ABO BLOOD GROUPS
... red blood cells, it will react with the antibody causing clumping or agglutination of the red blood cells ...
... red blood cells, it will react with the antibody causing clumping or agglutination of the red blood cells ...
2 Antibodies - WordPress.com
... Each antibody has a different shaped variable region (due to different amino acid sequences) that is complementary to one specific antigen. ...
... Each antibody has a different shaped variable region (due to different amino acid sequences) that is complementary to one specific antigen. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... d) nucleic acid II. State whether the following are True or False; state reason 6. CD 45 is a signal transduction molecule found on B lymphocytes. 7. Dendritic cell is not an example of professional antigen presenting cell. 8. Apoptosis is a physiological phenomena rather than a pathological one. 9. ...
... d) nucleic acid II. State whether the following are True or False; state reason 6. CD 45 is a signal transduction molecule found on B lymphocytes. 7. Dendritic cell is not an example of professional antigen presenting cell. 8. Apoptosis is a physiological phenomena rather than a pathological one. 9. ...
the original file
... 1. What is the evolutionary purpose of having both an innate and adaptive immune system that function as they do in humans? 2. Name 3 different types of barriers (mechanical, chemical, and microbial) that protect us from pathogens and list the key features for each category. 3. A dendritic cell phag ...
... 1. What is the evolutionary purpose of having both an innate and adaptive immune system that function as they do in humans? 2. Name 3 different types of barriers (mechanical, chemical, and microbial) that protect us from pathogens and list the key features for each category. 3. A dendritic cell phag ...
Crystal Structures of Shark Ig New Antigen Receptor Variable
... antibodies, including the unique IgNAR (Ig new antigen receptor) isotype. IgNARs are heavy chain homodimers, there is no associated light chain and binding affinity mainly resides in two complementarity determining regions. Given that sharks also possess heavylight chain antibodies, the question has ...
... antibodies, including the unique IgNAR (Ig new antigen receptor) isotype. IgNARs are heavy chain homodimers, there is no associated light chain and binding affinity mainly resides in two complementarity determining regions. Given that sharks also possess heavylight chain antibodies, the question has ...
Blank Jeopardy
... Name one antigen that is part of the C4 molecule of complement, and therefore not an intrinsic part of the RBC membrane. (An example of an HTLA antibody) ...
... Name one antigen that is part of the C4 molecule of complement, and therefore not an intrinsic part of the RBC membrane. (An example of an HTLA antibody) ...
SG9 Immune Response
... Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Differentiate between immunity and nonspecific resistance. Contrast the four types of acquired immunity. Define antigen. Explain the function of antibodies and describe their structural and chemical characteristics. Name the function of B cells. De ...
... Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Differentiate between immunity and nonspecific resistance. Contrast the four types of acquired immunity. Define antigen. Explain the function of antibodies and describe their structural and chemical characteristics. Name the function of B cells. De ...
Antigens and Antibodies, Cell Receptors
... and normal cells cytotoxic T lymphocytes may be able to destroy tumor cells ...
... and normal cells cytotoxic T lymphocytes may be able to destroy tumor cells ...
lecture-4-radioimmunassay
... has revolutionized research and clinical practice in many areas, e.g., – blood banking – diagnosis of allergies – endocrinology ...
... has revolutionized research and clinical practice in many areas, e.g., – blood banking – diagnosis of allergies – endocrinology ...
Adaptive or acquired immune system
... 3. Protective chemicals – acid pH of stomach, lipids on skin surface 4. Enzymes – lysozyme in saliva, intestinal secretions; digests cell walls of bacteria 5. Alternate complement pathway – cascade of serum proteins that are activated by bacterial cell wall components 2. Adaptive or acquired immune ...
... 3. Protective chemicals – acid pH of stomach, lipids on skin surface 4. Enzymes – lysozyme in saliva, intestinal secretions; digests cell walls of bacteria 5. Alternate complement pathway – cascade of serum proteins that are activated by bacterial cell wall components 2. Adaptive or acquired immune ...
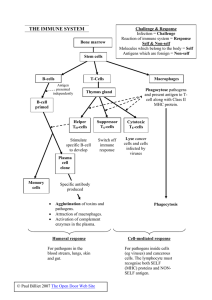
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... Self & Non-self Molecules which belong to the body = Self Antigens which are foreign = Non-self ...
... Self & Non-self Molecules which belong to the body = Self Antigens which are foreign = Non-self ...
Immunogens and Antigens
... carrier. • Merck makes similar vaccine of H. influenza b coupled to outer membrane protein complex of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B. • In each case, the hapten is rendered T-dependent. ...
... carrier. • Merck makes similar vaccine of H. influenza b coupled to outer membrane protein complex of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B. • In each case, the hapten is rendered T-dependent. ...
Glossary of Terms
... parasites, pollen and foreign cells. The term antigen may refer to the whole complex, or to a piece of the complex. T-cells generally see pieces of the antigen while B-cells can either bind to the whole antigen or to a piece of the antigen. Epitope:The small area on the antigen that the B-cell or T- ...
... parasites, pollen and foreign cells. The term antigen may refer to the whole complex, or to a piece of the complex. T-cells generally see pieces of the antigen while B-cells can either bind to the whole antigen or to a piece of the antigen. Epitope:The small area on the antigen that the B-cell or T- ...
Immunological Memory
... 5. How long is the latent period for this infection? 6. Explain this delay in production of antibodies. 7. The person was infected with the same antigen at 4 weeks. Use an arrow to mark on the graph the time of the second infection. 8. The person does not suffer any symptoms from the second infectio ...
... 5. How long is the latent period for this infection? 6. Explain this delay in production of antibodies. 7. The person was infected with the same antigen at 4 weeks. Use an arrow to mark on the graph the time of the second infection. 8. The person does not suffer any symptoms from the second infectio ...
immunotherapeutic targeting of aml with a novel cd123 car
... cytotoxic potential of T cells. CARs are made up of an antigen recognition domain derived from a monoclonal antibody, linked through hinge and transmembrane domains to a costimulatory domain and a CD3ζ intracellular signaling domain. The result is a high-specificity receptor targeted against a speci ...
... cytotoxic potential of T cells. CARs are made up of an antigen recognition domain derived from a monoclonal antibody, linked through hinge and transmembrane domains to a costimulatory domain and a CD3ζ intracellular signaling domain. The result is a high-specificity receptor targeted against a speci ...
A comprehensive platform for T cell Stimulation based on
... APC’s present antigen and create a stimulatory or inhibitory microenvironment for T cell stimulation Virus or Bacteria Tumor Cells Antigen Processing DC ...
... APC’s present antigen and create a stimulatory or inhibitory microenvironment for T cell stimulation Virus or Bacteria Tumor Cells Antigen Processing DC ...
Biology 4 Matching Quiz Chapter 19 Match the following terms on
... Match the following terms on the left to their descriptions on the right. 1. _______ hemoglobin ...
... Match the following terms on the left to their descriptions on the right. 1. _______ hemoglobin ...
Protection against Disease
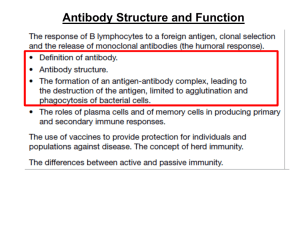
... The interlocking of and antibody and antigen could render a toxic antigen harmless if its active region was blocked by an antibody molecule Phagocytes can more easily track down and ingest pathogens if they are immobilised in an AAC The AAC also stimulates the activation of a number of plasma ...
... The interlocking of and antibody and antigen could render a toxic antigen harmless if its active region was blocked by an antibody molecule Phagocytes can more easily track down and ingest pathogens if they are immobilised in an AAC The AAC also stimulates the activation of a number of plasma ...
Slide 1
... – Very rare (0%) in Caucasians and Asians – 68% in Africans • Mutation in the promoter region of FYB (–33 T>C), which disrupts a binding site for the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 and results in the loss of Fy expression on RBCs. • Because the erythroid promoter controls expression only in e ...
... – Very rare (0%) in Caucasians and Asians – 68% in Africans • Mutation in the promoter region of FYB (–33 T>C), which disrupts a binding site for the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 and results in the loss of Fy expression on RBCs. • Because the erythroid promoter controls expression only in e ...
Chapter 8
... Naive T lymphocytes home to secondary lymphoid organs, where they may encounter antigens presented by mature dendritic cells on class I or class II MHC molecules and thus become activated ...
... Naive T lymphocytes home to secondary lymphoid organs, where they may encounter antigens presented by mature dendritic cells on class I or class II MHC molecules and thus become activated ...
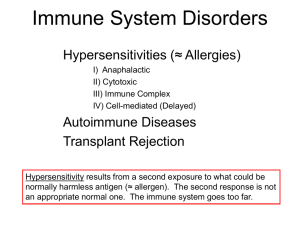
Immune System Disorders (Hypersensitivities ≈ Allergies)
... • Cell malfunction due to antibody binding (Grave’s Disease; thyroid gland). • Immune complex forms (rheumatoid arthritis; joints). • Cell-mediated destruction of specific cell types (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; insulin-secreting cells of pancreas). • Some individuals are genetically predis ...
... • Cell malfunction due to antibody binding (Grave’s Disease; thyroid gland). • Immune complex forms (rheumatoid arthritis; joints). • Cell-mediated destruction of specific cell types (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; insulin-secreting cells of pancreas). • Some individuals are genetically predis ...
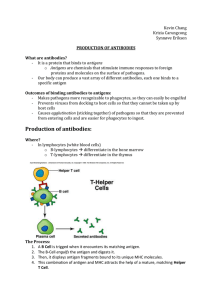
BLOCK F – Krizia,Kevin,Synnove – Production of Antibodies
... matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound antibody molecule on its surface that serves as a receptor for recognizing a specific antigen. When antigen binds to this receptor, the B cell is stimula ...
... matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound antibody molecule on its surface that serves as a receptor for recognizing a specific antigen. When antigen binds to this receptor, the B cell is stimula ...
antibody antigen interaction
... In general particulate antigens are more immunogenic than soluble ones. 5. Antigen Specificity Antigen Specificity depends on the specific actives sites on the antigenic molecules ...
... In general particulate antigens are more immunogenic than soluble ones. 5. Antigen Specificity Antigen Specificity depends on the specific actives sites on the antigenic molecules ...