What causes Winds? - Mona Shores Blogs
... cool air form convection currents. If cool air is present, warm air will rise to great heights and eventually cool. Cool air holds less water vapor than warm air. ...
... cool air form convection currents. If cool air is present, warm air will rise to great heights and eventually cool. Cool air holds less water vapor than warm air. ...
Severe-weather-study-guide
... 8. What should you do when you’re stuck outside in a thunderstorm? ...
... 8. What should you do when you’re stuck outside in a thunderstorm? ...
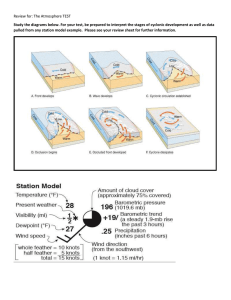
Review for: The Atmosphere TEST Study the diagrams below. For
... A cold, dense air mass displaces a warm air mass and forces the warm air to rise steeply When a warm and cold air mass meet’s what happens? Measures air pressure Measures wind speed Measures relative humidity Uses weather data to project upcoming weather conditions Captures visible and infrared (hea ...
... A cold, dense air mass displaces a warm air mass and forces the warm air to rise steeply When a warm and cold air mass meet’s what happens? Measures air pressure Measures wind speed Measures relative humidity Uses weather data to project upcoming weather conditions Captures visible and infrared (hea ...
“Meteorology”? - U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Resources Page
... • Minute water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere • Formed by rising warm air masses • Water vapor condenses forming water droplets • Numerous types found in three layers ...
... • Minute water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere • Formed by rising warm air masses • Water vapor condenses forming water droplets • Numerous types found in three layers ...
Name
... Troposphere – the lowest layer of the atmosphere. This is where we live & where all weather occurs. This layer contains 85% of the atmosphere’s mass ...
... Troposphere – the lowest layer of the atmosphere. This is where we live & where all weather occurs. This layer contains 85% of the atmosphere’s mass ...
Weather and Water Cycle Study Guide
... 4.climate: pattern of weather in an area over time. 5.current: stream of water that flows like a river in the ocean. 6.meteorology: study of weather. 7.freezing point: the temperature at which water freezes (32 degrees Fahrenheit ). 8.clouds: form when water vapor cools and condensation dust particu ...
... 4.climate: pattern of weather in an area over time. 5.current: stream of water that flows like a river in the ocean. 6.meteorology: study of weather. 7.freezing point: the temperature at which water freezes (32 degrees Fahrenheit ). 8.clouds: form when water vapor cools and condensation dust particu ...
metIstudyguide_S16
... 9. Air that has reached its water vapor capacity is _____________________. 10. Which can hold more water vapor… Warm air or cold air? 11. What is dew point? 12. Walking across hot pavement, warming your feet, is what form of heat transfer? 13. Hand receiving energy from a fire is heat transfer throu ...
... 9. Air that has reached its water vapor capacity is _____________________. 10. Which can hold more water vapor… Warm air or cold air? 11. What is dew point? 12. Walking across hot pavement, warming your feet, is what form of heat transfer? 13. Hand receiving energy from a fire is heat transfer throu ...
Meteorology MentorScienceOlympiad
... C. A seasonal reversal in wind direction and pressure distribution D. A cyclone or typhoon with winds over 100 mph Match the cloud type with the descriptions at left 47. _____Cirrus A. cover large areas and form in layers 48. _____Cumulonimbus B. produces thunderstorms 49. _____Stratus C. have flat ...
... C. A seasonal reversal in wind direction and pressure distribution D. A cyclone or typhoon with winds over 100 mph Match the cloud type with the descriptions at left 47. _____Cirrus A. cover large areas and form in layers 48. _____Cumulonimbus B. produces thunderstorms 49. _____Stratus C. have flat ...
Chapter 16 Teal Weather Jeopardy 2015
... Air Masses that form over the Northern Pacific Ocean are known as ____________. ...
... Air Masses that form over the Northern Pacific Ocean are known as ____________. ...
metIstudyguide F14
... 9. Air that has reached its water vapor capacity is _____________________. 10. Which can hold more water vapor… Warm air or cold air? 11. What is dew point? 12. The hot seat belt against skin is what form of heat transfer? 13. Earth receives energy from sun through which method? 14. Heat flow that c ...
... 9. Air that has reached its water vapor capacity is _____________________. 10. Which can hold more water vapor… Warm air or cold air? 11. What is dew point? 12. The hot seat belt against skin is what form of heat transfer? 13. Earth receives energy from sun through which method? 14. Heat flow that c ...
Weather Patterns and Climate
... Land and Sea Breeze • land and sea breeze animation • Unequal heating of air over land and water results in breezes near shorelines. • While the land is warm during the day, air above it rises, and a cool breeze blows in from the sea. ...
... Land and Sea Breeze • land and sea breeze animation • Unequal heating of air over land and water results in breezes near shorelines. • While the land is warm during the day, air above it rises, and a cool breeze blows in from the sea. ...
weather - Bibb County Schools
... 1. WEATHER – the condition of the atmosphere, including temperature, precipitation, and cloud cover, at a particular time and place. 2. METEOROLOGIST – a scientist who studies the weather. 3. PRECIPITATION – the movement of water, in solid or liquid form, from the atmosphere back to the surface of t ...
... 1. WEATHER – the condition of the atmosphere, including temperature, precipitation, and cloud cover, at a particular time and place. 2. METEOROLOGIST – a scientist who studies the weather. 3. PRECIPITATION – the movement of water, in solid or liquid form, from the atmosphere back to the surface of t ...
The atmosphere! - Studentportalen
... middle. The mesosphere extends from about 50#km to 80 or 85#km. Temperature decreasing with height." ...
... middle. The mesosphere extends from about 50#km to 80 or 85#km. Temperature decreasing with height." ...
what to know about meteorology list
... 11. The closer the air temperature is to the dew point, the higher the relative humidity. 12. Know this Process: Air is warmed, becomes less dense due to expansion; is forced upwards; expands and cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds ...
... 11. The closer the air temperature is to the dew point, the higher the relative humidity. 12. Know this Process: Air is warmed, becomes less dense due to expansion; is forced upwards; expands and cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds ...
Blog 2017_ Week 4 Jan 30
... of Earth’s atmospheric layers (including the ozone layer) and greenhouse gases. (Clarification statement: Earth’s atmospheric layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere.) SE64b.Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about how the sun, land, and water affect cli ...
... of Earth’s atmospheric layers (including the ozone layer) and greenhouse gases. (Clarification statement: Earth’s atmospheric layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere.) SE64b.Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about how the sun, land, and water affect cli ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.