* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
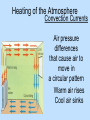
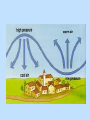
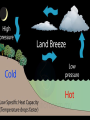
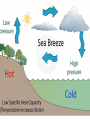
Meteorology Atmospheric Temperature There are 3 common ways that we can measure the temperature in our atmosphere 1-Fahrenheit 2-Celsius Page 13 ESRT 3-Kelvin Isotherms Lines of equal temperature on a chart/map (EYEBALL THE DATA) Heating of the Atmosphere Convection Currents Air pressure differences that cause air to move in a circular pattern Warm air rises Cool air sinks Heating of Air Air warms as it is compressed So, as air descends, the air compressed and it warms Compression Cooling of Air EXPANDING Air cools as it expands So as air rises, it expands and cools Atmospheric Pressure The pressure due to the weight of the overlying atmosphere pushing down on any given area Also called, barometric pressure, and air pressure Wind • Horizontal movement of air parallel to Earth’s surface Wind Speed • Winds are caused by differences in air pressure Wind Direction Wind moves from areas of HIGH pressure to areas of LOW pressure Coriolis Force Coriolis force (caused my Earth’s rotation) effects the direction of movement Pressure Gradient • Pressure Gradient = change in pressure change in distance D D = 100 Meters Pressure Gradient • The closer the lines, the faster the gradient • The farther the lines, the slower the gradient