2 Quarter Review Questions 1. The curved paths of global winds
... 4. What is the process that increases the salinity of the ocean water? p. 128 5. A local rise in the sea level near the shore caused by hurricane winds is a ____________ __________________. p.203 6. Deep currents are more or less dense than surface currents? ______________ Deep currents are warmer o ...
... 4. What is the process that increases the salinity of the ocean water? p. 128 5. A local rise in the sea level near the shore caused by hurricane winds is a ____________ __________________. p.203 6. Deep currents are more or less dense than surface currents? ______________ Deep currents are warmer o ...
Meteorology 3/2/2016 Which gas comprises a maximum of 4% of the
... 48) Form around mature low pressure areas, with one air mass overtaking another 49) Usually devolves into a shear line from two weak fronts ...
... 48) Form around mature low pressure areas, with one air mass overtaking another 49) Usually devolves into a shear line from two weak fronts ...
Unit Test: Atmospheric Forces
... 33. List the types of fronts and the weather associated with each. 34. What affects the angle at which the sun’s rays hit the Earth? 35. What weather effect results when a moving air mass hits a mountain, rises, cools, and loses most of its moisture through precipitation? 36. What are the two major ...
... 33. List the types of fronts and the weather associated with each. 34. What affects the angle at which the sun’s rays hit the Earth? 35. What weather effect results when a moving air mass hits a mountain, rises, cools, and loses most of its moisture through precipitation? 36. What are the two major ...
Quiz 1 Study List
... A major source of oxygen in Earths atmosphere comes from plants. Three physical states of water in the atmosphere – solid, liquid and gas/water vapor. Be prepared to give examples. The atmosphere/air also contains small particles of dust, volcanic ash, sea salt and dirt. Matter: anything tha ...
... A major source of oxygen in Earths atmosphere comes from plants. Three physical states of water in the atmosphere – solid, liquid and gas/water vapor. Be prepared to give examples. The atmosphere/air also contains small particles of dust, volcanic ash, sea salt and dirt. Matter: anything tha ...
Regents Earth Science
... 2. Air rising in convection currents gets cooler, making it colder at higher elevations. B. Sometimes, the surface air is colder than the air higher up. This is called a temperature inversion. 1. Occur on clear, dry nights 2. Chimney smoke can be seen hanging near the ground. C. Temperature range = ...
... 2. Air rising in convection currents gets cooler, making it colder at higher elevations. B. Sometimes, the surface air is colder than the air higher up. This is called a temperature inversion. 1. Occur on clear, dry nights 2. Chimney smoke can be seen hanging near the ground. C. Temperature range = ...
Heat Transfer and Winds
... are caused by differences in air pressure. As air becomes less dense when it is heated, its air pressure decreases. Cool, dense air with a higher pressure forces the warm air to rise. ...
... are caused by differences in air pressure. As air becomes less dense when it is heated, its air pressure decreases. Cool, dense air with a higher pressure forces the warm air to rise. ...
Section 6.2
... the direction the front is moving. • A warm front is shown using a line marked with semicircles. ...
... the direction the front is moving. • A warm front is shown using a line marked with semicircles. ...
6.2 Cloud formation
... the direction the front is moving. • A warm front is shown using a line marked with semicircles. ...
... the direction the front is moving. • A warm front is shown using a line marked with semicircles. ...
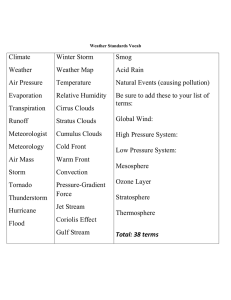
Weather Vocabulary
... Air Mass: a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height. Cold Front: forms when cold air moves under warm air which is less dense and pushes air up (produces thunderstorms heavy rain or snow). Convection Current: The circular movement of substances d ...
... Air Mass: a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height. Cold Front: forms when cold air moves under warm air which is less dense and pushes air up (produces thunderstorms heavy rain or snow). Convection Current: The circular movement of substances d ...
1. Explain how thunderstorms form Humid air rises rapidly and forms
... Weather Storms, Instruments and Ocean Currents Study Guide ...
... Weather Storms, Instruments and Ocean Currents Study Guide ...
Meteorology Test 7
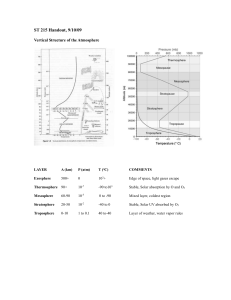
... 2. The upper limit of the troposphere is the highest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 3. The upper limit of the troposphere is the lowest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 4. Most weather on earth occurs in the troposphere, with only a f ...
... 2. The upper limit of the troposphere is the highest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 3. The upper limit of the troposphere is the lowest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 4. Most weather on earth occurs in the troposphere, with only a f ...
Meteorology Test 7
... 2. The upper limit of the troposphere is the highest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 3. The upper limit of the troposphere is the lowest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 4. Most weather on earth occurs in the troposphere, with only a f ...
... 2. The upper limit of the troposphere is the highest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 3. The upper limit of the troposphere is the lowest in (warm, cold) regions. It reaches a height of about ___ miles. 4. Most weather on earth occurs in the troposphere, with only a f ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.