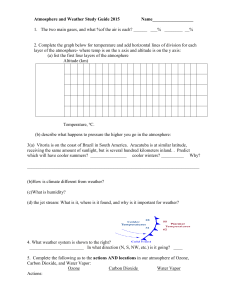
Ch 11/12/13 Earth`s Atmosphere Study Guide
... Where is the ozone layer? __________________________Why is it so important to life on Earth? _______________________________________________________ How does the temperature vary as one moves up the troposphere? _______________ In which layers does molecular heat increase? __________________________ ...
... Where is the ozone layer? __________________________Why is it so important to life on Earth? _______________________________________________________ How does the temperature vary as one moves up the troposphere? _______________ In which layers does molecular heat increase? __________________________ ...
Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
... • Have you ever noticed that the air near the ceiling is warmer than the air near the floor? Or that water in a pool is cooler at the deep end? • Examples: air movement in a home, pot of heating water. • Pick one of these examples and draw the circular pattern in your notes. ...
... • Have you ever noticed that the air near the ceiling is warmer than the air near the floor? Or that water in a pool is cooler at the deep end? • Examples: air movement in a home, pot of heating water. • Pick one of these examples and draw the circular pattern in your notes. ...
Weather - s3.amazonaws.com
... a. shapeless flash over wide area b. is cloud-to-cloud bolt hidden by the clouds c. common in Puget Sound area ...
... a. shapeless flash over wide area b. is cloud-to-cloud bolt hidden by the clouds c. common in Puget Sound area ...
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Latent Heat In addition
... Question: If not the sun, then where does the atmosphere get its energy from? Answer: Most of the atmosphere's energy comes from from the Earth below It works kind of like the following..... ...
... Question: If not the sun, then where does the atmosphere get its energy from? Answer: Most of the atmosphere's energy comes from from the Earth below It works kind of like the following..... ...
Unit 2 Section 5 Vertical Motion in the Atm
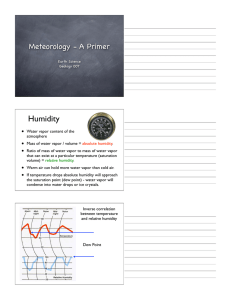
... the amount of water vapor in the air to the maximum amount that air can hold at that temperature 54. When relative humidity reaches 100 percent, the air has reached saturation pressure and cannot absorb any more water vapor. 55. Why do high humidity levels make people feel uncomfortable? because lit ...
... the amount of water vapor in the air to the maximum amount that air can hold at that temperature 54. When relative humidity reaches 100 percent, the air has reached saturation pressure and cannot absorb any more water vapor. 55. Why do high humidity levels make people feel uncomfortable? because lit ...
notes for meteorofe - pams
... Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. ...
... Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. ...
File - Winnipeg Ground School
... b) tropopause, stability, pressure c) atmosphere, stability, moisture d) troposphere, temperature, moisture 6) Air masses which are being cooled from below are characterized by a) strong winds, cumulus cloud, good visibility b) uniform temperature, good visibility c) decreasing humidity, poor visibi ...
... b) tropopause, stability, pressure c) atmosphere, stability, moisture d) troposphere, temperature, moisture 6) Air masses which are being cooled from below are characterized by a) strong winds, cumulus cloud, good visibility b) uniform temperature, good visibility c) decreasing humidity, poor visibi ...
Test Review-Atmosphere Intro
... Test 2: Intro/Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere The following is a list of topics to help guide you in your studies. This is not to be used as your only source of studying!!! Topics on the exam may include but are not limited to the following: 1. ESRT Temperature & Pressure a. Reading both charts, co ...
... Test 2: Intro/Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere The following is a list of topics to help guide you in your studies. This is not to be used as your only source of studying!!! Topics on the exam may include but are not limited to the following: 1. ESRT Temperature & Pressure a. Reading both charts, co ...
Weather Vocabulary Words
... Is formed when cold air mass meets up with a warm air mass. The denser, cooler air pushes the warmer air upwards at a rapid pace. Temperatures will drop When water vapor rises, cools, and changes from a gas to a liquid Large storm clouds that reach high up in the air Large, puffy, white clouds that ...
... Is formed when cold air mass meets up with a warm air mass. The denser, cooler air pushes the warmer air upwards at a rapid pace. Temperatures will drop When water vapor rises, cools, and changes from a gas to a liquid Large storm clouds that reach high up in the air Large, puffy, white clouds that ...
Meteorology
... Wet Adiabatic Lapse Rate If a rising air mass reaches its dew point, water vapor will begin to condense. Condensation releases heat energy, which warms the air mass, slowing down its rate of cooling. Wet Adiabatic Lapse Rate is usually near 4.9 °C/km. If rising air cools more than surrounding air, i ...
... Wet Adiabatic Lapse Rate If a rising air mass reaches its dew point, water vapor will begin to condense. Condensation releases heat energy, which warms the air mass, slowing down its rate of cooling. Wet Adiabatic Lapse Rate is usually near 4.9 °C/km. If rising air cools more than surrounding air, i ...
Chapter 4 Reading Questions and Vocabulary
... The ENSO is a disruption to _________________________________ in which warm water and increased precipitation build up in the region of _________________________ while drought and cold water occur in the region of _______________________________ ...
... The ENSO is a disruption to _________________________________ in which warm water and increased precipitation build up in the region of _________________________ while drought and cold water occur in the region of _______________________________ ...
Understanding Heat Transfers Conduction, Convection and Radiation
... Convection Heat COLD AIR SINKS Where is the freezer compartment put in a fridge? It is put at the top, because cool air sinks, so it cools the food on the way down. ...
... Convection Heat COLD AIR SINKS Where is the freezer compartment put in a fridge? It is put at the top, because cool air sinks, so it cools the food on the way down. ...
iip______________________hplasiip
... 1. Define the following: a) air mass b) maritime air c) continental air 2. What are the three main sources of the air masses of North America? 3. What are the three main factors that determine the weather in an air mass? 4. List the characteristics of a cold air mass and a warm air mass. 5. Define a ...
... 1. Define the following: a) air mass b) maritime air c) continental air 2. What are the three main sources of the air masses of North America? 3. What are the three main factors that determine the weather in an air mass? 4. List the characteristics of a cold air mass and a warm air mass. 5. Define a ...
Air Masses 100
... 1. Energy from sun radiates to the ground 2. The Ground conducts heat to air molecules 3. Heated molecules rise up through convection ...
... 1. Energy from sun radiates to the ground 2. The Ground conducts heat to air molecules 3. Heated molecules rise up through convection ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #3 (Chapters 5 and 6
... 6. The atmosphere is “stable” when the environmental lapse rate is small, that is, when there is a _________________________________________________________________________ between the surface air and the air aloft. Therefore, the atmosphere “stabilizes” when the air aloft _______________________ an ...
... 6. The atmosphere is “stable” when the environmental lapse rate is small, that is, when there is a _________________________________________________________________________ between the surface air and the air aloft. Therefore, the atmosphere “stabilizes” when the air aloft _______________________ an ...
Introduction to Meteorology Homework #3 (Chapters 5 and 6) Due
... 6. The atmosphere is “stable” when the environmental lapse rate is small, that is, when there is a _________________________________________________________________________ between the surface air and the air aloft. Therefore, the atmosphere “stabilizes” when the air aloft _______________________ an ...
... 6. The atmosphere is “stable” when the environmental lapse rate is small, that is, when there is a _________________________________________________________________________ between the surface air and the air aloft. Therefore, the atmosphere “stabilizes” when the air aloft _______________________ an ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.