow, gallons per minute ...
Corelite-1 - Waymond Scott
... greater than rn are sent back to the edge routers they came from and the deficit counter decremented until it is zero again ...
... greater than rn are sent back to the edge routers they came from and the deficit counter decremented until it is zero again ...
Project 1: Computational Modeling of Flow and Surfactant Transport
... advantage of these hypotheses and attempt to directly simulate large scale motion while modeling the small scale eddies. The LES method has been successfully used for many years in computing complex turbulent flows and proved to be the best approach in terms of accuracy and computational time. Howev ...
... advantage of these hypotheses and attempt to directly simulate large scale motion while modeling the small scale eddies. The LES method has been successfully used for many years in computing complex turbulent flows and proved to be the best approach in terms of accuracy and computational time. Howev ...
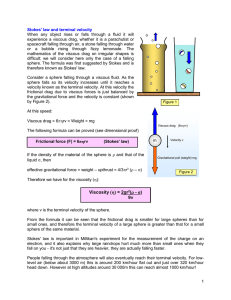
Stokes` law - schoolphysics
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
PowerPoint Slides - University of Toronto Physics
... • Consider an ideal fluid, flowing through a tube which narrows. ...
... • Consider an ideal fluid, flowing through a tube which narrows. ...
viscoelastic fluid flow with the presence of magnetic field past
... over a hot vertical porous plate with the presence of magnetic field. The result of those show that Prandtl number has more pronouncing effect on the temperature distribution rather than the viscosity parameter, as well as the thermal radiation parameter. Research about boundary layer flow past stre ...
... over a hot vertical porous plate with the presence of magnetic field. The result of those show that Prandtl number has more pronouncing effect on the temperature distribution rather than the viscosity parameter, as well as the thermal radiation parameter. Research about boundary layer flow past stre ...
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4: Bernoulli Equation
... Consider Inviscid Flow: If a flow is inviscid, it has zero viscosity, and likewise no thermal conductivity or heat transfer. In practice, there are no inviscid fluids, since all fluids support shear. ...
... Consider Inviscid Flow: If a flow is inviscid, it has zero viscosity, and likewise no thermal conductivity or heat transfer. In practice, there are no inviscid fluids, since all fluids support shear. ...
S2 File.
... is, where the cross sectional area diameter is smaller than the length), it will behave as an aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geometrically. Also, where the density of the particle is less than 1, the particle will behave as an aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geomet ...
... is, where the cross sectional area diameter is smaller than the length), it will behave as an aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geometrically. Also, where the density of the particle is less than 1, the particle will behave as an aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geomet ...
CH3080_cyclone_separator_format_error
... Suitable for separating particles about 5 μm in diameter; smaller particles down to about 0.5 μm can be separated where agglomeration occurs. ...
... Suitable for separating particles about 5 μm in diameter; smaller particles down to about 0.5 μm can be separated where agglomeration occurs. ...
Lecture 39
... Stagnation pressure Pstag = pressure at a stagnation point where the velocity is slowed down to zero nearly isentropically. This is the pressure at the nose (stagnation point) of a probe in the flow. Static pressure P = pressure that would be measured by an infinitesimal pressure sensor moving with ...
... Stagnation pressure Pstag = pressure at a stagnation point where the velocity is slowed down to zero nearly isentropically. This is the pressure at the nose (stagnation point) of a probe in the flow. Static pressure P = pressure that would be measured by an infinitesimal pressure sensor moving with ...
Waters 996 PDA Variable Pathlength Flow Cell: Preparative HPLC
... At very high concentrations of analyte, the linear range of the detector will be exceeded so that there is little or no increase in absorbance with increase in concentration. This typically happens between 1.5 and 2 AU with HPLC UV/Vis detectors. The left panel shows the ideal and actual performance ...
... At very high concentrations of analyte, the linear range of the detector will be exceeded so that there is little or no increase in absorbance with increase in concentration. This typically happens between 1.5 and 2 AU with HPLC UV/Vis detectors. The left panel shows the ideal and actual performance ...
Flow over immerse bodies
... the direction normal to the upstream velocity. On the other hand, the pressure force on a flat plate normal to the flow provides the entire drag. If the viscosity were zero, the pressure drag on any shaped object (symmetrical or not) in a steady flow would be zero. There perhaps would be large press ...
... the direction normal to the upstream velocity. On the other hand, the pressure force on a flat plate normal to the flow provides the entire drag. If the viscosity were zero, the pressure drag on any shaped object (symmetrical or not) in a steady flow would be zero. There perhaps would be large press ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.