Chapter 5 Pressure Variation in Flowing Fluids
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
The actual equation that is provided you is where would be some
... where p0 would be some initial pressure. We did a bunch of these problems. Guage pressure is based on the idea that the atmospheric pressure is zero pressure. Absolute pressure uses a perfect vacuum – zero pascals – as its zero pressure. So guage pressure differs from absolute pressure by one atmosp ...
... where p0 would be some initial pressure. We did a bunch of these problems. Guage pressure is based on the idea that the atmospheric pressure is zero pressure. Absolute pressure uses a perfect vacuum – zero pascals – as its zero pressure. So guage pressure differs from absolute pressure by one atmosp ...
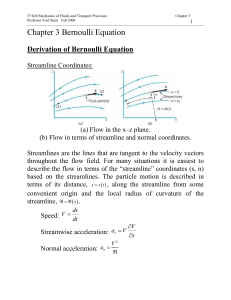
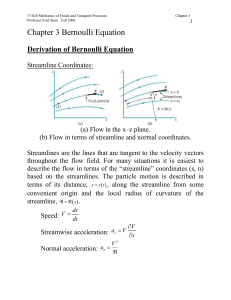
Chapter 3 Bernoulli Equation
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer Through Packed Beds of
... The purpose of this study was to simulate flow and heat transfer in packed beds with low N using COMSOL, a commercially available multiphysics computer program. Typically this type of study would be performed using a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software package such as Fluent, but it was des ...
... The purpose of this study was to simulate flow and heat transfer in packed beds with low N using COMSOL, a commercially available multiphysics computer program. Typically this type of study would be performed using a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software package such as Fluent, but it was des ...
Hydrostatic Forces on Plane Surfaces
... easy to compress, and fully expands to fill its container. The re is thus no free surface. Consequently, an important characteristic of a fluid from the viewpoint of fluid mechanics is its compressibility. Another characteristic is its viscosity . Whereas a solid shows its elasticity in tension, com ...
... easy to compress, and fully expands to fill its container. The re is thus no free surface. Consequently, an important characteristic of a fluid from the viewpoint of fluid mechanics is its compressibility. Another characteristic is its viscosity . Whereas a solid shows its elasticity in tension, com ...
CVE 240 – Fluid Mechanics
... Rise and fall of liquid in a capillary tube is caused by surface tension. Capillarity depends on the relative magnitudes of the cohesion of the liquid to walls of the containing vessel. When the adhesive forces between liquid and solid are larger than the liquid's cohesive forces, the meniscus in a ...
... Rise and fall of liquid in a capillary tube is caused by surface tension. Capillarity depends on the relative magnitudes of the cohesion of the liquid to walls of the containing vessel. When the adhesive forces between liquid and solid are larger than the liquid's cohesive forces, the meniscus in a ...
CHAPTER 13
... plasma state. The solid state is a substance with definite volume and shape. The second state is the fluids (liquids + gases), which is a substance that can flow. Liquids has a definite volume but no definite shape. Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape. The third state is the plasma ...
... plasma state. The solid state is a substance with definite volume and shape. The second state is the fluids (liquids + gases), which is a substance that can flow. Liquids has a definite volume but no definite shape. Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape. The third state is the plasma ...
Fluid Mechanics - GTU e
... Rise and fall of liquid in a capillary tube is caused by surface tension. Capillarity depends on the relative magnitudes of the cohesion of the liquid to walls of the containing vessel. When the adhesive forces between liquid and solid are larger than the liquid's cohesive forces, the meniscus in a ...
... Rise and fall of liquid in a capillary tube is caused by surface tension. Capillarity depends on the relative magnitudes of the cohesion of the liquid to walls of the containing vessel. When the adhesive forces between liquid and solid are larger than the liquid's cohesive forces, the meniscus in a ...
Convection and Radiation
... The wind we feel outside is often the result of convection currents. You can understand this by the winds you feel near an ocean. Warm air is lighter than cold air and so it rises. During the daytime, cool air over water moves to replace the air rising up as the land warms the air over it. ...
... The wind we feel outside is often the result of convection currents. You can understand this by the winds you feel near an ocean. Warm air is lighter than cold air and so it rises. During the daytime, cool air over water moves to replace the air rising up as the land warms the air over it. ...
Characterization of flow contributions to drag and lift of a circular
... surrounding the cylinder could be investigated by studying their fingerprint at the body surface, however the non-locality of the pressure renders this approach difficult. In the case of bluff bodies, it can be shown [2] that the high drag is due to a strong base pressure induced by flow separation ...
... surrounding the cylinder could be investigated by studying their fingerprint at the body surface, however the non-locality of the pressure renders this approach difficult. In the case of bluff bodies, it can be shown [2] that the high drag is due to a strong base pressure induced by flow separation ...
MOVING BUBBLES, DROPS, AND OTHER FLUID BLOBS
... cases. There are specific reasons why a fluid blob moving in another fluid is more interesting to tudy than a solid moving in a fluid. A fluid blob can deform in shape and can flow internally. There are many types of motion posible because these characteristics are controlled by the viscous forces, ...
... cases. There are specific reasons why a fluid blob moving in another fluid is more interesting to tudy than a solid moving in a fluid. A fluid blob can deform in shape and can flow internally. There are many types of motion posible because these characteristics are controlled by the viscous forces, ...
Three-dimensional numerical analysis to predict behavior of driftage carried by tsunami
... and vertical wall e is 0.5. For computational purposes, the cylindrical driftage was modeled as an octagonal pillar with cross-sectional area and volume equal to that of the actual cylinder (driftage). Figure 8 shows the results of a comparison between the vertical 2D trajectory of the driftage obta ...
... and vertical wall e is 0.5. For computational purposes, the cylindrical driftage was modeled as an octagonal pillar with cross-sectional area and volume equal to that of the actual cylinder (driftage). Figure 8 shows the results of a comparison between the vertical 2D trajectory of the driftage obta ...
Viscous Dissipation Effects For Liquid Flow In Microchannels
... density, _ is the viscosity of the fluid, and cp is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure. In the above governing equations, the conservation of energy equation ( 4) is also considered not because of the existence of any external heat source, but because energy comes from the viscous effec ...
... density, _ is the viscosity of the fluid, and cp is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure. In the above governing equations, the conservation of energy equation ( 4) is also considered not because of the existence of any external heat source, but because energy comes from the viscous effec ...
(buoyancy-driven) stack ventilation
... • modern low energy buildings are typically tightly sealed and employ mechanical ventilation heat recovery rather than relying on natural ventilation • this gives a consistent supply of fresh air, without a significant heating energy penalty • heat recovery in an MVHR system is typically achieved us ...
... • modern low energy buildings are typically tightly sealed and employ mechanical ventilation heat recovery rather than relying on natural ventilation • this gives a consistent supply of fresh air, without a significant heating energy penalty • heat recovery in an MVHR system is typically achieved us ...
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
... Solution of Pipe Flow Problems Flow Measurement © Fox, Pritchard, & McDonald ...
... Solution of Pipe Flow Problems Flow Measurement © Fox, Pritchard, & McDonald ...
Fluid Mechanics: Fluid mechanics may be defined as that branch of
... • Whereas in liquids these spacing are relatively large, and then less inter-molecules cohesive forces between them, and then can move freely, but it still has a definite volume (no definite shape, has free interface). • While these forces is extremely small in gasses, and then have greater freedom ...
... • Whereas in liquids these spacing are relatively large, and then less inter-molecules cohesive forces between them, and then can move freely, but it still has a definite volume (no definite shape, has free interface). • While these forces is extremely small in gasses, and then have greater freedom ...
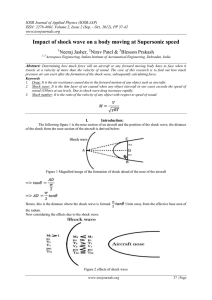
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) ISSN: 2278-4861.
... Abstract: Determining how much force will an aircraft or any forward moving body have to face when it travels at a velocity of more than the velocity of sound. The core of this research is to find out how much pressure air can exert after the formation of the shock wave, subsequently calculating for ...
... Abstract: Determining how much force will an aircraft or any forward moving body have to face when it travels at a velocity of more than the velocity of sound. The core of this research is to find out how much pressure air can exert after the formation of the shock wave, subsequently calculating for ...
Dynamics and stability of a fluid filled cylinder rolling on an inclined
... shell motion. From this solution, we show that the terminal state is associated with a constant acceleration. We also show that this state is independent of the liquid viscosity and only depends on the ratio of the shell mass to the fluid mass. We then analyze the stability of this unsteady flow fie ...
... shell motion. From this solution, we show that the terminal state is associated with a constant acceleration. We also show that this state is independent of the liquid viscosity and only depends on the ratio of the shell mass to the fluid mass. We then analyze the stability of this unsteady flow fie ...
Pressure and Fluid Flow_ppt_RevW10
... When you are swimming at a depth h, the pressure outside you in the water is Patm+ gh. Inside your lungs, which are directly connected to the air by the snorkel, the pressure is Patm. So your lungs have to breathe against a gauge pressure of gh. You can expand your chest against a pressure only ...
... When you are swimming at a depth h, the pressure outside you in the water is Patm+ gh. Inside your lungs, which are directly connected to the air by the snorkel, the pressure is Patm. So your lungs have to breathe against a gauge pressure of gh. You can expand your chest against a pressure only ...
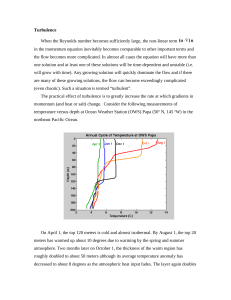
Turbulence When the Reynolds number becomes sufficiently large
... in the momentum equation inevitably becomes comparable to other important terms and the flow becomes more complicated. In almost all cases the equation will have more than one solution and at least one of these solutions will be time-dependent and unstable (i.e. will grow with time). Any growing sol ...
... in the momentum equation inevitably becomes comparable to other important terms and the flow becomes more complicated. In almost all cases the equation will have more than one solution and at least one of these solutions will be time-dependent and unstable (i.e. will grow with time). Any growing sol ...
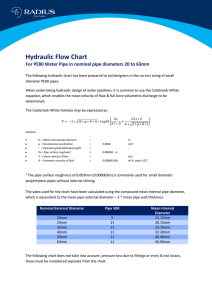
Hydraulic Flow Chart
... The following hydraulic chart has been prepared to aid designers in the correct sizing of small diameter PE80 pipes. When undertaking hydraulic design of water pipelines, it is common to use the Colebrook-White equation, which enables the mean velocity of flow & full bore volumetric discharge to be ...
... The following hydraulic chart has been prepared to aid designers in the correct sizing of small diameter PE80 pipes. When undertaking hydraulic design of water pipelines, it is common to use the Colebrook-White equation, which enables the mean velocity of flow & full bore volumetric discharge to be ...
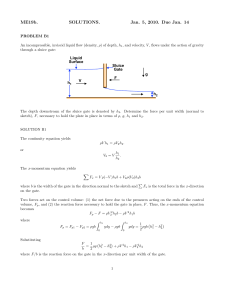
ME19b. SOLUTIONS. Jan. 5, 2010. Due Jan. 14
... The pressure in the cavity is simply given by the vapor pressure, pv , of the water at the operating water temperature (po > pv ). It is to be assumed that the effect of friction, the effect of gravity, the density of the vapor and the amount of water vaporized at the free surface are all negligible ...
... The pressure in the cavity is simply given by the vapor pressure, pv , of the water at the operating water temperature (po > pv ). It is to be assumed that the effect of friction, the effect of gravity, the density of the vapor and the amount of water vaporized at the free surface are all negligible ...
Study of shear thinning and shear thickening in 2D fluids
... slow), the fluid responds by developing a shear stress. The ratio of this shear stress to shear rate yields the viscosity coefficient. If this relationship is linear, so that for zero shear rate, the shear stress is also close to zero, such fluids are called Newtonian fluids. In other words, once th ...
... slow), the fluid responds by developing a shear stress. The ratio of this shear stress to shear rate yields the viscosity coefficient. If this relationship is linear, so that for zero shear rate, the shear stress is also close to zero, such fluids are called Newtonian fluids. In other words, once th ...
Analysis of technological processes and equipment
... to help remove contaminants. Analysis of these processes can be complex because the fluid is composed of multiple phases which are often undergoing complex biochemical reactions. Initial experimental studies are conducted on a laboratory scale before they are scaled up to the larger treatment facili ...
... to help remove contaminants. Analysis of these processes can be complex because the fluid is composed of multiple phases which are often undergoing complex biochemical reactions. Initial experimental studies are conducted on a laboratory scale before they are scaled up to the larger treatment facili ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.