Characteristics of the Atmosphere
... equals that consumed by all processes. The amount of oxygen in the air is in a state of balance and has not changed significantly over hundreds or thousands of years. ...
... equals that consumed by all processes. The amount of oxygen in the air is in a state of balance and has not changed significantly over hundreds or thousands of years. ...
Topic 5 Temperature, Pressure, and Moisture
... • The fact that supercells (thunderstorms) occur where warm, moist air meets cold, dry air suggests the source of energy for both t-storm and tornado: • latent heat is in the warm, moist air. Latent heat is heat you can't detect with ...
... • The fact that supercells (thunderstorms) occur where warm, moist air meets cold, dry air suggests the source of energy for both t-storm and tornado: • latent heat is in the warm, moist air. Latent heat is heat you can't detect with ...
images file
... • As air rises the temperature of its surrounding air falls. • Temperature of the air parcel must remain warmer than the surrounding air to continue rising. • Temperature of the surrounding air as a function of altitude is known as the environmental lapse rate (ELR). ...
... • As air rises the temperature of its surrounding air falls. • Temperature of the air parcel must remain warmer than the surrounding air to continue rising. • Temperature of the surrounding air as a function of altitude is known as the environmental lapse rate (ELR). ...
Air and Weather - Beaver Dam Elementary
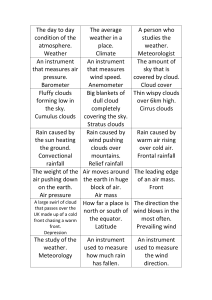
... Air Temperature How hot or cold air is Air Pressure Force of air pushing on an area Precipitation ANY form of water that falls from clouds ...
... Air Temperature How hot or cold air is Air Pressure Force of air pushing on an area Precipitation ANY form of water that falls from clouds ...
dry adiabatic lapse rate
... A stack 100 m tall emits a plume at 20oC. The prevailing lapse rates are shown in the figure below. How high will the plume rise (if we assume dry adiabatic conditions)? The prevailing lapse rate is subadiabatic to 200 m and there is an inversion above 200 m. The smoke at 20oC finds itself surrounde ...
... A stack 100 m tall emits a plume at 20oC. The prevailing lapse rates are shown in the figure below. How high will the plume rise (if we assume dry adiabatic conditions)? The prevailing lapse rate is subadiabatic to 200 m and there is an inversion above 200 m. The smoke at 20oC finds itself surrounde ...
climate pared down
... When air moving inland from the ocean that contains a large amount of water vapor meets the windward side of a mountain range (the side facing the wind), it rises and begins to experience adiabatic cooling. Because water vapor condenses as air cools, clouds form and ...
... When air moving inland from the ocean that contains a large amount of water vapor meets the windward side of a mountain range (the side facing the wind), it rises and begins to experience adiabatic cooling. Because water vapor condenses as air cools, clouds form and ...
5-6 Meteorology Review 2
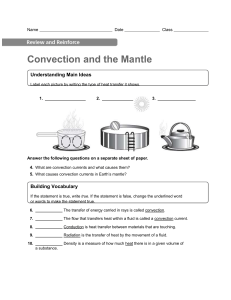
... 6. Why do parts of the Earth receive more direct sunlight than other parts? Which areas of the planet receive the least amount of direct sunlight? What does it mean to call carbon dioxide a greenhouse gas? How does conduction differ from convection? ...
... 6. Why do parts of the Earth receive more direct sunlight than other parts? Which areas of the planet receive the least amount of direct sunlight? What does it mean to call carbon dioxide a greenhouse gas? How does conduction differ from convection? ...
psci 131 winter 2014 practice exam – meteorology
... Solid particles small enough to remain suspended in the air. 4. Ozone is an effective absorber of heat, and helps keep the Earth’s surface warm. TRUE or FALSE 5. The most important factor in determining the temperature at a given location is a. Cloud cover b. The angle at which solar rays are striki ...
... Solid particles small enough to remain suspended in the air. 4. Ozone is an effective absorber of heat, and helps keep the Earth’s surface warm. TRUE or FALSE 5. The most important factor in determining the temperature at a given location is a. Cloud cover b. The angle at which solar rays are striki ...
Meteorology_Practice_Test
... 1. A ______ _______ is defined as the transition zone where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass. 2. A ______ ______ is defined as the transition zone where a warm air mass is replacing a cold air mass. 3. ____________ is the evaporation of water from plants into the atmosphere. 4. ______ ...
... 1. A ______ _______ is defined as the transition zone where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass. 2. A ______ ______ is defined as the transition zone where a warm air mass is replacing a cold air mass. 3. ____________ is the evaporation of water from plants into the atmosphere. 4. ______ ...
WPF-Weather101
... • At night, the land cools off faster than the ocean due to differences in their heat capacity." • The pressure over the water will become lower than that of the land, setting up a land-breeze. " ...
... • At night, the land cools off faster than the ocean due to differences in their heat capacity." • The pressure over the water will become lower than that of the land, setting up a land-breeze. " ...
Solar - Weather
... Land heats up faster than water (= the ocean). – The air over the land will also heat quickly. – Warm air rises, starting a convection current. – This brings moist ocean air inland. • Ocean air holds a lot of water vapor. • Warm air can also hold more water vapor. – When air cools, it may no longer ...
... Land heats up faster than water (= the ocean). – The air over the land will also heat quickly. – Warm air rises, starting a convection current. – This brings moist ocean air inland. • Ocean air holds a lot of water vapor. • Warm air can also hold more water vapor. – When air cools, it may no longer ...
Wind - Canvas
... The sun warms up the land and the sea. The temperature of the land increases faster than the temperature of the water Air over the land becomes warmer than air over the sea. The warm air over the land becomes less dense and the warm air rises The cooler, more dense air over the ocean moves tow ...
... The sun warms up the land and the sea. The temperature of the land increases faster than the temperature of the water Air over the land becomes warmer than air over the sea. The warm air over the land becomes less dense and the warm air rises The cooler, more dense air over the ocean moves tow ...
1AER200-MET1
... Humidity and Dew point • Warm air can hold more moisture. • The water vapor a volume of air can hold is governed by its temperature. • Air is said to be saturated when it contains the maximum amount of water it can hold at that temperature. • Dew point - the temperature to which unsaturated air mus ...
... Humidity and Dew point • Warm air can hold more moisture. • The water vapor a volume of air can hold is governed by its temperature. • Air is said to be saturated when it contains the maximum amount of water it can hold at that temperature. • Dew point - the temperature to which unsaturated air mus ...
AVSC 1010 - optical cloud studies
... and lacy. They are high altitude clouds CUMULUS CLOUDS PG. 409:piled up lower altitude clouds that look “bumpy.” CUMULONIMBUS CLOUDS PG. 409: FOG PG. 415: a large mass of water vapor condensed to fine particles, at or just above the earth’s surface. ...
... and lacy. They are high altitude clouds CUMULUS CLOUDS PG. 409:piled up lower altitude clouds that look “bumpy.” CUMULONIMBUS CLOUDS PG. 409: FOG PG. 415: a large mass of water vapor condensed to fine particles, at or just above the earth’s surface. ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.