Anatomy term File - Progetto e
... • Planes are imaginary flat surfaces that are used to divide the body or organs into definite areas & include: – Midsagittal (medial) and parasagittal, frontal (coronal), transverse (cross-sectional or horizontal) and oblique. ...
... • Planes are imaginary flat surfaces that are used to divide the body or organs into definite areas & include: – Midsagittal (medial) and parasagittal, frontal (coronal), transverse (cross-sectional or horizontal) and oblique. ...
Simple Invertebrates
... 3. Amoebocytes - carry food to other cells; help in reproduction 4. Spongin - flexible protein skeleton. 5. Spicules - tiny needles of silica or calcium carbonate that make up the skeleton. ...
... 3. Amoebocytes - carry food to other cells; help in reproduction 4. Spongin - flexible protein skeleton. 5. Spicules - tiny needles of silica or calcium carbonate that make up the skeleton. ...
Evolutionary Trends in Animals
... 7. In all animals except sponges, the zygote undergoes cell divisions forming a hollow ball of cells called a(n) ____________________. 8. The ______________________ is the layer of cells in the blastula that gives rise to the outer layer of skin, the nervous system, and the sense organs. 9. The ____ ...
... 7. In all animals except sponges, the zygote undergoes cell divisions forming a hollow ball of cells called a(n) ____________________. 8. The ______________________ is the layer of cells in the blastula that gives rise to the outer layer of skin, the nervous system, and the sense organs. 9. The ____ ...
Phylum Mollusca - Cloudfront.net
... • Bivalvia- mollusk with TWO shells • Cephalopoda – mollusk with and internal shell or no shell at all. Exception chambered nautilus ...
... • Bivalvia- mollusk with TWO shells • Cephalopoda – mollusk with and internal shell or no shell at all. Exception chambered nautilus ...
ANATOMICAL PLANES AND REGIONS
... Abdominopelvic cavity • Abdominal cavity - liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, intestines, spleen, kidneys, ureters • Pelvic cavity - bladder, certain reproductive organs, and part of the large intestine ...
... Abdominopelvic cavity • Abdominal cavity - liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, intestines, spleen, kidneys, ureters • Pelvic cavity - bladder, certain reproductive organs, and part of the large intestine ...
Fever of Unknown Origin
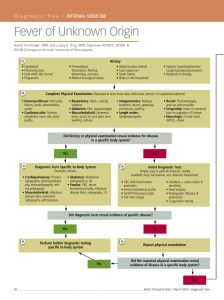
... Did the repeated physical examination reveal evidence for disease in a specific body system? ...
... Did the repeated physical examination reveal evidence for disease in a specific body system? ...
Terminology Power Point
... Foundation of the word Usually indicates a body part or structure Combining form is a root plus a vowel to allow elements to ...
... Foundation of the word Usually indicates a body part or structure Combining form is a root plus a vowel to allow elements to ...
Chapter 11 Structure and
... obtain food and oxygen, keep a stable environment within their bodies, reproduce, and move about to meet their needs. How are animals classified? Animals are classified according to how they are related, which is based on their evolutionary history. 1. Anatomy is the structure of an organism. Physio ...
... obtain food and oxygen, keep a stable environment within their bodies, reproduce, and move about to meet their needs. How are animals classified? Animals are classified according to how they are related, which is based on their evolutionary history. 1. Anatomy is the structure of an organism. Physio ...
The Coroners Inquest - Department of Health
... Coroners Autopsy • Autopsy authorisation forms should provide information on the case • Discuss case with supervising consultant • If death occurred in hospital case notes, A&E notes etc. should be consulted • Identify known or suspected infection risks • If further information is required contact ...
... Coroners Autopsy • Autopsy authorisation forms should provide information on the case • Discuss case with supervising consultant • If death occurred in hospital case notes, A&E notes etc. should be consulted • Identify known or suspected infection risks • If further information is required contact ...
intro to animals (metazoa) - Speedway High School
... ONE OPENING = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Ex: Planaria TWO OPENINGS- most efficient Allows specialization (different parts do different jobs) Most animals have this kind ...
... ONE OPENING = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Ex: Planaria TWO OPENINGS- most efficient Allows specialization (different parts do different jobs) Most animals have this kind ...
Chapter 1 Power Point Notes - River Dell Regional School District
... “cutting up”; the structural make-up of an organism ...
... “cutting up”; the structural make-up of an organism ...
Chapter 28 / The Animal Kingdom: Acoelomates
... Chapter 28 / Introduction to the Animal Kingdom I. Introduction to Animals A. Characteristics 1. multicellular eukaryotes 2. cells are specialized to perform specific functions cells→tissues→organs→organism 3. heterotrophs 4. motile at some point in their life 5. sensory systems well-developed to re ...
... Chapter 28 / Introduction to the Animal Kingdom I. Introduction to Animals A. Characteristics 1. multicellular eukaryotes 2. cells are specialized to perform specific functions cells→tissues→organs→organism 3. heterotrophs 4. motile at some point in their life 5. sensory systems well-developed to re ...
desktop vocab matching
... A body plan in which the left and right sides are mirror images of each other ...
... A body plan in which the left and right sides are mirror images of each other ...
Intro to Animals
... NO OPENINGS-absorb through skin Ex: tapeworm ONE OPENING = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Ex: Planaria TWO OPENINGS- most efficient Allows specialization (different parts do different jobs) Most animals have this kind EX: human ...
... NO OPENINGS-absorb through skin Ex: tapeworm ONE OPENING = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Ex: Planaria TWO OPENINGS- most efficient Allows specialization (different parts do different jobs) Most animals have this kind EX: human ...
Introduction to Animals Notes
... NO OPENINGS-absorb through skin Ex: tapeworm ONE OPENING = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Ex: Planaria TWO OPENINGS- most efficient Allows specialization (different parts do different jobs) Most animals have this kind EX: human ...
... NO OPENINGS-absorb through skin Ex: tapeworm ONE OPENING = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Ex: Planaria TWO OPENINGS- most efficient Allows specialization (different parts do different jobs) Most animals have this kind EX: human ...
Homework 1 - cloudfront.net
... 1. Label A points to the ____________________ cavity. 2. Label B points to the ____________________ cavity. 3. Label C points to the ____________________ cavity. 4. Label D points to the ____________________. 5. Label E points to the ____________________ cavity. 6. Label F points to the ____________ ...
... 1. Label A points to the ____________________ cavity. 2. Label B points to the ____________________ cavity. 3. Label C points to the ____________________ cavity. 4. Label D points to the ____________________. 5. Label E points to the ____________________ cavity. 6. Label F points to the ____________ ...
Anatomical Position and Directional Terms
... arms are at the sides of the body with palms turned forward. ...
... arms are at the sides of the body with palms turned forward. ...
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 1 LECTURE NOTES
... e) Respiratory f) Circulatory g) Excretory h) Nervous i) Endocrine j) Immune k) Reproductive Complexity and body size: complex organization permits, and to some extent promotes, the evolution of large body size. Body Fluids: Extracellular Components The body fluids are subdivided into two major grou ...
... e) Respiratory f) Circulatory g) Excretory h) Nervous i) Endocrine j) Immune k) Reproductive Complexity and body size: complex organization permits, and to some extent promotes, the evolution of large body size. Body Fluids: Extracellular Components The body fluids are subdivided into two major grou ...
DNA Technology - Loyalsock Township School District
... Reproduction and Development Homeoboxes • Developmental genes that regulate the expression of other genes • Found in all animals Hox genes • Important role in embryo development • Arose from duplication of homeobox genes ...
... Reproduction and Development Homeoboxes • Developmental genes that regulate the expression of other genes • Found in all animals Hox genes • Important role in embryo development • Arose from duplication of homeobox genes ...
Ch. 32 Intro to Animal Evolution
... muscular • Most reproduce sexually, with diploid stage dominating life cycle ...
... muscular • Most reproduce sexually, with diploid stage dominating life cycle ...
segmented.ppt fall 2012
... 3. Intestine: long intestine stretches length of body to aid in digestion of soil 4. Ganglion: brain-like organ 5. Aortic Arches: Heart of worm; really 5 enlarged blood vessels. ...
... 3. Intestine: long intestine stretches length of body to aid in digestion of soil 4. Ganglion: brain-like organ 5. Aortic Arches: Heart of worm; really 5 enlarged blood vessels. ...
File
... The Role of Probability Blood is a good example of evidence that can have class characteristics. Suppose two blood stains are compared and both are found to be of human origin, type A. The frequency of occurrence in the population of type A blood is 26% - hardly offering a basis for establishing th ...
... The Role of Probability Blood is a good example of evidence that can have class characteristics. Suppose two blood stains are compared and both are found to be of human origin, type A. The frequency of occurrence in the population of type A blood is 26% - hardly offering a basis for establishing th ...
幻灯片 1
... human structures which are useful in medicine, especially in the surgical technique, but also in ...
... human structures which are useful in medicine, especially in the surgical technique, but also in ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.