Chapter 4
... increased transmission of diseases due to stagnant warm water and lack of winter kill-off of insect vectors (malaria, dengue fever) and deterioration of fresh water in times of drought. • Significantly higher rainfall may occur across much of the southern US, Cuba, northern Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, s ...
... increased transmission of diseases due to stagnant warm water and lack of winter kill-off of insect vectors (malaria, dengue fever) and deterioration of fresh water in times of drought. • Significantly higher rainfall may occur across much of the southern US, Cuba, northern Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, s ...
Bad Meteorology: The reason clouds form when air cools is because
... evaporate more readily (with, of course, the caveat that evaporation is also influenced by things other than temperature, as described above). ...
... evaporate more readily (with, of course, the caveat that evaporation is also influenced by things other than temperature, as described above). ...
weather words quizzes!
... L is for the flashes of light produced by electrical discharges in thunderstorms O is for the description we use when the sky is completely covered with clouds U is for the direction air goes to create clouds D is for the very tiny droplets of water that sometimes fall from clouds S is for the sheet ...
... L is for the flashes of light produced by electrical discharges in thunderstorms O is for the description we use when the sky is completely covered with clouds U is for the direction air goes to create clouds D is for the very tiny droplets of water that sometimes fall from clouds S is for the sheet ...
Weather Tools and Symbols - Milton 7th Grade Advanced Science
... is less dense which has less pressure) High pressure is caused from cold air sinking (cold air is more dense which causes more pressure) ...
... is less dense which has less pressure) High pressure is caused from cold air sinking (cold air is more dense which causes more pressure) ...
ExamView Pro - Untitled.tst
... 33. the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place 34. Climate refers to weather patterns that have been observed over many years. 35. air temperature, humidity, type and amount of precipitation, air pressure, and the speed and direction of the wind 36. Seasons occur because Earth’s axis is ...
... 33. the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place 34. Climate refers to weather patterns that have been observed over many years. 35. air temperature, humidity, type and amount of precipitation, air pressure, and the speed and direction of the wind 36. Seasons occur because Earth’s axis is ...
Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
... T F 32) Thunderstorms are most likely to occur when the atmosphere is absolutely unstable. T F 33) Clear skies are associated with subsidence or sinking motion. T F 34) The wet adiabatic lapse rate is greater than the dry adiabatic lapse rate. ...
... T F 32) Thunderstorms are most likely to occur when the atmosphere is absolutely unstable. T F 33) Clear skies are associated with subsidence or sinking motion. T F 34) The wet adiabatic lapse rate is greater than the dry adiabatic lapse rate. ...
Layers of the Atmosphere
... o If given a picture of water and sand during the day and during the night you should be able to show the direction of the wind, and explain why the wind is blowing that direction. o If given a key you should be able to give the direction, speed, and coverage shown by a wind barb. Advanced: o Be abl ...
... o If given a picture of water and sand during the day and during the night you should be able to show the direction of the wind, and explain why the wind is blowing that direction. o If given a key you should be able to give the direction, speed, and coverage shown by a wind barb. Advanced: o Be abl ...
Natural Causes for Climate Change
... Energy is input from the sun and is moved from low latitudes to high latitudes through the atmosphere and ocean currents. ...
... Energy is input from the sun and is moved from low latitudes to high latitudes through the atmosphere and ocean currents. ...
L2 Climate Basics 2
... of warm rising air which creates an area of low pressure, and a body of cooling falling air which creates an area of high pressure. 4) Winds move FROM the areas of high pressure TO the areas of low pressure. 5) There are three main types of global atmospheric circulation cells – Hadley, Ferrel and P ...
... of warm rising air which creates an area of low pressure, and a body of cooling falling air which creates an area of high pressure. 4) Winds move FROM the areas of high pressure TO the areas of low pressure. 5) There are three main types of global atmospheric circulation cells – Hadley, Ferrel and P ...
Presentation
... What wavelength ranges are for shortwave and longwave? What are their sources? What is shortwave in? Why are shortwave absorbed not symmetrical with latitude? At what latitude does most heat and mass transfer occur? ...
... What wavelength ranges are for shortwave and longwave? What are their sources? What is shortwave in? Why are shortwave absorbed not symmetrical with latitude? At what latitude does most heat and mass transfer occur? ...
http://www.cabrillo.edu/academics/metgeo/meteorology
... 50. The ultimate cause of the sea breeze is the unequal heating of land and water. 51. A southwest wind blows toward the northeast. 52. The most important force causing the air's motion is due to the earth's rotation. 53. The sea breeze is a simple thermal circulation that does not involve a pressur ...
... 50. The ultimate cause of the sea breeze is the unequal heating of land and water. 51. A southwest wind blows toward the northeast. 52. The most important force causing the air's motion is due to the earth's rotation. 53. The sea breeze is a simple thermal circulation that does not involve a pressur ...
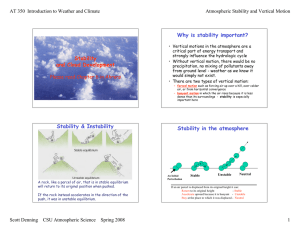
Atmospheric Stability
... less than an unsaturated parcel • If a rising air parcel becomes saturated condensation occurs • Condensation warms the air parcel due to the release of latent heat • So, a rising parcel cools less if it is ...
... less than an unsaturated parcel • If a rising air parcel becomes saturated condensation occurs • Condensation warms the air parcel due to the release of latent heat • So, a rising parcel cools less if it is ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.