Notes on Worms ch. 14, 16
... Digestive System: Includes a mouth, pharynx, and an intestine GVC- Gastrovascular cavity present Mainly carnivorous – feed on small crustaceons, nematodes, rotifers, and insects Flatworms have a system called: protonephridia/ can be used for osmoregulation or excretion System is mainly osmoregulato ...
... Digestive System: Includes a mouth, pharynx, and an intestine GVC- Gastrovascular cavity present Mainly carnivorous – feed on small crustaceons, nematodes, rotifers, and insects Flatworms have a system called: protonephridia/ can be used for osmoregulation or excretion System is mainly osmoregulato ...
Terminology
... – Process of getting a person back to his or her normal level of function following an injury or illness ...
... – Process of getting a person back to his or her normal level of function following an injury or illness ...
Dissection Guide to the Rat
... were made down the center of the body cavity and down to the feet and through to the arms. These cuts were made so the skin could be neatly folded back and pinned in place. ...
... were made down the center of the body cavity and down to the feet and through to the arms. These cuts were made so the skin could be neatly folded back and pinned in place. ...
Zoology Semester Exam Study Guide 1st semester 1. Which of the
... b. They maintain a constant internal body temperature. c. They have two legs. d. They can fly. 2. An endotherm is an animal that a. has a low rate of metabolism. c. can generate its own body heat. b. stores large amounts of food in its stomach. d. can see color very well. 3. In which part of a bird’ ...
... b. They maintain a constant internal body temperature. c. They have two legs. d. They can fly. 2. An endotherm is an animal that a. has a low rate of metabolism. c. can generate its own body heat. b. stores large amounts of food in its stomach. d. can see color very well. 3. In which part of a bird’ ...
The Human Body
... The Thorax Thoracic Cavity contains the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. ...
... The Thorax Thoracic Cavity contains the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. ...
BIOL 1010 Human Anatomy
... To relate the common language of anatomy to the functional morphology of the human body. To provide a baseline of knowledge for the study of physiology. Illustrate the principle that structure and function are related. ...
... To relate the common language of anatomy to the functional morphology of the human body. To provide a baseline of knowledge for the study of physiology. Illustrate the principle that structure and function are related. ...
1 anatomy terms and planes - PA
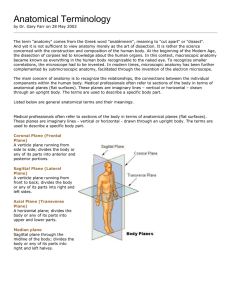
... Anatomical Position • This is a reference position that allows for the use of consistent directional terminology. • All descriptions of location are made from within anatomical position. Subject is facing forward with palms forward, thumbs facing to the sides. ...
... Anatomical Position • This is a reference position that allows for the use of consistent directional terminology. • All descriptions of location are made from within anatomical position. Subject is facing forward with palms forward, thumbs facing to the sides. ...
Scanning the Human Body
... images of the organs and tissues within your body. • The magnetic field temporarily realigns hydrogen atoms in your body. Radio waves cause these aligned atoms to produce very faint signals, which are used to create crosssectional MRI images — like slices in a loaf of bread • An fMRI (functional MRI ...
... images of the organs and tissues within your body. • The magnetic field temporarily realigns hydrogen atoms in your body. Radio waves cause these aligned atoms to produce very faint signals, which are used to create crosssectional MRI images — like slices in a loaf of bread • An fMRI (functional MRI ...
No Slide Title
... 2. Which term above best describes the location of the fingers in relationship to the elbow? a –distal 3. Which term best describes the location of the brain in relationship to the spinal cord? e –superior ...
... 2. Which term above best describes the location of the fingers in relationship to the elbow? a –distal 3. Which term best describes the location of the brain in relationship to the spinal cord? e –superior ...
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Human Body
... 14. Describe the different types of medical imaging and what they are used to detect. ...
... 14. Describe the different types of medical imaging and what they are used to detect. ...
Chapter 1 study guide
... Thoracic ▪ Mediastinum ▪ midportion of thoracic cavity; heart, trachea located here ▪ Pleural cavities ▪ right and left lungs located here Abdominopelvic cavity ▪ Abdominal cavity contains stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and lowest part of intestine ▪ Pelvic cavity contains reproductive ...
... Thoracic ▪ Mediastinum ▪ midportion of thoracic cavity; heart, trachea located here ▪ Pleural cavities ▪ right and left lungs located here Abdominopelvic cavity ▪ Abdominal cavity contains stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and lowest part of intestine ▪ Pelvic cavity contains reproductive ...
Chapter 1 Powerpoint Review
... of the responses to the stimulus is to shut off the original stimulus or reduce its intensity. C. Positive feedback mechanisms control infrequent events that occur "explosively." D. Blood clotting is an example of a typical negative feedback mechanism. ...
... of the responses to the stimulus is to shut off the original stimulus or reduce its intensity. C. Positive feedback mechanisms control infrequent events that occur "explosively." D. Blood clotting is an example of a typical negative feedback mechanism. ...
Directional Terms cont
... farther from the trunk or farther from another specified point of reference than another part (fingers are distal to the wrist). • Superficial: means situated near the surface. Peripheral also means outward or near the surface. • Deep: is used to describe parts that are more internal. ...
... farther from the trunk or farther from another specified point of reference than another part (fingers are distal to the wrist). • Superficial: means situated near the surface. Peripheral also means outward or near the surface. • Deep: is used to describe parts that are more internal. ...
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and
... Liver: Follow the green outline of the liver. Notice that most of the organ resides on the right side of the body. A thin region extends to the left side, running beneath the diaphragm. Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract: The stomach, small intesine and colon are indiscriminantly labeled in purple. Note ho ...
... Liver: Follow the green outline of the liver. Notice that most of the organ resides on the right side of the body. A thin region extends to the left side, running beneath the diaphragm. Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract: The stomach, small intesine and colon are indiscriminantly labeled in purple. Note ho ...
Invertebrate Power Point Sponges to Earthworms File
... Inhabit soil, saltwater and freshwater Bilateral, Secondary Radial symmetry Body is cylindrical and tapered at both ends Have a psuedocoelom- layer between the mesoderm and internal organs, filled with fluid e) Cuticle- tough outer layer that prevents the host from digesting the worm f) One-way dige ...
... Inhabit soil, saltwater and freshwater Bilateral, Secondary Radial symmetry Body is cylindrical and tapered at both ends Have a psuedocoelom- layer between the mesoderm and internal organs, filled with fluid e) Cuticle- tough outer layer that prevents the host from digesting the worm f) One-way dige ...
the language of anatomy
... *What is the standard body position for the anatomical reference point? Anatomical Position: the body is erect with feet together, standing at attention with palms forward. Most directional terms used will refer to the body as if it were in this position, regardless of the actual position. Remembe ...
... *What is the standard body position for the anatomical reference point? Anatomical Position: the body is erect with feet together, standing at attention with palms forward. Most directional terms used will refer to the body as if it were in this position, regardless of the actual position. Remembe ...
SO YOU WANT TO BE A MEDICAL DETECTIVE A medical detective can be
... the forensic pathologist attempts to determine the identification of the deceased, the time of death, the manner of death (natural, accident, suicide or homicide) the cause of death and if the death was by injury, the nature of the instrument used to cause the death. First, the forensic pathologist ...
... the forensic pathologist attempts to determine the identification of the deceased, the time of death, the manner of death (natural, accident, suicide or homicide) the cause of death and if the death was by injury, the nature of the instrument used to cause the death. First, the forensic pathologist ...
Document
... Anatomical Terms Study Guide In Anatomy specific terms are used to explain the location of body organs, systems, as well as body movements. Fill in the missing words to make the passage correct using words from the word bank provided. reference, side, stand, body, arms, hands, anatomical, forward. ...
... Anatomical Terms Study Guide In Anatomy specific terms are used to explain the location of body organs, systems, as well as body movements. Fill in the missing words to make the passage correct using words from the word bank provided. reference, side, stand, body, arms, hands, anatomical, forward. ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.