* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aula Teórica 17
Wind-turbine aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hemodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Flow measurement wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Lift (force) wikipedia , lookup
Boundary layer wikipedia , lookup
Compressible flow wikipedia , lookup
Hydraulic machinery wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Flow conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Reynolds number wikipedia , lookup
Coandă effect wikipedia , lookup
Aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
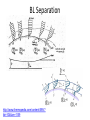
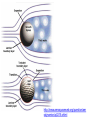
Aula Teórica 24 Introdução à Camada Limite. Potential flow • No Friction; flow in front of the object is symmetric of the flow in the back and there is no pressure resistance, i.e. there is no drag. • If the flow did not follow the surface of the object, the velocity would not decrease and consequently the pressure could not increase. • This is what happens when BL separation occurs. BL Separation http://www.thermopedia.com/content/595/? tid=104&sn=1159 Boundary Layer Separation • The concavity of the velocity profile depends on the sign of the pressure gradient: is negative when the pressure decays and positive otherwise. Favourable pressure gradient • There is no force that can invert the flow, i.e. there is no separation of the boundary layer. • Acceleration is the result of the pressure gradient and of the divergence od the diffusive flux (negative) Null pressure gradient Positive pressure gradient Shear stress is maximum at the inflexion point, decreasing towards the wall. Faster fluid drags slower fluid. Adverse pressure gradient • In case of the adverse pressure gradient pressure force decreases the velocity and can invert the sense of the flow. • For layers close to the wall the forward shear stress (above) is larger that the backward shear (below) and thus friction contribute to keep the forward movement, i.e. reduces the probability of flow separation. Turbulent BL separate latter than laminar BL BL separate latter in fusiform (aerodynamic) geometries. Is this profile ok? http://www.aerospaceweb.org/question/aer odynamics/q0215.shtml Cd for circular Cylinders Shape and friction resitance Flow around a cylinder for different values of Re aerofoils http://www.comsol.com/showroom/animations/963/ • Sebenta de Mecânica dos Fluidos