Meteorology Chapter 4 Worksheet 2 Name: Circle the letter that
... 12) During the process of adiabatic cooling, the temperature decreases because the air has: a) been compressed. b) lost heat to the colder air at higher altitudes. c) lost some of its water vapor. d) expanded to a larger volume. e) emitted infrared radiation. ...
... 12) During the process of adiabatic cooling, the temperature decreases because the air has: a) been compressed. b) lost heat to the colder air at higher altitudes. c) lost some of its water vapor. d) expanded to a larger volume. e) emitted infrared radiation. ...
Transfer of Thermal Energy worksheet
... Conduction is the transfer of heat energy from one substance to another or within a substance. Have you ever left a metal spoon in a pot of soup being heated on a stove? After a short time the handle of the spoon will become hot. This is due to transfer of heat energy from molecule to molecule or fr ...
... Conduction is the transfer of heat energy from one substance to another or within a substance. Have you ever left a metal spoon in a pot of soup being heated on a stove? After a short time the handle of the spoon will become hot. This is due to transfer of heat energy from molecule to molecule or fr ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 4 – Meteorology Review (CH 22
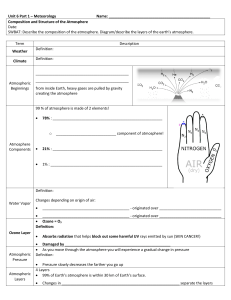
... 6. What are three factors that affect the percentage of water I the atmosphere? 7. Compare an atom of oxygen to an atom of ozone. 8. What purpose does the ozone serve? 9. What are particulates, and how do large and small particulates differ (besides their size!) 10. As altitude increases what happen ...
... 6. What are three factors that affect the percentage of water I the atmosphere? 7. Compare an atom of oxygen to an atom of ozone. 8. What purpose does the ozone serve? 9. What are particulates, and how do large and small particulates differ (besides their size!) 10. As altitude increases what happen ...
Quiz Key Energy Movement
... 1. The type of heat transfer that does not require physical contact or a medium is: A. Conduction. B. Convection. C. Radiation. Rationale: A is incorrect because conduction is the mode of transfer through a material. B is incorrect because convection is the mode of heat transfer through air. C is co ...
... 1. The type of heat transfer that does not require physical contact or a medium is: A. Conduction. B. Convection. C. Radiation. Rationale: A is incorrect because conduction is the mode of transfer through a material. B is incorrect because convection is the mode of heat transfer through air. C is co ...
NSTA Meteorology Reading 8 • Weather`s Central Actor: Water
... ‣ Water absorbs and retains so much thermal energy, that the ocean tends to moderate Earth’s air temperature and climate ‣ Water has a large latent heat = the amount of energy associated with changes of state; results from hydrogen bonding - Water, Precipitation, and Clouds ‣ Condensation nuclei are ...
... ‣ Water absorbs and retains so much thermal energy, that the ocean tends to moderate Earth’s air temperature and climate ‣ Water has a large latent heat = the amount of energy associated with changes of state; results from hydrogen bonding - Water, Precipitation, and Clouds ‣ Condensation nuclei are ...
Meteorology Pre Test #1 On Chapter 1
... 19. Ozone is continually created in our atmosphere by solar radiation. 20. The troposphere is part of the homosphere. 21. The stratosphere is an example of a temperature inversion. 22. The tropopause is found where the air temperature stops decreasing with height. 23. At one time the earth's atmosph ...
... 19. Ozone is continually created in our atmosphere by solar radiation. 20. The troposphere is part of the homosphere. 21. The stratosphere is an example of a temperature inversion. 22. The tropopause is found where the air temperature stops decreasing with height. 23. At one time the earth's atmosph ...
Meteorology Chapter 5 Worksheet 2 Name: Circle the letter that
... b. moist air moving over a cold surface. c. inversions and a warm water surface. d. steep lapse rate and cold surface. e. steep lapse rate and a warm surface. ...
... b. moist air moving over a cold surface. c. inversions and a warm water surface. d. steep lapse rate and cold surface. e. steep lapse rate and a warm surface. ...
Notes
... ⇒ Unsaturated air cools at a constant rate of 10OC for every 1,000 meters of ascent (5.5OF per 1,00 feet). ⇒ On the other hand, descending air comes under increasing pressure and is compressed and heated 10OC for every 1,000 meters of descent. ⇒ This rate of cooling or heating applies only to ...
... ⇒ Unsaturated air cools at a constant rate of 10OC for every 1,000 meters of ascent (5.5OF per 1,00 feet). ⇒ On the other hand, descending air comes under increasing pressure and is compressed and heated 10OC for every 1,000 meters of descent. ⇒ This rate of cooling or heating applies only to ...
Global and Local Winds - Clinton Public Schools
... • Most deserts on the Earth are located here because of the ...
... • Most deserts on the Earth are located here because of the ...
1. What are the two most abundant permanent gasses, and roughly
... 37.On the slope of a valley, why does the wind typically blow downslope during the night? Why might things be different during the day? 38.Explain how the three forms of heat transfer combine to affect air temperature on a sunny day. 39.Why is temperature typically not measured at ground level, but ...
... 37.On the slope of a valley, why does the wind typically blow downslope during the night? Why might things be different during the day? 38.Explain how the three forms of heat transfer combine to affect air temperature on a sunny day. 39.Why is temperature typically not measured at ground level, but ...
JUNIOR CERTIFICATE GEOGRAPHY
... The air above the ground heats up and rises up quickly as it gets lighter As the air rises it also cools quickly and condenses to form clouds and then begins to rain This gives rise to heavy short bursts of rain and then dries up soon after CYCLONIC RAIN – rain from a depression or low pressures sys ...
... The air above the ground heats up and rises up quickly as it gets lighter As the air rises it also cools quickly and condenses to form clouds and then begins to rain This gives rise to heavy short bursts of rain and then dries up soon after CYCLONIC RAIN – rain from a depression or low pressures sys ...
Properties of the atmosphere
... section if you do not have room to write. Draw three circles around the Earth on the next page. The first one has been drawn for you Label the four major layers of the atmosphere by writing the proper name on the diagram below Draw a line and label it with the thickness of the layers with the proper ...
... section if you do not have room to write. Draw three circles around the Earth on the next page. The first one has been drawn for you Label the four major layers of the atmosphere by writing the proper name on the diagram below Draw a line and label it with the thickness of the layers with the proper ...
4 pt 5 pt 1 pt
... This is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun due to geography, such as land masses or bodies of water, elevation, or differences in temperature. ...
... This is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun due to geography, such as land masses or bodies of water, elevation, or differences in temperature. ...
Global and Local Winds
... equator where no winds blow because the warm rising air creates an area of low pressure ...
... equator where no winds blow because the warm rising air creates an area of low pressure ...
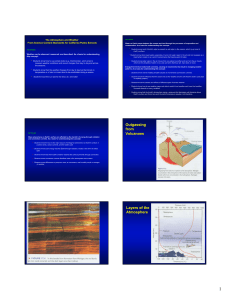
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.