* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download METEOROLOGY PART II REVIEW S13
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Thunderstorm wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
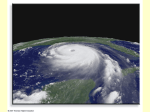
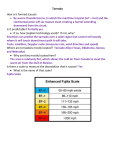
Name: __________________________________ Earth-Environmental Review METEOROLOGY PART II - Chapters 19, 20 Vocabulary Air pressure Barometer Cyclone Anticyclone Divergence Convergence Coriolis Effect Trade Winds Prevailing Westerlies Polar Easterlies Anemometer Jet stream El Nino La Nina Air mass cP, cT, mP, mT Front Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Mid-Latitude Cyclone Thunderstorm Cumulus Stage Mature Stage Dissipating Stage Tornado Mesocyclone Updraft Hurricane Storm Surge Eye Wall 1. What is the Coriolis Effect? What would happen to the Coriolis Effect if the earth did not spin on its axis? 2. Label each wind cell showing wind direction and names of each zone we discussed in class. 3. At what latitude are rainforests found mostly?______ At what latitude are Deserts found Mostly?_____ How does convection impact these locations? 4. Describe the jet stream and how it can affect the formation of hurricanes. 5. What devices do scientists use to measure the following: - Wind Speed: ________________________ - Humidity: __________________________ - Temperature: _______________________ 6. FRONTS Information (weather, temperature etc) Drawing COLD WARM STATIONARY OCCLUDED 7. PRESSURE CENTERS Characteristics/ Air Pressure (circulation, air flow etc.) Weather LOW HIGH 8. What must happen in the air above for a divergence at the surface to be maintained? What type of pressure center accompanies surface divergence? 9. What do isobars represent? What would the weather conditions be if the isobars are close together? 10. Describe the weather that usually accompanies… -- a drop in barometric pressure: -- a rise in barometric pressure: 11. Name an area on Earth that you’d expect to be dominated by… -- low-pressure systems: -- high-pressure systems: 12. How do clouds impact the Earth’s temperature during the day and night? 13. How does proximity to the ocean impact the Earth’s temperature fluctuations? 14. What causes thunderstorms to dissipate and die out? 15. What causes a mesocyclone to form? Do all mesocyclones produce tornadoes? 16. What is the energy source for a hurricane? What 2 factors cause a hurricane to lose power over land? 17. Why don’t hurricanes form often on the West coast of Spain? Include the word currents in your answer. 18. Explain why hurricanes have lower wind speeds but they often cause more damage than tornadoes. 19. Compare and contrast the four types of air masses. Continental Polar Maritime Polar Maritime Tropical Continental Tropical 20. How can continental polar air be responsible for lake-effect snowstorms in the Great Lakes Region? (Look at figure 3 on page 560) 21. What kinds of air masses influence the weather patterns over Florida? (Look at figure 3 on page 560)