Chapter 3 Water and Atmosphere
... the aneroid barometer under high pressure and which shows it under low pressure? ...
... the aneroid barometer under high pressure and which shows it under low pressure? ...
Powerpoint
... • Troposphere: From earth’s surface to where the air stops becoming colder with height; up to 11 km from earth’s surface; controls all the weather; the layer is well mixed by ascending/descending air masses ...
... • Troposphere: From earth’s surface to where the air stops becoming colder with height; up to 11 km from earth’s surface; controls all the weather; the layer is well mixed by ascending/descending air masses ...
Weather Unit Notes - Lindbergh School District
... Evaporation: Water turns from liquid to gas. Condensation: Water turns from gas to liquid Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. Sling ...
... Evaporation: Water turns from liquid to gas. Condensation: Water turns from gas to liquid Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. Sling ...
1aIntro to Weather
... The Sun is the source of nearly all the energy that drives Earth’s weather (and climate, even though the amount of the Sun’s radiation intercepted by Earth is very small) The surface of the Earth is not heated equally; this drives ocean currents and creates winds that attempt to redistribute heat fr ...
... The Sun is the source of nearly all the energy that drives Earth’s weather (and climate, even though the amount of the Sun’s radiation intercepted by Earth is very small) The surface of the Earth is not heated equally; this drives ocean currents and creates winds that attempt to redistribute heat fr ...
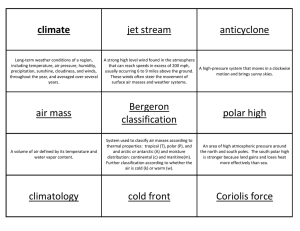
Climate Cards Activity
... System used to classify air masses according to thermal properties: tropical (T), polar (P), and and arctic or antarctic (A) and moisture distribution: continental (c) and maritime(m). Further classification according to whether the air is cold (k) or warm (w). ...
... System used to classify air masses according to thermal properties: tropical (T), polar (P), and and arctic or antarctic (A) and moisture distribution: continental (c) and maritime(m). Further classification according to whether the air is cold (k) or warm (w). ...
1/12/2012 Chap. 1 - UA Atmospheric Sciences
... from satellites is an important technological development in meteorology. Other important developments include computers, internet, and Doppler radar. visible band ...
... from satellites is an important technological development in meteorology. Other important developments include computers, internet, and Doppler radar. visible band ...
8-Energy Transfer within the Climate System
... permanent bands of high and low pressure parallel to the equator allowing energy to be transported through the atmosphere as it moves towards the North and South Poles. ...
... permanent bands of high and low pressure parallel to the equator allowing energy to be transported through the atmosphere as it moves towards the North and South Poles. ...
11.8 NOTES What causes local winds?
... Winds are produced by temperature differences caused by the unequal heating of Earth’s surface. Local winds are small-scale winds produced by local changes in air pressure. A breeze coming from the sea toward land is called a sea breeze. A breeze going from the land to the sea is a land breeze. Land ...
... Winds are produced by temperature differences caused by the unequal heating of Earth’s surface. Local winds are small-scale winds produced by local changes in air pressure. A breeze coming from the sea toward land is called a sea breeze. A breeze going from the land to the sea is a land breeze. Land ...
Weather, Climate, and Biomes
... Lightening is electricity that results from charges when water vapor molecules collide with each other Lightening bolts are hot! (30,000-50,000°F) ...
... Lightening is electricity that results from charges when water vapor molecules collide with each other Lightening bolts are hot! (30,000-50,000°F) ...
Weather Unit 2
... tropics, a band around the equator from 23.5° N (the Tropic of Cancer) to 23.5° S (the Tropic of Capricorn) solar radiation is most intense The warmth leads to a lot of evaporation, and as warm, moist air rises, it cools, the water condenses, and the water falls back to the earth as rain. Thus ...
... tropics, a band around the equator from 23.5° N (the Tropic of Cancer) to 23.5° S (the Tropic of Capricorn) solar radiation is most intense The warmth leads to a lot of evaporation, and as warm, moist air rises, it cools, the water condenses, and the water falls back to the earth as rain. Thus ...
8th Grade Fourth Six Weeks Vocabulary
... A large, tropical weather system consisting of an extreme low pressure air mass with heavy rains and wind speeds of at least 119km/h Energy of motion A directional movement of ocean water; surface currents result from steady winds over the ocean surface; deep currents result from density variations ...
... A large, tropical weather system consisting of an extreme low pressure air mass with heavy rains and wind speeds of at least 119km/h Energy of motion A directional movement of ocean water; surface currents result from steady winds over the ocean surface; deep currents result from density variations ...
Wind
... speed winds that blow in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere •Separates warm air from cold air ...
... speed winds that blow in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere •Separates warm air from cold air ...
The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature
... best described as sheets or layers that cover much or all of the sky ...
... best described as sheets or layers that cover much or all of the sky ...
LACEMOPS - Texas State University
... The air that descends from the mountain warms up and vapor pressure increase which results the relatively humid to lower and air becomes drier. thus, mountain barrier can affect precipitation/winds and these factors affect the climate. ...
... The air that descends from the mountain warms up and vapor pressure increase which results the relatively humid to lower and air becomes drier. thus, mountain barrier can affect precipitation/winds and these factors affect the climate. ...
Unit 6: Weather & Climate
... If your hair stands on end, or your skin tingles, drop to the ground but try to keep as little contact with the ground as possible ...
... If your hair stands on end, or your skin tingles, drop to the ground but try to keep as little contact with the ground as possible ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.